Scoliosis is a spinal condition that causes an abnormal curvature of the spine. While most cases are mild and require no treatment, the curvature can impact breathing and other bodily functions in severe cases.
The symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the curvature, but common signs include uneven shoulders or hips, a visible curve in the spine, and back pain.
Scoliosis is a condition that causes an abnormal curvature of the spine. While some people with may not experience any discomfort, others may suffer from a range of symptoms, including back pain, uneven shoulders or hips, and breathing difficulties.
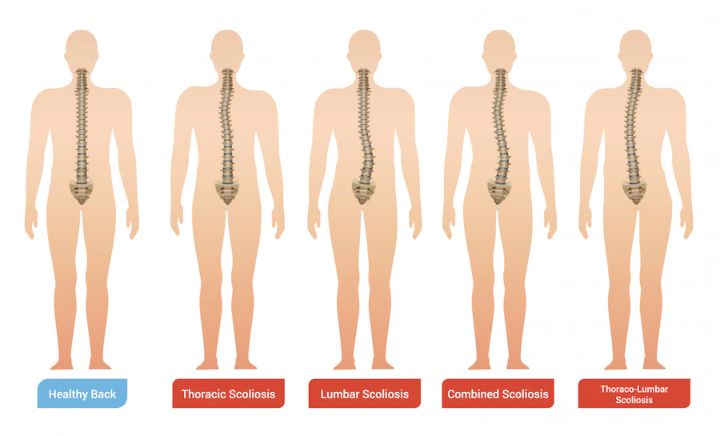
Photo Credit: macrovector
Although this condition can develop at any age, it often appears in children during growth spurts. Early detection is important, as it can help prevent progression of the condition.
The most common symptom is an abnormal curvature of the spine, which can cause the shoulders, hips, or waist to appear uneven. Other symptoms may include:
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a doctor or specialist for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosing often involves a physical examination, including a visual spine assessment and a neurological evaluation. X-rays or other imaging tests may also be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of the spinal curvature.
Early detection and diagnosis of scoliosis are crucial, as it can help prevent further progression of the condition and allow for prompt treatment to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Photo Credit: Freepik
Scoliosis is a complex condition with several possible causes. The majority of cases are idiopathic, meaning the cause is unknown. However, other types can be attributed to specific factors.
Idiopathic scoliosis is the most common form of this condition, and it typically develops during adolescence. This type has no known cause, but researchers have identified certain risk factors that may increase an individual’s likelihood of developing the condition. Factors such as age, gender, and family history can increase the risk of this condition, but the majority of cases occur sporadically without a known cause.
Congenital scoliosis is present at birth and is often caused by abnormalities in the development of the spine. This type can be caused by malformations in the spinal vertebrae, which can lead to an abnormal curvature of the spine. The severity can vary depending on the extent of the malformation.
Neuromuscular scoliosis is caused by muscular or neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy. These conditions can cause muscle weakness or paralysis, leading to an abnormal curvature of the spine. This can develop at any time in life, and the severity of the condition can vary depending on the underlying condition.
Understanding the different causes is important in determining the most appropriate treatment approach for each individual. A thorough evaluation by a specialist can identify the specific type and guide the development of a personalised treatment plan.
Conservative therapies are often the first step in treating this condition, especially for children and teenagers with mild to moderate curvature. Non-surgical treatments aim to reduce the progression and alleviate symptoms, utilizing exercises, bracing, and physical therapy.
Photo Credit: prostooleh
Exercise is essential in managing scoliosis, as it can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and improve posture. Physiotherapists create custom exercise programs tailored to the individual needs of each patient. These exercises aim to address muscle imbalances and improve flexibility and core strength, which can help reduce the severity of the curve.
Bracing may also be recommended for individuals with moderate to severe condition. Braces are worn for several hours each day, with the goal of preventing the progression of the curve. The type of brace and length of time worn depends on the individual’s age, severity of the curve, and other factors.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary. Surgery is typically only recommended for severe cases that are likely to worsen over time or cause health complications. During surgery, the surgeon will fuse the vertebrae together to prevent further curvature. While surgery can be effective, it does come with risks and a long recovery time.
Idiopathic scoliosis is the most common type, affecting roughly 80% of individuals. Treatment options depend on the curve’s severity and the patient’s age. Conservative methods such as exercises and bracing may be prescribed for mild to moderate cases, while surgery may be recommended for more severe cases.
Neuromuscular scoliosis occurs due to conditions such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, or spinal muscular atrophy. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying condition and may include a combination of non-surgical methods such as physical therapy, bracing, and surgical interventions.
Congenital scoliosis occurs due to a spinal defect present at birth. Treatment may involve a combination of surgery, bracing, and physical therapy, depending on the severity of the curve and other factors. Surgery is typically recommended for severe cases, which can include spinal fusion or the implantation of growing rods to help straighten the spine as the child grows.
Overall, the best treatment approach will depend on the individual’s specific condition, severity of their curve, and other factors. Consulting with a specialist can help ensure that patients receive personalized care and management that is tailored to their needs.
Photo Credit: Freepik
Scoliosis is not just a condition that affects children and teenagers. It can also develop in adults, and while the causes and symptoms are similar, managing the condition can present unique challenges.
In adults, this condition can be caused by any of the same factors that lead to developing this condition in children, such as idiopathic, congenital, and neuromuscular scoliosis. Additionally, it can also develop in adults as a result of degenerative changes in the spine that occur naturally with age. These changes can cause the spine to curve and lead to the development of this condition.
The symptoms of scoliosis in adults are similar to those in children and teenagers. These can include back pain, uneven shoulders, uneven waistline, and a visible curvature of the spine. However, adults with this condition may also experience other symptoms such as difficulty breathing or decreased mobility.
Treating scoliosis in adults can be challenging, as the spine is less flexible and may not respond as well to conservative treatments such as exercises or bracing. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature of the spine. However, the decision to undergo surgery should be made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the severity of the curvature, the age and overall health of the patient, and their preferences.
Other treatment options for adults may include pain management techniques such as medications, physical therapy, or chiropractic care. Your doctor may also recommend certain lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and getting regular exercise to help manage the condition.
People of all ages are affected by this condition, but early detection and intervention in children can significantly improve outcomes for this condition.
Regular screenings during childhood can help identify the condition before it progresses and becomes more difficult to treat. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons recommends that children have their spines checked at least twice during their growth period, between the ages of 10 and 14.
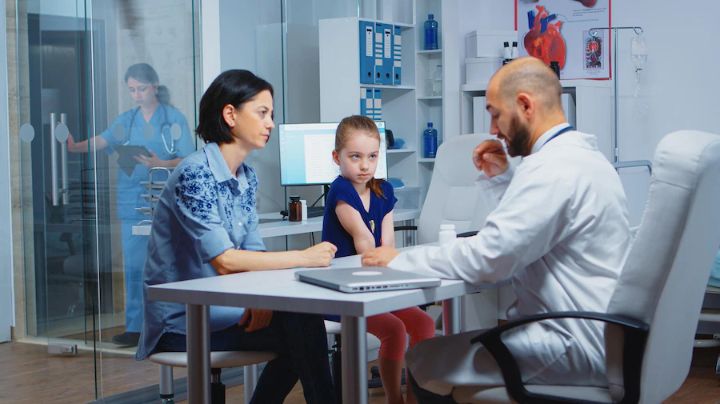

Photo Credit: DCStuido
Screenings are typically conducted by a healthcare professional, who will examine the back for any signs of curvature or asymmetry. If scoliosis is suspected, further diagnostic testing may be recommended.
Early intervention in children can help prevent or slow the progression of spinal curvature. Various conservative treatment options may be used for children with mild to moderate scoliosis, including bracing, physical therapy, and exercises designed to correct posture and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine.
Surgical intervention may be necessary for children with more severe case to address the curvature and prevent further progression. However, early detection and intervention can help minimize the need for surgery and may even eliminate the need for it altogether.
Early detection and intervention are critical in managing scoliosis in children. Regular screenings and prompt treatment can help prevent the condition from progressing and improve outcomes for children with this condition.
While conservative treatments such as exercises and bracing can help manage mild to moderate scoliosis, advanced cases may require surgical intervention.
Spinal fusion is the most common surgical procedure for this condition, which involves fusing the affected vertebrae into a single bone to limit movement and correct the curvature. This procedure can halt the progression and improve spinal stability, but it also comes with risks such as infection and nerve damage.
Several types of spinal fusion procedures exist, including anterior fusion, posterior fusion, and combined fusion. Anterior fusion involves accessing the spine through the front of the body and fusing the affected vertebrae using a bone graft.
Posterior fusion involves accessing the spine through the back and using a metal rod and screws to hold the affected vertebrae in place while a bone graft grows and fuses them together. Combined fusion combines both anterior and posterior approaches for optimal correction.
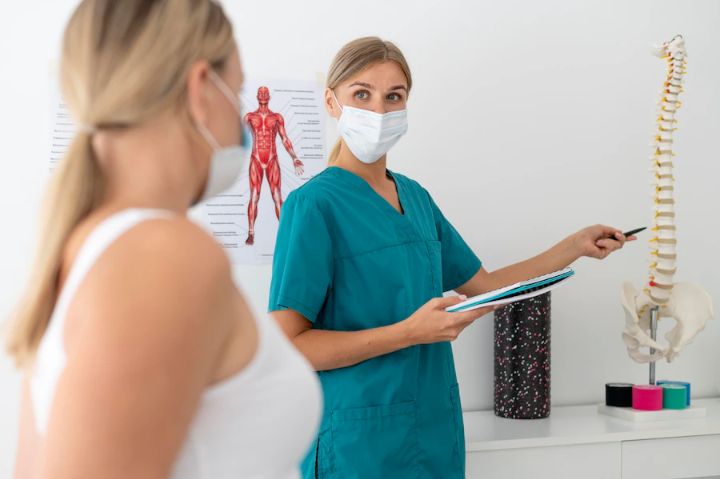

Photo Credit: Freepik
It’s important to note that spinal fusion is not always a permanent solution, and patients may need additional surgeries or revisions in the future. That’s why it’s crucial to seek treatment from a specialists with the expertise and experience to provide comprehensive care and management.
Scoliosis specialists are healthcare professionals who have specialized training and experience in diagnosing and treating this condition.
They can provide personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs and ongoing monitoring and management. This can include non-surgical interventions such as bracing and exercise and surgical procedures when necessary.
When seeking treatment, it’s important to find a specialist who has experience with your specific type, whether it’s idiopathic, congenital, or neuromuscular. By working with a specialist, you can ensure that you receive the best possible care and achieve optimal outcomes.
In conclusion, while this can be a challenging condition to manage, there are a variety of treatment options available, including advanced surgical procedures and specialized care from experts. By seeking early detection and personalized treatment, patients with scoliosis can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Common symptoms include spinal curvature, uneven shoulders, and back pain.
This is typically diagnosed through physical examinations and imaging tests.
This condition can be caused by factors such as idiopathic (of unknown cause), congenital (present at birth), and neuromuscular scoliosis (related to muscular or neurological conditions).
Treatment options include conservative methods such as exercises, bracing, and physical therapy, as well as surgical interventions when necessary.
Scoliosis in adults presents unique challenges and potential complications. There are specialized treatment options available for adult patients.
Early detection through screenings and early intervention are crucial in managing this condition in children and preventing its progression.