Spondylosis is a degenerative spinal disorder that commonly affects people as they age. This condition can cause discomfort, pain, and limited mobility. There are different types of spondylosis, such as cervical spondylosis, which affects the neck, and lumbar spondylosis, which affects the lower back.
If left untreated, this condition can significantly impact daily life. However, there are treatments available, such as exercises and physical therapy, that can improve symptoms and restore function. Early diagnosis and prevention are crucial for managing it effectively.
Spondylosis, a degenerative spinal disorder, is often caused by a combination of factors. One of the primary causes of spondylosis is aging, which leads to wear and tear on the spinal bones and discs. Genetics and previous injuries to the spine can also contribute to its development. In some cases, lifestyle habits such as poor posture and lack of exercise can also increase the risk of spondylosis.
It’s important to understand the underlying causes of spondylosis to prevent and treat the condition effectively. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking prompt medical treatment for any injuries, individuals can reduce their risk of developing spondylosis or worsening an existing condition.
Spondylosis is a degenerative spinal disorder that can cause a range of symptoms. It is important to be aware of these symptoms to seek medical help if they persist or worsen over time.
One of the most common symptoms of spondylosis is neck pain and stiffness. This can be caused by degeneration of the cervical spine and can lead to limited range of motion. Neck pain may also radiate to the shoulders and arms.
Along with neck pain, it can also cause back pain and stiffness, particularly in the lower back. Lumbar spondylosis is a common form of the condition that affects the lower back.
In some cases, spondylosis can cause numbness or tingling in the arms or legs. This may be due to nerve compression or inflammation in the spinal cord.
As this condition progresses, it may lead to muscle weakness in the affected areas. This can make it difficult to perform daily activities, including walking, lifting objects, or even holding a book.
Spondylosis can also cause limited range of motion in the affected areas, making it difficult to perform certain movements without pain or discomfort. This can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
Diagnosing spondylosis starts with a comprehensive medical evaluation performed by a healthcare professional. The evaluation aims to uncover the symptoms and contributing factors associated with this condition.
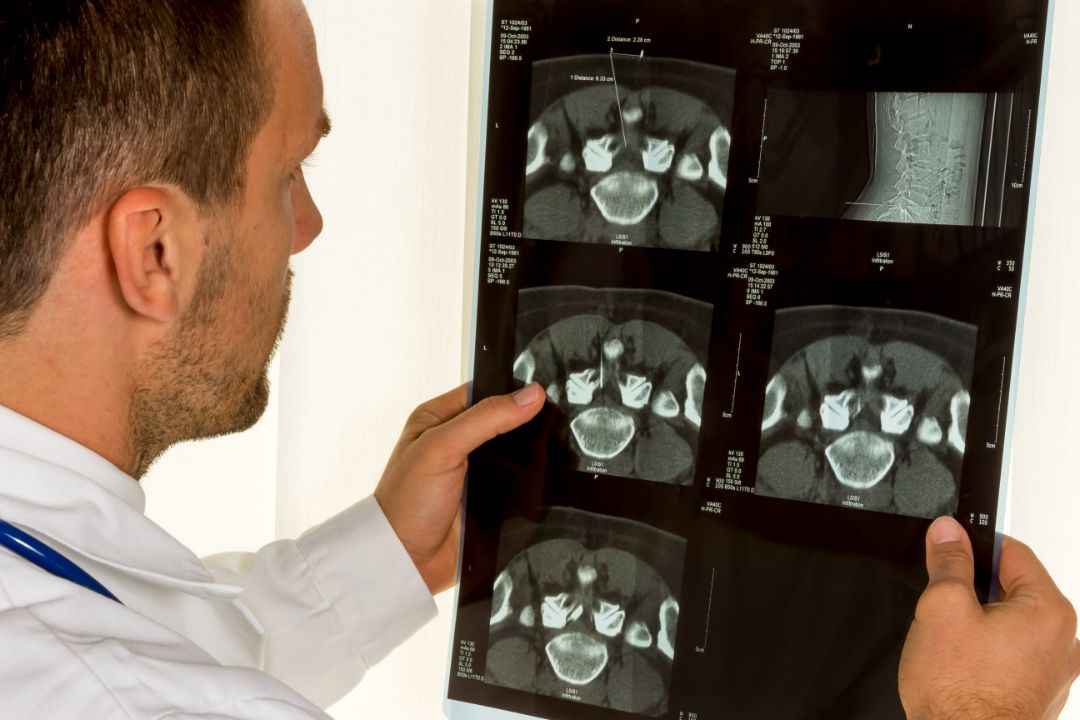
Photo Credit: westend61, Envato
During the medical evaluation, a physician or other healthcare professional will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination. They will ask about any symptoms the individual has experienced and whether any factors may have contributed to the development of the condition.
After the initial medical evaluation, the healthcare professional may order diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis of spondylosis. These tests may include:
In some cases, a healthcare professional may refer an individual to a specialist, such as a neurologist or orthopedic surgeon, for further evaluation and treatment.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating spondylosis, as it can vary depending on the severity and location of the condition. However, there are several treatments available to manage pain and improve quality of life.
In more severe cases, invasive treatments may be necessary to manage pain and improve mobility. These include:
It is important to discuss all treatment options with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for individual needs.

Photo Credit: myelogram
Physical therapy and exercises can help manage spondylosis-related pain and improve spinal flexibility. Here are some exercises that can help:
Sit or stand with your arms at your sides. Squeeze your shoulder blades together, hold for 5 seconds, and release. Repeat 10 times.
Lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet flat on the floor. Tighten your abdominal muscles and lift your head and shoulders off the ground. Hold for 5 seconds and release. Repeat 10 times.
Before beginning any exercise program, be sure to consult with your healthcare provider or physical therapist to determine what exercises are safe and appropriate for your specific condition.
Photo Credit: jorditudela, Envato
While it may not be possible to prevent the onset of this condition entirely, there are a few measures individuals can take to lower their risk or delay its onset. Here are some of the most effective:
These lifestyle choices and habits, when adopted and maintained, can go a long way in promoting good spinal health and reducing the risk of spondylosis.
In conclusion, it is a degenerative spinal disorder that can cause pain and discomfort in affected individuals. However, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, individuals can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Effective treatments for spondylosis may include conservative options such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary. It is important to work with healthcare professionals to develop an individualised treatment plan and attend regular follow-up appointments.
Photo Credit: DC_Studio, Envato
In addition to treatment, lifestyle choices and habits can play a crucial role in preventing or delaying the onset of this condition. Maintaining good posture, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption are important steps individuals can take for overall spinal health.
Research and advancements in spondylosis treatment and management continue to provide hope for individuals living with the condition. Healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals affected need to stay abreast of new developments and therapies.
Ultimately, individuals can take control of their condition by seeking medical evaluation for persistent or worsening symptoms, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and working with healthcare professionals to develop an effective treatment plan.
Spondylosis is a degenerative spinal disorder.
The different types include cervical spondylosis and lumbar spondylosis.
The available treatments for spondylosis include exercises and other conservative options, as well as surgery in severe cases.
Common symptoms of spondylosis include neck pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion.
Spondylosis is diagnosed through medical evaluation and tests, such as physical examinations and imaging tests.