Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a condition that affects the spine and can cause chronic pain and discomfort. It occurs when the spinal discs, which act as cushions between the vertebrae, break down over time.
Symptoms of DDD can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of disc degeneration. Common signs include back pain, neck pain, and numbness or tingling in the affected areas.
Causes of DDD can include aging, genetics, lifestyle choices, and injuries. Over time, the spinal discs lose their strength and elasticity, resulting in the breakdown of the cushioning material between the vertebrae.
Photo Credit: kjpargeter
Treatment options for DDD can vary based on the severity of symptoms. Non-surgical approaches such as physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications may help manage pain. Surgical interventions such as spinal fusion or artificial disc replacement can also relieve severe cases. Exercise and rehabilitation are also important components of managing DDD.
Degenerative disc disease is a common condition that affects the spinal discs. The spinal discs are the soft, cushiony structures that sit between each vertebra in the spine and provide shock absorption and flexibility to the spine.
Over time, these discs can degenerate and lose their ability to function properly. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area.
Several factors can contribute to the development and progression of degenerative disc disease. These include:
As the discs degenerate, they can become thinner and less flexible, which can cause the vertebrae to rub against each other. This can lead to the formation of bone spurs, which can further restrict movement and cause pain.
In some cases, degenerative disc disease can also lead to other spinal conditions, such as spinal stenosis or spondylolisthesis. These conditions can cause more severe symptoms and may require more aggressive treatment options.
Degenerative disc disease typically progresses slowly over time. As the discs degenerate, they may become more prone to injury or damage, exacerbating symptoms and leading to further degeneration.
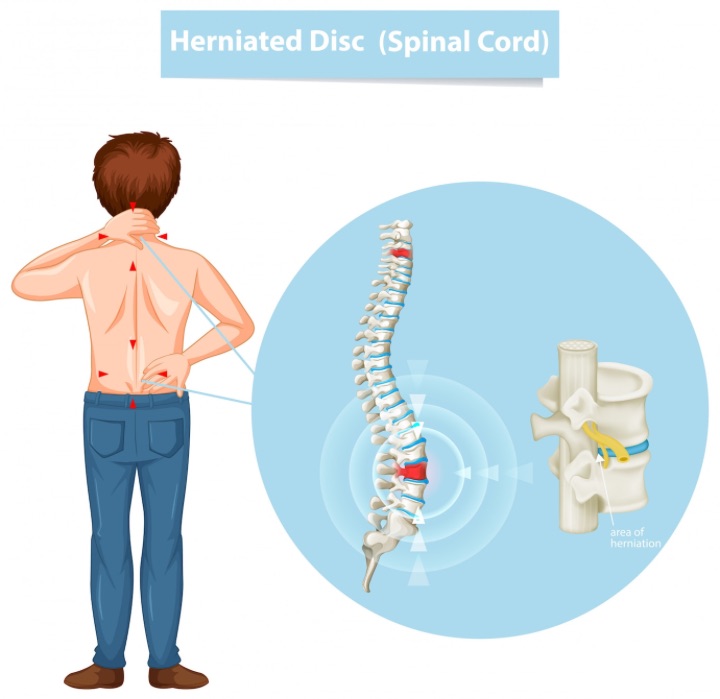
Photo Credit: brgfx
In some cases, degenerative disc disease can progress to the point where it affects the nerve roots or spinal cord. This can cause more severe symptoms, such as muscle weakness or bowel or bladder control loss.
To prevent degenerative disc disease progression, seeking treatment as soon as possible is important. Treatment options may vary depending on the severity and location of the disc degeneration.
Degenerative disc disease can cause a range of symptoms that can vary in severity depending on the location and extent of disc degeneration. The most common symptom is back pain, which may be felt in the lower back, upper back, or neck.
The pain may be constant or intermittent and may worsen with certain movements or activities. Some people also experience muscle spasms, stiffness, and reduced flexibility in the affected area.
In addition to pain, degenerative disc disease can cause numbness and tingling in the arms, legs, hands, or feet. This is due to the compression of nerves that occurs when the spinal discs degenerate and lose height.
Other symptoms can include weakness in the affected areas, particularly in the legs, and difficulty walking or standing for prolonged periods of time. In some cases, degenerative disc disease can also lead to bladder or bowel problems, although this is rare.

Photo Credit: gpointstudio
Disc degeneration is a natural part of the aging process; however, certain factors can accelerate the breakdown of spinal discs. Understanding the causes of degenerative disc disease can help individuals take preventative measures to protect their spinal health.
The most common cause of disc degeneration is aging. As we get older, our spinal discs’ water and protein content decreases, causing them to lose their flexibility and shock-absorbing abilities. This makes them more susceptible to damage and wear and tear over time.
Genetics can also play a role in the development of degenerative disc disease. Some people may be more predisposed to the condition due to inherited genes affecting their spinal discs’ strength and durability.
Unhealthy lifestyle choices like smoking, lack of exercise, and poor nutrition can contribute to disc degeneration. Smoking has been linked to accelerated disc degeneration, as it reduces the amount of oxygen that reaches the spinal discs. Lack of exercise and poor nutrition can lead to weakened spinal muscles and a lack of essential nutrients to support spinal health.
Injuries can also cause or accelerate disc degeneration. Trauma to the spine, such as whiplash or a fall, can damage spinal discs and increase the risk of degeneration over time. Repeated movements that strain the spine, such as heavy lifting or twisting, can also contribute to disc degeneration.

Photo Credit: jcomp
When it comes to treating degenerative disc disease, various options are available, both surgical and non-surgical. The best approach for you will depend on the severity of your condition and how much it affects your daily life. Here are some treatment options to consider:
Physical Therapy: Working with a physical therapist can help you strengthen your back muscles, improve your posture, and reduce your pain. They can also show you exercises to do at home to help manage your symptoms.
Medication: Over-the-counter pain medication such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen can manage pain and reduce inflammation. Your doctor may also prescribe stronger pain medication or muscle relaxers if needed.
Lifestyle Modifications: Changing your lifestyle can help prevent further damage and manage your symptoms. This can include losing weight, quitting smoking, and avoiding activities that worsen your symptoms.
Spinal Fusion: This procedure involves fusing two or more spinal vertebrae together to reduce movement and stabilize the spine. This can help alleviate pain and improve overall function.
Artificial Disc Replacement: This involves removing and replacing the damaged spinal disc with an artificial one. This can help maintain motion in the spine while relieving pain.
It’s important to note that surgery is not always the best option for everyone and should be considered as a last resort. Always consult with your doctor before making any decisions about your treatment.
Regardless of the type of treatment you choose, exercise and rehabilitation should always be a part of your plan. This can help improve your range of motion, flexibility, and strength. A physical therapist can help you create a safe and effective exercise plan for your specific condition.
Overall, managing degenerative disc disease requires a comprehensive approach involving treatments, lifestyle modifications, and rehabilitation. Working closely with your healthcare team can help you find the best plan to manage your symptoms and maintain your quality of life.
Degenerative disc disease is a condition that affects the spinal discs, causing them to break down and deteriorate over time.
Common symptoms of degenerative disc disease include back pain, neck pain, numbness, and tingling in the affected areas. The specific symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the disc degeneration.
Various factors, including aging, genetics, lifestyle choices, and injuries can cause degenerative disc disease. These factors contribute to the breakdown of spinal discs and the development of the condition.
Treatment options for degenerative disc disease include non-surgical approaches such as physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications. Surgical interventions like spinal fusion and artificial disc replacement may be considered in more severe cases. Exercise and rehabilitation are also important in managing the condition.