Shoulder impingement, also known as subacromial impingement or shoulder impingement syndrome, is a common condition that can cause pain and discomfort in the shoulder. It occurs when the tendons or bursa in the shoulder become compressed or pinched between the bones of the shoulder joint.
Some common symptoms of shoulder impingement include pain in the shoulder, weakness in the arm, difficulty lifting objects, and a limited range of motion. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including repetitive overhead movements, poor posture, and trauma to the shoulder.
If you suspect that you may have shoulder impingement, it is important to seek medical attention as early diagnosis is key to successful treatment. Your doctor will perform a physical exam, take a medical history, and may order imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment options for shoulder impingement vary depending on the severity of the condition but may include physical therapy exercises, medication, and in some cases, surgery. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive rehabilitation plan to aid in recovery and prevent future occurrences.
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a common condition that can cause pain and discomfort in the shoulder joint. It occurs when the tendons and bursa in the shoulder become compressed or pinched, resulting in inflammation and pain.

Photo Credit: stevanovicigor, Envato
Subacromial impingement is the most common type of shoulder impingement syndrome. It occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff and the bursa that cushions them become compressed between the top of the upper arm bone and the acromion, a bony projection of the shoulder blade. Over time, this can lead to irritation, inflammation, and pain.
Did you know? Shoulder impingement syndrome is also referred to as rotator cuff impingement syndrome or swimmer’s shoulder.
Several factors can contribute to the development of shoulder impingement syndrome, including poor posture, repetitive overhead movements, and weak shoulder muscles. Other risk factors include age, as the tendons lose elasticity over time, and certain sports or occupations that require repetitive shoulder motions.
Diagnosing shoulder impingement syndrome typically involves a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. During the physical exam, a healthcare provider will evaluate the range of motion of the shoulder joint, assess for pain or tenderness in specific areas, and conduct a series of tests to check for rotator cuff strength and stability.
Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasounds may also confirm a diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of shoulder pain. These tests can provide a detailed view of the shoulder joint, allowing healthcare providers to evaluate the tendons, muscles, and bones for signs of injury or damage.
Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for the effective treatment of shoulder impingement syndrome, as delaying treatment can lead to further injury and complications.
Shoulder impingement can be a painful and debilitating condition, but several treatment and rehabilitation options are available to help manage and improve symptoms. Early detection is key to successful management, followed by prompt and appropriate treatment. This section will outline the various options available to individuals with shoulder impingement, including non-surgical and surgical interventions, physical therapy exercises, and the importance of a comprehensive rehabilitation plan.
Non-surgical interventions are often the first line of defense against shoulder impingement. These interventions may include rest, ice, and the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation. Other non-surgical interventions may include:
Physical therapy exercises are a key component of non-surgical interventions and are aimed at strengthening the muscles around the shoulder joint, improving range of motion, and reducing pain. Exercises may include stretching, strengthening, and endurance training and are tailored to the individual’s specific needs and goals. A physical therapist will work closely with the individual to design a comprehensive rehabilitation plan that may include both in-clinic and at-home exercises.
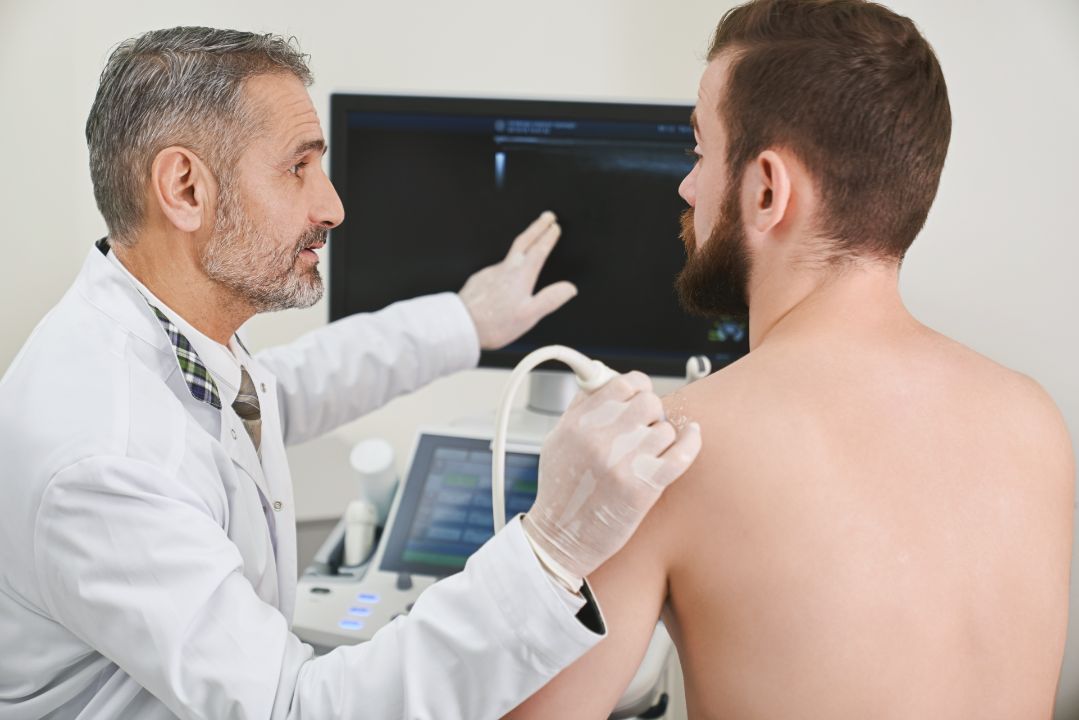
Photo Credit: serhiibobyk, Envato
Surgical intervention may be required if non-surgical interventions do not provide adequate relief. Surgery is typically reserved for individuals with severe, persistent symptoms that have not responded to other treatments. The most common surgical approach for shoulder impingement is arthroscopic surgery, a minimally invasive procedure in which a small camera and instruments are inserted into the shoulder joint through small incisions. The surgeon can then use these instruments to remove any bone spurs or other obstructions that may be causing the impingement.
Regardless of the treatment approach, a comprehensive rehabilitation plan is essential for successful management of shoulder impingement. This plan may include physical therapy exercises, modifications to daily activities, and lifestyle changes to help prevent future occurrences. It is important to work closely with a physical therapist or healthcare provider to design a rehabilitation plan that addresses individual needs and goals, and to follow the plan closely to ensure optimal outcomes.
Overall, while shoulder impingement can be a challenging condition to manage, there are several effective treatment and rehabilitation options available. By working closely with a healthcare provider and following a comprehensive rehabilitation plan, individuals with shoulder impingement can experience significant relief from symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Shoulder impingement is a condition that can be prevented by taking certain measures. Here are some tips and strategies to help reduce the risk of developing this condition:
One of the main causes of shoulder impingement is poor posture. When you hunch your shoulders or slouch, your shoulders become misaligned, which can lead to impingement. To improve your posture, you should:
Strengthening exercises can help to improve your shoulder stability and reduce the risk of impingement. Here are a few exercises to try:

Photo Credit: vladans, Envato
Modifying your lifestyle habits can also help to prevent shoulder impingement. Here are some things to consider:
“Prevention is better than cure – taking steps to prevent shoulder impingement can save you from discomfort and potential surgery down the track.”
Shoulder impingement is a common condition that causes pain and discomfort in the shoulder joint. Here are some of the frequently asked questions about shoulder impingement:
The most common symptoms of shoulder impingement include pain, weakness, and limited range of motion in the affected shoulder. The pain may worsen when raising the arm, reaching overhead, or sleeping on the affected side.
Shoulder impingement is a condition that occurs when the rotator cuff tendons and/or the bursa become compressed or pinched between the bones of the shoulder. This can lead to inflammation, pain, and limited range of motion. Other shoulder conditions, such as rotator cuff or labral tears, may also cause pain and discomfort, but the underlying causes and treatments may differ.
If you experience persistent pain, weakness, or limited range of motion in your shoulder, it is recommended that you seek medical help. Your doctor or physical therapist can evaluate your symptoms, perform diagnostic tests, and recommend appropriate treatments to help relieve your pain and restore your shoulder function.
With proper diagnosis and treatment, most people with shoulder impingement can recover and return to their normal activities. Talk to your healthcare provider for guidance if you have concerns about your shoulder health.