Osteoporosis is a condition that affects the bones, causing them to become weak, brittle, and more prone to fractures. It is a major health concern, particularly for older adults and women.
Over 1 million people in Australia are affected by osteoporosis or low bone density. As bones become thinner and more porous, they lose their strength, making even minor slips, trips, and falls a concern.
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become brittle and fragile, increasing the risk of fractures. It occurs when bones lose minerals such as calcium more quickly than the body can replace them, causing a reduction in bone density. This reduction weakens the bones and makes them more susceptible to fractures.
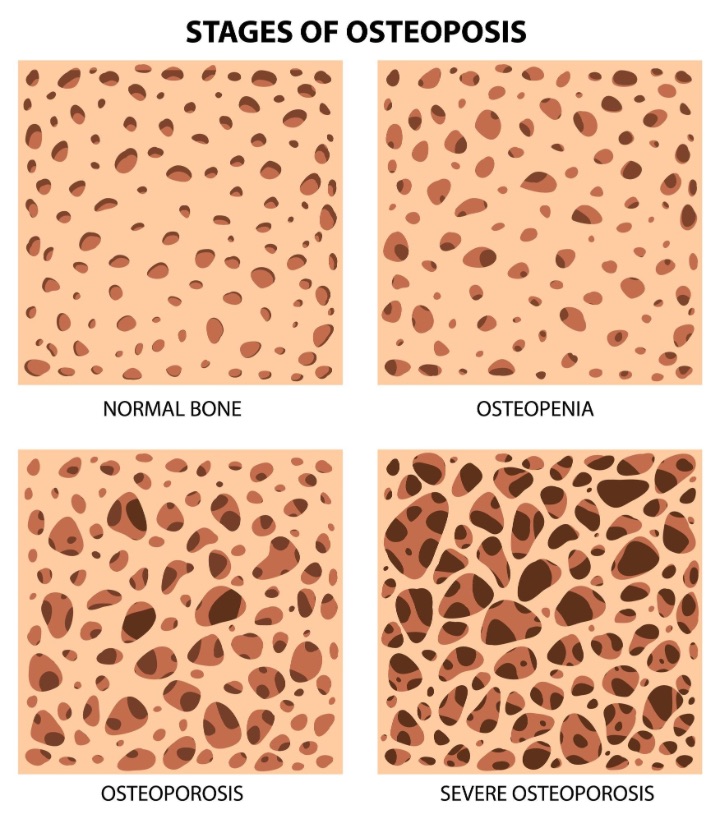
Photo Credit: brgfx
While this can affect any bone in the body, the most commonly affected bones are the hips, wrists, and spine. The condition affects both men and women but is more prevalent in women, especially after menopause.
Several risk factors can contribute to the development of osteoporosis. Some of these factors are modifiable, while others are not.
Prevention is crucial when it comes to osteoporosis. Several strategies can help maintain optimal bone health and prevent the development of this condition.
By implementing these prevention strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of developing osteoporosis and maintain good bone health.
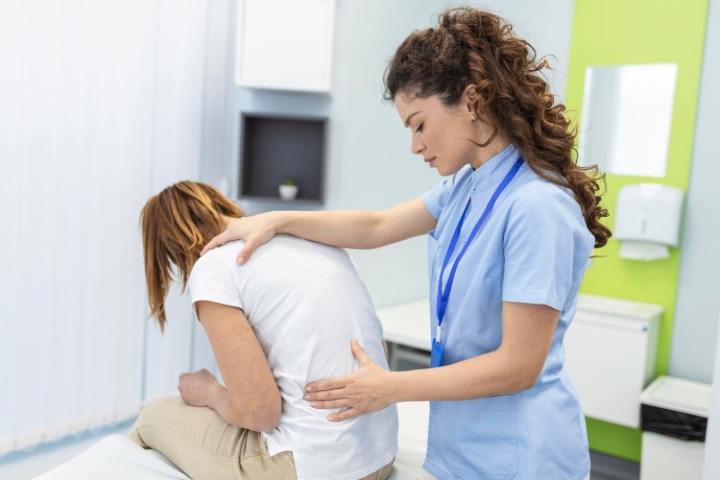

Photo Credit: stefamerpik
Osteoporosis is known to be a “silent disease” as it often doesn’t show any symptoms until a fracture occurs. However, some symptoms can indicate the presence of this condition.
One of the most common symptoms of osteoporosis is bone pain. Pain in the back and neck can be an early sign of the condition. The pain may be constant or intermittent, and it can worsen when performing activities such as standing or walking for an extended period.
Fractures are a common symptom of this condition. They can happen in any bone, but are most commonly seen in the hip, wrist, and spine. Fractures can occur due to a fall or even a minor bump, and they can be painful, leading to immobility and decreased quality of life.
Another symptom of osteoporosis is a gradual loss of height. This can be due to the compression of the vertebrae in the spine, which can cause a reduction in height over time. This can result in a stooped posture and may lead to pain and discomfort.
Osteoporosis is a complex condition with various risk factors contributing to its development. Identifying these risk factors is essential to prevent or manage the condition.
Age and gender are also significant risk factors. As individuals age, their bone density decreases and become prone to this condition. Women, especially those who reach menopause, are at higher risk of developing this condition due to reduced production of estrogen hormone. Men also experience a decline in sex hormones, but at a slower rate than women.
Several medical conditions can contribute to the development of osteoporosis, including Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and hyperthyroidism. Cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and hormonal therapies can also increase the risk of this condition.
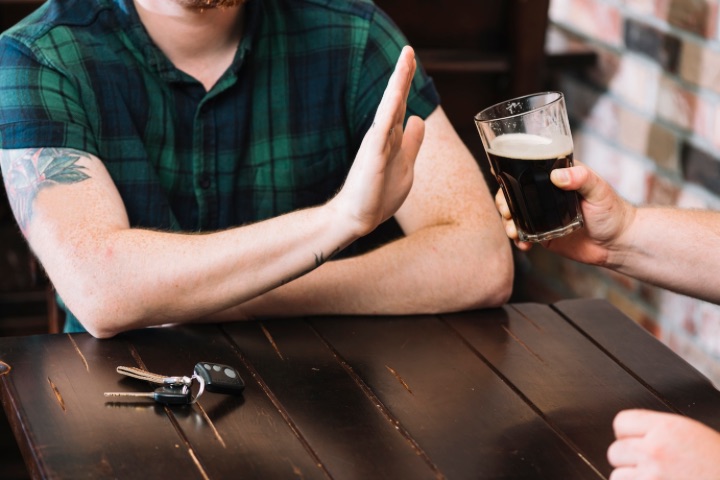

Photo Credit: Freepik
A sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact bone health and increase the risk of osteoporosis. A diet low in calcium and vitamin D can also contribute to developing this condition.
Individuals with a family history of osteoporosis are at higher risk of developing the condition. Genetic factors play a significant role in bone development and density.
Individuals with a small body frame and low body weight have less bone mass, putting them at higher risk of osteoporosis. This is because they have less bone to lose than those with larger frames.
By understanding the risk factors for osteoporosis, individuals can take preventative measures to lower their risk or manage the condition. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help to reduce the risk of developing the condition.
Diagnosing osteoporosis involves various procedures to assess bone density, strength, and structure. Bone density tests are the most common diagnostic tool used to confirm this condition and assess fracture risk.
The most commonly used test measures bone mineral density (BMD) using a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan. Other imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can also provide information about bone structure and health.
Early detection is crucial to prevent further bone loss and fractures. Management strategies typically include lifestyle changes, medication, and nutritional considerations.
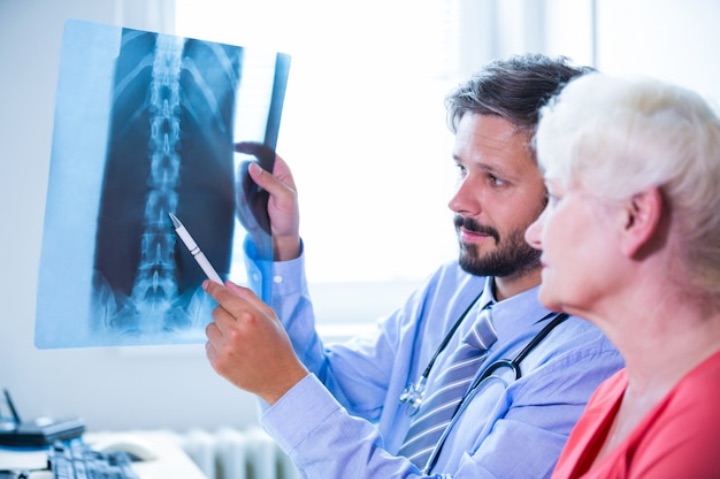

Photo Credit: peoplecreations
Individuals are advised to consume adequate calcium and vitamin D to support bone health and prevent further bone loss. Weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, and strength training are also recommended to improve bone strength and reduce fracture risk.
Several medications are available to treat osteoporosis. These include bisphosphonates, hormonal therapies, and monoclonal antibodies. These medications either slow down bone loss or increase bone formation to improve bone strength and reduce fracture risk. Medications should be used under the guidance of a medical professional who can evaluate individual risks and benefits.
Calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone health. Individuals should consume adequate calcium and vitamin D through diet and/or supplements. Calcium-rich foods include dairy products and dark green vegetables. Foods high in vitamin D include fatty fish and fortified foods like milk and cereal.

Photo Credit: jcomp
Overall, early detection, lifestyle changes, medication, and nutrition are essential for managing osteoporosis and preventing further bone loss and fractures.
While there is no cure for osteoporosis, several treatment options are available to manage the condition and prevent further bone loss. These options include lifestyle changes, medications, and nutritional considerations.
One of the most important things individuals can do to manage this condition is make lifestyle changes promoting bone health, such as quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is also critical for maintaining bone health.
This can include incorporating more dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods into the diet. Additionally, regular exercise can help to strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures.
Several medications are available to help slow down bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures. These include bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, and denosumab. However, discussing the potential benefits and risks of these medications with a healthcare professional before starting any treatment is important.
In addition to a balanced diet, individuals with osteoporosis may need to take supplements to ensure they are getting enough calcium and vitamin D. Calcium supplements are available in various forms, including tablets and chews, while vitamin D supplements are typically taken as a softgel.
Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining bone health and reducing the risk of fractures. Strength training exercises, such as weight lifting and resistance band exercises, can help to build bone density and increase muscle strength.

Photo Credit: Drazen Zigic
Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking and jogging, can also benefit bone health. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to develop an exercise plan that is safe and appropriate for individual needs.
Overall, managing osteoporosis requires lifestyle changes, medications, and exercise. Individuals with this condition can maintain bone health and prevent further bone loss with proper treatment and care.
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by decreased bone density and increased fragility, leading to a higher risk of fractures.
Common symptoms include bone pain, fractures (especially in the wrists, hips, and spine), and loss of height.
Risk factors for osteoporosis include age, gender (women are at higher risk), hormonal changes (such as menopause), lifestyle choices (such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption), and certain medical conditions (such as rheumatoid arthritis and hyperthyroidism).
Osteoporosis is diagnosed through bone density tests, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans, and imaging techniques to assess the condition of the bones.
Treatment options for osteoporosis include lifestyle changes (such as diet and exercise), medications (such as bisphosphonates and hormone therapy), and nutritional considerations (such as ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D intake).
Yes, exercise is crucial in managing osteoporosis by strengthening bones, improving balance, and reducing the risk of fractures. Weight-bearing exercises and resistance training are particularly beneficial.