Spinal stenosis is a condition that occurs when the spaces within the spine narrow, putting pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area.
Spinal stenosis is a condition that causes the spinal canal to narrow, potentially compressing the spinal cord and the nerves that branch out from it. This compression can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, muscle weakness, and numbness.
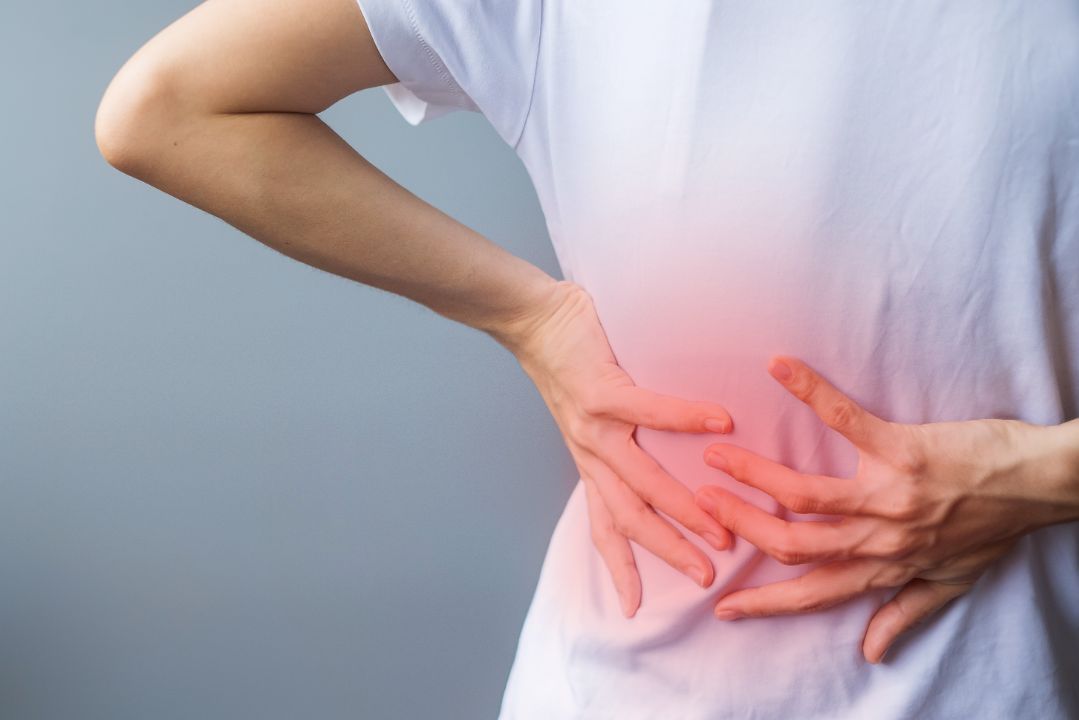
Photo Credit: JoPanwatD, Envato
There are two types of spinal stenosis: lumbar spinal stenosis, which affects the lower back, and cervical spinal stenosis, which affects the upper back and neck. Lumbar spinal stenosis is the more common of the two.
Lumbar spinal stenosis occurs when the spinal canal in the lower back narrows, compressing the spinal cord and nerve roots that branch out from it. This can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the lower back, hips, and legs. The pain may worsen when walking or standing for extended periods and may improve when sitting or bending forward.
Cervical spinal stenosis occurs when the spinal canal in the neck area narrows, compressing the spinal cord and nerve roots. This can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the neck, shoulders, and arms. Other symptoms can include difficulty with coordination, balance, and bladder or bowel function.
Spinal stenosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including age-related changes in the spine, spinal injuries, and conditions such as arthritis. In the next section, we will explore the causes and risk factors in more detail.
Spinal stenosis can cause a range of symptoms that vary depending on the location of the spinal canal narrowings. The most common symptoms include:
The symptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis may differ from those of cervical spinal stenosis. In lumbar cases, individuals may experience leg pain and weakness, while in cervical ones, symptoms may include neck pain and weakness in the arms and hands.
Spinal stenosis is caused by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This narrowing can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
While this condition can affect people of all ages, it is most commonly seen in those over the age of 50. Other risk factors for the condition include a family history of this issue, being overweight, and having a job or lifestyle that requires repetitive spinal movements or heavy lifting.
As we age, the structures in our spine begin to break down and degenerate. This can cause the discs between our vertebrae to dry out and shrink, which can lead to herniated discs. Bone spurs may also form on the vertebrae, which can narrow the spinal canal and put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
A spinal injury, such as a fracture or dislocation, can cause damage to the structures of the spine and lead to spinal issues. Injuries to the spinal cord itself can also cause damage and lead to the development of the condition.
Conditions such as arthritis can cause inflammation in the joints of the spine, which can cause them to become enlarged and narrow the spinal canal. Additionally, conditions such as Paget’s disease can cause the bones in the spine to become thicker and misshapen, which can also lead to this condition.
Photo Credit: DC_Studio, Envato
There are a variety of treatment options available for spinal stenosis, depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Treatment options can be grouped into non-surgical and surgical approaches.
If non-surgical treatments have failed, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the spine. Common surgical procedures for spinal stenosis include:
Regardless of which treatment option is chosen, pain management is an important aspect of living with spinal stenosis. Pain relief methods may include:
Ultimately, the most effective treatment for spinal stenosis will depend on the individual’s specific situation. A doctor can help determine the best course of action based on symptoms, underlying conditions, and overall health.
Living with spinal stenosis can be challenging, but there are ways to manage the condition and improve your quality of life. Here are some strategies for pain relief and prevention:
When it comes to relieving pain, there are various methods that may be effective. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help alleviate pain. In some cases, prescription painkillers may be necessary. It’s important to talk to your doctor about the best pain relief option for you.
Other pain management techniques include hot and cold therapy, massage, and gentle stretching exercises. Physical therapy can also help reduce pain and improve mobility.

Photo Credit: ORION_production, Envato
Simple lifestyle modifications can also help manage this condition. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the pressure on your spine, while exercises such as walking, swimming, and yoga can help improve flexibility and strengthen muscles. Avoiding activities that cause pain or discomfort can also help prevent further damage to your spine.
Preventing the progression of spinal stenosis is crucial to managing the condition. In addition to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding smoking and minimizing alcohol consumption can help improve spinal health. Regular check-ups with your doctor can also ensure that any changes to your spine are caught early and treated promptly.
Managing this spinal issue is a journey, and it may take time to find the right treatment plan for you. By taking a proactive approach to pain relief and prevention, however, you can improve your overall health and well-being.
Spinal stenosis is a condition where the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This can result in various symptoms and complications.
Common symptoms of spinal stenosis include pain in the back or neck, numbness or tingling in the extremities, muscle weakness, and difficulty walking or maintaining balance.
Spinal stenosis can be caused by age-related changes in the spine, spinal injuries, and conditions such as arthritis. Risk factors include advanced age, genetic predisposition, and certain occupations or activities that put stress on the spine.

Photo Credit: insidecreativehouse, Envato
Treatment options for spinal stenosis include non-surgical approaches such as physical therapy, exercises, pain management techniques, and medications. In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary.
Managing spinal stenosis involves pain relief methods such as hot/cold therapy, medication management, lifestyle modifications like regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight, and preventive measures to reduce the risk of further complications.