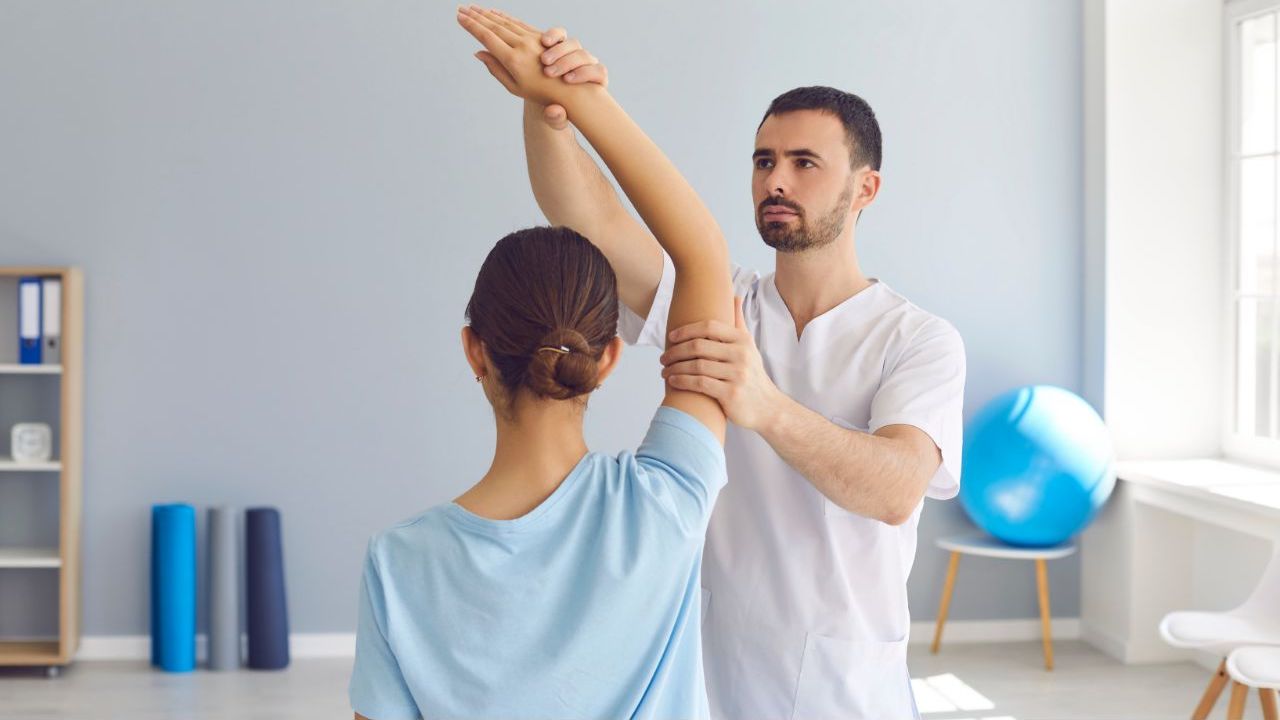


Physiotherapy, commonly known as physical therapy, is a dynamic and evidence-based healthcare profession that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of various musculoskeletal issues.
It aims to restore movement and function in individuals affected by injury, illness, or disability while reducing the risk of future injuries.
In Australia, physiotherapists are highly skilled professionals who undergo extensive training at accredited educational institutions to achieve registration with the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA).
The history of physiotherapy in Australia can be traced back to the early 20th century. In 1907, formal training in this field began, initially affiliated with university medical schools and teaching hospitals.
This made Australia the first country to teach and examine all aspects of physical therapy: exercise, massage and manipulation, and electrotherapy.
Interestingly, physiotherapy became institutionalized during World War I when women were recruited to work with soldiers returning from battle. They provided physical therapy services that aimed to help injured soldiers regain their strength and mobility as they recovered from injuries sustained during combat.
One notable milestone came during World War II when Mary McMillan organized outpatient orthopedic clinics specifically tailored towards treating war-related injuries suffered by servicemen at home or abroad – a testament to how far-reaching and influential physiotherapy has become over its rich history Down Under.
The scope of practice in physiotherapy is vast and caters to a diverse range of individuals, from those experiencing chronic pain to athletes requiring rehabilitation. With an increasing demand for skilled professionals who can effectively address musculoskeletal issues such as back, joint, neck, and shoulder pains, the role of a physiotherapist has expanded significantly in recent years.

Physiotherapists collaborate with allied health assistants and engage in advanced extended-scope roles that extend beyond traditional treatment approaches. This multidisciplinary approach allows them to work alongside medical professionals like doctors and nurses in delivering patient-centered care tailored to individual needs.
In Australia specifically, physiotherapy is evidence-informed and delivered by competent health professionals within the profession’s defined scope of practice.
Physiotherapy works by first assessing and diagnosing the patient’s condition and then creating a treatment plan that includes techniques like manual therapy, exercise therapy, electrotherapy, hydrotherapy, and acupuncture.
It is a collaborative approach where patients are actively involved in their own recovery.
A crucial first step in your physiotherapy journey is the assessment and diagnosis stage, wherein a skilled physiotherapist evaluates your musculoskeletal system to identify any underlying issues causing you pain or discomfort.
Through comprehensive assessments, your practitioner will observe movement patterns, posture, muscle strength, and flexibility to pinpoint specific areas of concern.
During this initial appointment, the physiotherapist will also take into account your medical history and daily activities that could contribute to your current condition.
This thorough analysis helps them diagnose the root cause of chronic pain in joints or muscles and lays a foundation for an effective treatment plan tailored specifically for you.
After a thorough assessment and diagnosis, physiotherapists develop a treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs. This can include a combination of manual therapy, exercise therapy, electrotherapy, hydrotherapy, acupuncture, and even yoga.
Treatment planning aims to reduce pain and stiffness while improving function and mobility. Physiotherapists take into consideration the patient’s lifestyle, goals, and preferences when developing the treatment plan. The plan may involve ongoing monitoring and adjustments to ensure progress toward desired outcomes.
Overall, physiotherapy focuses on restoring physical function using validated therapeutic interventions for patients with back or neck pain or joint problems caused by injury or disease.
Physiotherapy uses a range of techniques and approaches to reduce pain, improve mobility, and restore function. Here are some of the most commonly used techniques:
Physiotherapists use evidence-based approaches to determine the most effective techniques for each patient’s needs. By working collaboratively with their patients, physiotherapists strive to achieve optimal outcomes for every individual they treat through a personalised treatment plan that addresses specific issues related to mobility and movement disorders affecting parts of the musculoskeletal system.
Physiotherapy involves a collaborative approach that emphasises the importance of patient participation and decision-making throughout the treatment process.
This means physiotherapists work closely with patients to understand their unique needs, goals, and concerns. They also involve other healthcare professionals in the patient’s care plan when necessary.
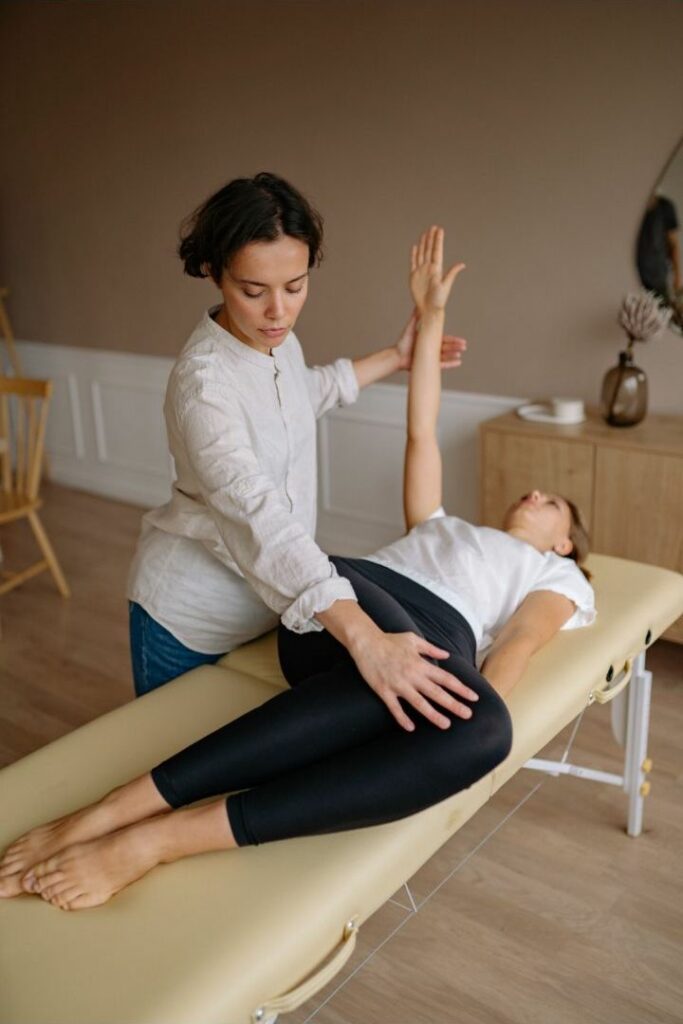

Photo Credit: Yan Krukau, Pexels
Positive interactions between patients and therapists are linked with reduced pain levels and improved outcomes. Through collaboration between patients and physiotherapists, an individualized treatment plan can be developed, tailored to meet each person’s specific needs.
Physiotherapy offers pain relief, improved function and mobility, rehabilitation and recovery, and management of chronic conditions.
Physiotherapy is known for its ability to provide natural, long-lasting pain relief. One of the main benefits of physiotherapy is that it can help reduce pain and stiffness in the body’s muscles, joints, and bones.
This is achieved through various techniques such as manual therapy, exercise therapy, and electrotherapy.
Studies have shown that a physiotherapist’s treatment can help reduce pain, increase mobility, and improve overall strength and well-being.
Furthermore, physical therapy offers an alternative option for managing chronic pain without relying heavily on medication or invasive procedures.
Physiotherapy effectively improves function and mobility in those suffering from chronic pain in the back, joints, neck, shoulders or any part of the musculoskeletal system.
By assessing movement dysfunctions and addressing these with strengthening and stretching techniques specific to each patient’s needs, physiotherapists can restore lost function and help their patients move with greater ease.
For example, a patient suffering from chronic lower back pain may have developed poor posture. A physiotherapist would work with them to identify any underlying muscle imbalances contributing to poor posture, then use exercises tailored to their condition to strengthen weak muscles while lengthening tight ones.
This approach can have significant effects on improved function and mobility over time.
Physiotherapy is essential to rehabilitation and recovery from various health conditions, including chronic pain. Physiotherapy in rehab aims to improve movement, muscle strength, flexibility, and endurance.
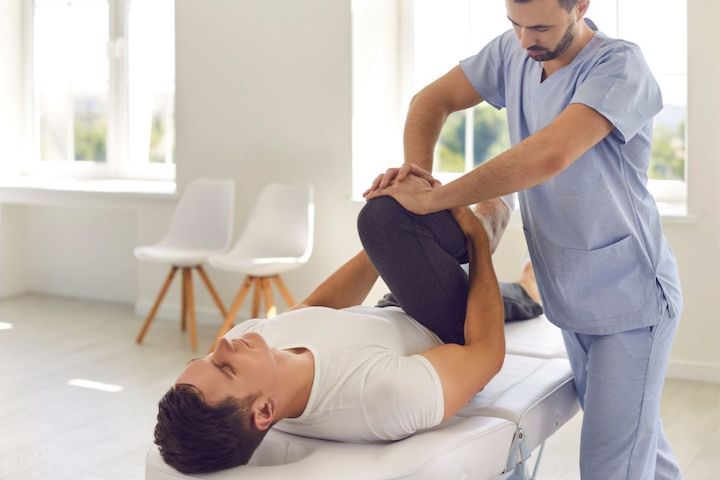

Physiotherapists work with their clients to create personalized treatment plans that are tailored to their specific needs. Treatment options may include manual therapy techniques such as massage and joint mobilization or exercise therapy like stretching and strengthening exercises.
Additionally, physiotherapists often use electrotherapy (such as ultrasound) and hydrotherapy for their patients’ benefit.
Rehabilitation programs designed by qualified physiotherapists can help ease chronic pain symptoms through a multidisciplinary approach involving other healthcare professionals in addition to physiotherapists focusing on physical aspects like mobility restoration alongside psychological ones like stress management techniques.
Physiotherapy can play a crucial role in managing chronic conditions such as arthritis, osteoporosis, and other musculoskeletal disorders. Physiotherapists work closely with patients to develop personalized care plans that may involve guided exercise programs or manual therapies to help improve mobility and reduce pain.
Additionally, physiotherapy can aid individuals with chronic health issues such as Type 2 diabetes and obesity by providing support through regular monitoring and maintenance of weight loss goals.
Physiotherapy offers a range of specialised areas including musculoskeletal, neurological, cardiothoracic, pediatric and geriatric physiotherapy.
Musculoskeletal physiotherapy is a specialised branch of physiotherapy that can help treat chronic pain in the back, joints, neck, shoulders or any part of the musculoskeletal system.
This type of therapy aims to reduce stiffness and pain while improving mobility and function. A musculoskeletal physiotherapist will assess your condition through a range of techniques such as manual therapy, exercise therapy, electrotherapy and hydrotherapy.
The treatment plan developed by the therapist will be specific to your needs and goals. It may involve exercises to improve strength and flexibility, hands-on techniques to improve joint movement or massage to release tense muscles.
Musculoskeletal physiotherapists are experts in managing various conditions including osteoporosis, sports injuries and arthritis. And as the most common type of pain and injury that physiotherapy can help with is often related to the bones, its importance cannot be overstated enough.
Neurological physiotherapy is a specialized area of physiotherapy that focuses on treating individuals with neurological conditions, such as stroke and multiple sclerosis.
This type of therapy differs from traditional physiotherapy as it helps the brain form new synaptic connections to improve movement and function. Neurological physiotherapists offer examination and treatment of physical problems caused by injuries to the nervous or neuromuscular system.
For example, they may work with patients who have difficulty walking or using their hands due to damage to the brain or spinal cord. Learn how physical therapy can help patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) and spinal cord injury.
Cardiothoracic physiotherapy is a specialized area that focuses on treating patients with conditions that affect the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. There are even cardiovascular exercises within physical therapy to specialize the conditions.
This type of therapy involves preventing, rehabilitating, and compensating clients with diseases related to these systems. Physiotherapists use various techniques to manage cardiovascular conditions such as supervised mobilization and exercise programs aimed at managing pain & stiffness and reducing symptoms associated with the condition.
Physiotherapists who specialize in this area often work alongside other healthcare professionals in hospitals or medical centres to support patients suffering from chronic illnesses or disabilities affecting their hearts or lungs.
They also work closely with athletes looking to improve their performance by improving their breathing capacity and endurance through tailored exercises based on individual needs.
Pediatric physiotherapy is a specialized field of physiotherapy that focuses on improving the physical development of children. Paediatric physiotherapists are experts in child development, particularly in relation to the development of movement.
They have expertise and skills in treating various conditions in children, including neurological disorders, sports injuries, and cerebral palsy.
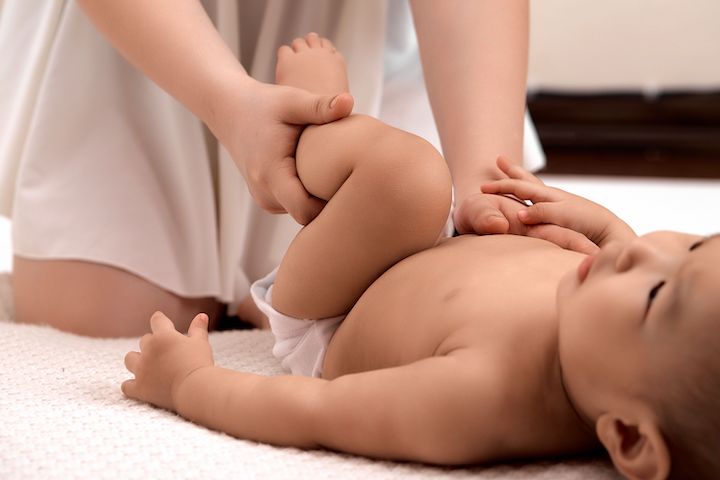
Through pediatric physical therapy sessions, kids can develop their motor skills and improve their overall physical health. This type of treatment can also help children with developmental delays or disabilities reach important milestones such as crawling or walking.
Pediatric physiotherapists use specialized exercises tailored specifically to each child’s age and condition to achieve these goals.
Geriatric physiotherapy is a specialized field that focuses on providing therapy for conditions and ailments related to aging. This includes problems such as decreased bone density, reduced muscle strength, and mobility issues.
Physiotherapy treatments for the elderly are designed specifically to tackle challenges associated with aging and improve physical and mental well-being.
Patients who seek out geriatric physiotherapy can expect fun yet effective sessions that provide both physical improvement and a mental lift. The problems faced in geriatric physiotherapy are categorized into three different groups: those due to aging, those caused by diseases or injuries during old age, and finally, those attributable to medications.
Geriatric physical therapists specialize in identifying these issues so they can tailor treatment plans accordingly to address each patient’s unique needs. For an in-depth detail, see our dedicated article on physical therapy in geriatric care.
Orthopedic physiotherapy is a specialised area of physiotherapy that focuses on the musculoskeletal system. This includes bones, muscles, joints and tendons.
Using a range of techniques such as mobilisation, manipulation and massage therapy, orthopedic physiotherapists work to optimise your physical potential.
Whether you have suffered an injury or are recovering from post-operative surgery, they can create a personalised treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Physiotherapists use a variety of techniques and approaches, including manual therapy, exercise therapy, electrotherapy, hydrotherapy and acupuncture to help patients manage pain, improve function and mobility, and promote healing.
Manual therapy is a hands-on approach used in physiotherapy to treat various conditions such as chronic pain and stiffness in the back, joints, neck, shoulders or any part of the musculoskeletal system.
Physiotherapists use manual therapy techniques like massage, myofascial release, and soft tissue mobilisation to improve movement and reduce pain.
Manual therapy can also speed up healing by increasing blood flow to affected areas. In conjunction with education and exercise, manual therapy can be an effective treatment option for chronic pain patients.
One of the main techniques used in physiotherapy is exercise therapy. This type of therapy focuses on using physical activity to help restore function and improve movement.
Exercise therapy can involve various activities, from simple stretching exercises to more complex movements targeting specific muscles or joints. The principles of therapeutic exercise are crucial in developing safe and effective programs that can help reduce pain, increase strength, and improve the overall quality of life.
Electrotherapy is a powerful tool many physiotherapists use to treat chronic pain, musculoskeletal injuries, muscle wasting and nerve pain. This therapy uses electrical signals to interfere with the transmission of neural pain signals into the brain, effectively slowing down or blocking the sensation of pain.
While electrotherapy has been an established part of physiotherapy practices since its earliest days, its delivery has changed remarkably over time.
Physiotherapists often use electrotherapy in conjunction with other therapies like exercises, massage, and heat therapy to help manage chronic conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia or even post-surgery healing.
Electrotherapy can also be used for emotional disorders like depression or anxiety by stimulating areas of the central nervous system associated with mood regulation.
Hydrotherapy is a form of physiotherapy that uses the unique properties of water to treat musculoskeletal issues. This can include aquatic exercises, such as swimming or walking in water, as well as using saunas and other water-based therapies. Aquatic therapy is a common one used for rehabilitation; see here for more details:
One key benefit of hydrotherapy is its ability to provide stress relief to cells. By applying various techniques in physical therapy, such as pressure changes and temperature variations, hydrotherapy can help reduce stiffness and pain while improving mobility and quality of life for those living with chronic pain or injury.
Acupuncture is a popular modality used in Western medicine to treat chronic pain, including musculoskeletal pain. For physiotherapists, it’s seen as an effective way to manage pain and stimulate the body’s own healing processes.
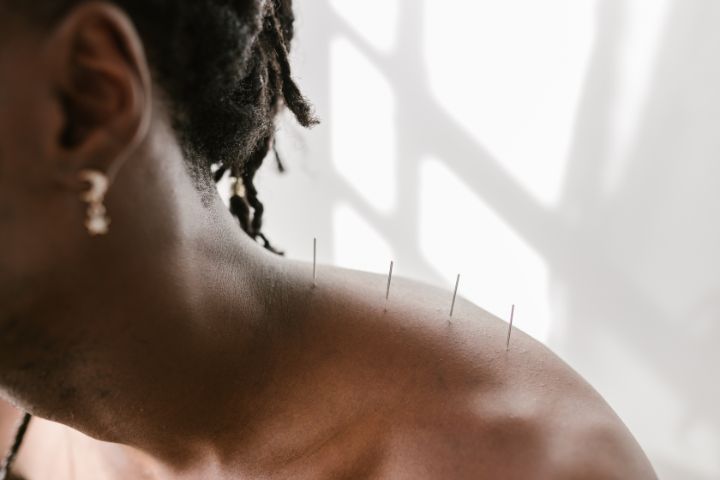

Photo Credit: RODNAE Productions, Pexels
Decades of research have shown that the sensory stimuli evoked by needling are responsible for specific physiological responses, making acupuncture an excellent option for those seeking drug-free relief from injuries or other chronic issues.
Additionally, dry needling is a technique often used in conjunction with acupuncture, which involves penetrating the skin with needles to improve or restore function.
Physiotherapy is an effective treatment for various conditions such as back pain, sports injuries, arthritis, stroke and other neurological disorders, respiratory conditions and more.
If you suffer from chronic pain in your back, you’re not alone. In fact, lower back pain is one of the most common health complaints among adults worldwide. The good news is that physiotherapy can be extremely effective in treating this type of pain.
Physiotherapists are experts at identifying and managing muscle and joint issues like spasms, sprains, tears, and weakness that can cause back pain.
Research shows that physiotherapy can improve joint and muscle movement and function, reduce back pain and even address psychosocial factors associated with treatment outcomes such as self-efficacy and catastrophising.
Sports injuries are a common concern for many individuals, particularly athletes and active people. Physiotherapy plays an essential role in the treatment of sports injuries, helping to manage pain, improve function and mobility, and support rehabilitation and recovery. Additionally, it is a massive part of any injury prevention measures. See how it works, below:
Physiotherapists work closely with athletes of all levels to provide tailored exercise programs that aid recovery from injury while also improving overall physical fitness to prevent future injuries.
Additionally, they may use techniques such as manual therapy or electrotherapy to help reduce pain and stiffness associated with sports-related injuries. Also look at our article on using physical therapy to help recover from sports injury.
If you have chronic pain in your joints, then it’s highly likely that physiotherapy will become an important part of your management plan. Physiotherapists are essential to the healthcare team who help manage arthritis and other musculoskeletal conditions by examining different rehab modalities and treatment techniques tailored to each patient’s needs.
Joint mobilisation, electrotherapy, hydrotherapy, muscle strengthening, exercises, and self-management are some of the various approaches used during physiotherapy sessions for people with arthritis or knee osteoarthritis.
In conjunction with other treatments such as medication or surgery if required, these techniques can significantly reduce stiffness and manage pain levels while also improving function and mobility.
Physiotherapy is essential for rehabilitation for individuals affected by stroke and other neurological disorders. Physiotherapists use their knowledge and expertise to help patients recover motor function and movement of joints, muscles, and tendons that may have been impacted due to brain or nerve problems.
See how physical therapy can help with stroke rehabilitation and stroke prevention.
Post-stroke depression can also be effectively treated through physiotherapy with the help of antidepressant medications and psychotherapy sessions. Patients who receive regular physiotherapy treatment show significant improvement in their ability to carry out daily activities independently and their overall quality of life.
Physiotherapy plays a significant role in managing and treating patients with respiratory conditions. It can enhance airway clearance in respiratory diseases associated with hypersecretion and relieve symptoms such as shortness of breath and impaired airway function.
For chronic bronchitis patients, physiotherapy treatment has improved pulmonary clearance compared to a control group. Physiotherapists use breathing exercises, coughing techniques, and chest physical therapy to help manage breathlessness and improve overall respiratory health.
Physiotherapy can benefit athletes, active individuals, elderly people, children with developmental delays, pregnant women, and those with chronic conditions.
Physiotherapy can be especially beneficial for athletes and active individuals who require optimal physical performance to excel in their field.
A strong athlete-physiotherapist relationship is essential for effective diagnosis, treatment planning, injury management, and recovery. Sports physiotherapy techniques include manual therapy, exercise therapy, electrotherapy, hydrotherapy, acupuncture and more to address specific needs unique to each individual.
[IMPORTANT FACTS]:
– Sports physiotherapist plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance of athletes.
– A strong athlete-physiotherapist relationship is necessary for effective treatment.
– Techniques used by sports physiotherapy include manual therapy and exercise therapy among others.
– Physiotherapists minimize injury risks that could reduce athletic performances while maximizing potential at the same time.
Physiotherapy can be incredibly beneficial for elderly individuals who experience chronic pain, mobility issues or have a history of falls. As we age, our bodies undergo physiological changes that impact muscular and skeletal function, but physiotherapists are trained to help older patients strengthen muscles and restore mobility.
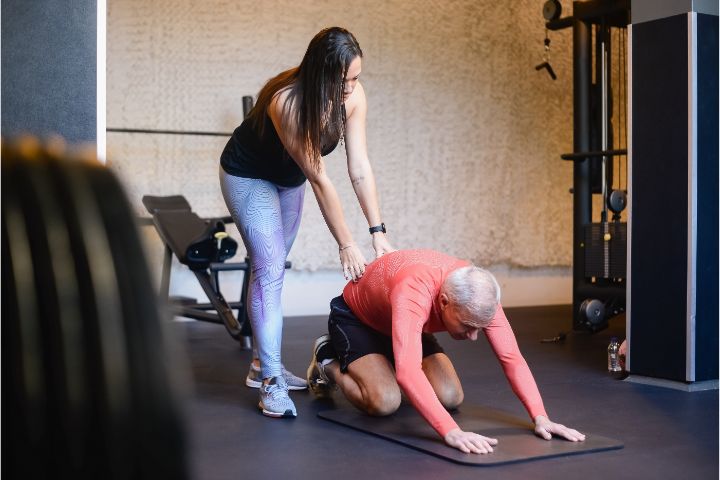

Photo Credit: Kampus Productions
Regular physical activity through physiotherapy can improve balance, strength, and overall health in older adults while reducing the risk of future injuries like falls. Learn more about geriatric care through physical therapy in our dedicated article as well.
Aged care physiotherapy services provide rehabilitation services and prevent falls by carefully guiding elderly patients through exercises specific to their needs in a safe and effective manner.
Paediatric physiotherapists work with children of all ages to help them overcome physical difficulties they are experiencing, including delays in their development. Physiotherapy treatment can improve motor developmental milestones such as rolling, sitting, crawling, and walking as well as physical development such as balance.
For instance, physiotherapy can assist children with Global Developmental Delay (GDD) to develop and improve their motor skills. GDD is a condition where a child fails to meet several milestones in his or her growth and development at the expected times.
Pregnancy can be challenging for many women, with back pain, joint discomfort, and muscle strain being common complaints. Thankfully, physiotherapy can play an important role in helping pregnant women manage their symptoms and reduce their pain.
In addition to exercise programs, some physiotherapists may also provide advice on posture and positioning during pregnancy to help minimize discomfort. They may recommend compression wear or bracing solutions as well.
If you’re living with chronic pain in your back, joints, neck, shoulders or any part of your musculoskeletal system, physiotherapy can be an effective treatment option.
Physiotherapists are experts in movement and function and can help manage and prevent the onset of national health-priority diseases.
Physiotherapists can also be part of multidisciplinary teams that treat chronic conditions. Furthermore, they assist in rehabilitating chronic health conditions such as arthritis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, back pain and osteoporosis.
You can expect an initial assessment and evaluation to determine your condition during a physiotherapy session. The physiotherapist will then develop a treatment plan based on the examination and diagnosis, which may include various techniques such as manual therapy, exercise therapy, electrotherapy, hydrotherapy or acupuncture.
Patients can expect a comprehensive physical evaluation during an initial physiotherapy session to determine their condition. The assessment includes testing for strength and range of motion and an analysis of painful movement.
Physiotherapists will also ask standardised questions to gather information about the type, amount, timeline, and aggravating factors of a patient’s condition. This helps them tailor treatment plans specific to each individual’s needs.
Patients’ evaluation findings along with physiotherapy interventions and evaluations are documented in consultation records by the therapist. These consultations help track progress throughout the healing process accurately.
During a physiotherapy session, the physiotherapist collaborates with the patient to develop an individualised treatment plan for their chronic pain or injury.
The plan may include a range of options, such as manual therapy, exercise therapy, electrotherapy, hydrotherapy, acupuncture and more. Physiotherapists are highly trained to assess and diagnose musculoskeletal conditions and work closely with patients to develop effective management strategies that address their specific needs.
For example, suppose you have back pain due to poor posture at work or spending prolonged hours hunched over your computer screen. In that case, your physiotherapist can develop a targeted plan incorporating posture correction techniques and exercises that strengthen any muscle imbalances in your body that could contribute to the problem.
During a physiotherapy session, your physiotherapist will implement various techniques to help improve movement and reduce pain. Manual therapy is often used, including soft tissue mobilisation, joint mobilisations, and manipulations.
Other techniques that may be implemented include electrotherapy, hydrotherapy, and acupuncture. These methods can help manage pain and improve function while promoting overall healing.
Ongoing monitoring and adjustments are essential to physical therapy treatment, especially for people with chronic pain in the back, joints, neck, shoulders or any part of the musculoskeletal system.
For instance, if a patient is experiencing increased pain or stiffness during exercises prescribed by their physiotherapist, they may need to adjust the intensity or frequency to prevent further injury.
Similarly, if there are signs of improvement after several sessions, the therapist can gradually increase exercise difficulty levels to keep pushing towards recovery goals.
Patient safety is crucial while providing ongoing monitoring and adjustments. Physiotherapists must be aware of this daily while working in clinical settings. Additionally, delivering customised programs that cater to each patient’s needs ensures better outcomes while managing chronic pain effectively.
Choosing the right physiotherapist is crucial for your recovery and overall health. In Australia, there are several factors to consider when selecting a physiotherapist. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision.
First and foremost, ensure that the physiotherapist is registered with the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA). This guarantees they have met the necessary education and training standards to practice in Australia.
Experience is another crucial factor. A physiotherapist with several years of experience, particularly in treating conditions similar to yours, can provide more effective treatment. Feel free to ask about their areas of specialisation and their experience in those areas.
Word-of-mouth referrals and recommendations can be a reliable source of information. Ask your doctor, friends, or family members if they can recommend a good physiotherapist. Online reviews and ratings can also provide insights into a physiotherapist’s reputation.
However, remember that everyone’s experience is unique; what works for one person may not work for you. Use these recommendations as a starting point, but make your own assessment.
A good physiotherapist should be able to communicate clearly and effectively. They should explain your condition, treatment plan, and progress in a way that you can understand. They should also listen to your concerns and answer your questions patiently.

Photo Credit: StudioRoman
Interpersonal skills are equally important. You should feel comfortable and at ease with your physiotherapist. They should be empathetic, respectful, and supportive. Remember, a positive therapeutic relationship can enhance your recovery.
Consider the location of the physiotherapy clinic. Is it easily accessible from your home or workplace? Does it have convenient operating hours? If you have mobility issues, check if the clinic is wheelchair-accessible.
Also, consider the availability of the physiotherapist. Can they accommodate your schedule? How long do you have to wait for an appointment? Remember, regular and timely treatment sessions are crucial for your recovery.
In conclusion, choosing the right physiotherapist involves careful consideration of their credentials, experience, reputation, communication skills, and the location and accessibility of their clinic. Take your time to make an informed decision, and don’t hesitate to switch physiotherapists if you’re not satisfied with your treatment.
Physiotherapy’s a healthcare profession that helps improve and restore physical function and performance.
The three types of physiotherapy are musculoskeletal, neurological, and cardiothoracic.
Yes, physiotherapy can work for back pain. It uses techniques to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
The ATAR score needed for physiotherapy varies, but it’s generally high due to the competitive nature of the course.
Yes, a physiotherapist can do massage as part of their treatment plan.
Physiotherapy can treat a wide range of conditions, including injuries, chronic diseases, and disorders related to muscles, bones, joints, and nerves.
In Australia, physiotherapists need a Bachelor’s Degree in Physiotherapy or a Master’s Degree if they have a related undergraduate degree. They also need to be registered with the Physiotherapy Board of Australia.
A physiotherapy session typically involves an assessment of your condition, followed by a personalized treatment plan that may include exercises, manual therapy, and education about your condition.
In some cases, Medicare can cover physiotherapy, especially if it’s part of a chronic disease management plan.
No, you don’t typically need a referral to see a physiotherapist. However, a referral may be needed for Medicare or insurance purposes.
There are no results matching your search.
Reset