Rotator cuff tears are a common injury that can cause pain, weakness, and limited mobility in the shoulder. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize and support the shoulder joint, allowing for a wide range of motion. When a tear occurs, it can significantly impact daily life and activities.
If you suspect that you may have a rotator cuff tear, it’s important to seek medical attention right away. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and improve outcomes.
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and allowing for a wide range of motion in the arm. A torn rotator cuff occurs when one or more of these muscles or tendons are partially or completely torn, resulting in pain, weakness, and limited mobility in the affected shoulder.
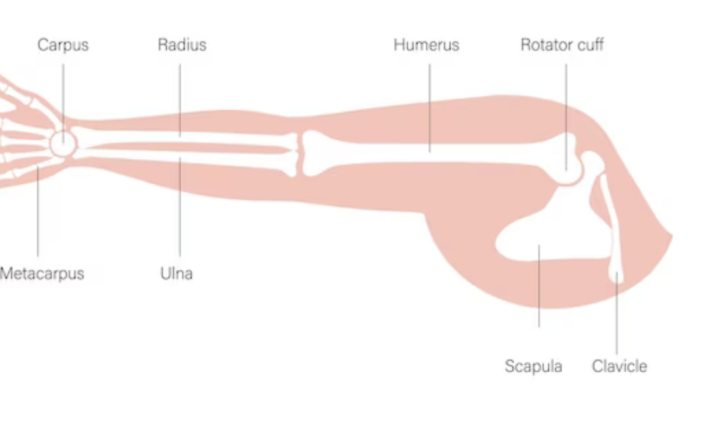
Photo Credit: user19987712
Rotator cuff injuries can be caused by a variety of factors, including acute trauma such as a fall or an impact to the shoulder, as well as chronic conditions like repetitive overhead motions or degenerative changes due to aging. In some cases, there may be no identifiable cause of a rotator cuff tear.
The symptoms of a rotator cuff tear can vary depending on the severity and location of the tear, as well as the individual’s age and overall health. Common symptoms may include:
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause and severity of your injury.
A rotator cuff tear is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans, and a thorough medical history review. Your doctor may ask you to perform certain movements and tests to assess your range of motion, strength, and pain level in the affected shoulder.
Imaging tests can help confirm the presence of a tear and determine the injury’s size, location, and severity. In some cases, an arthroscopy may be performed, which involves using a small camera and surgical tools to repair the tear through small incisions in the shoulder.
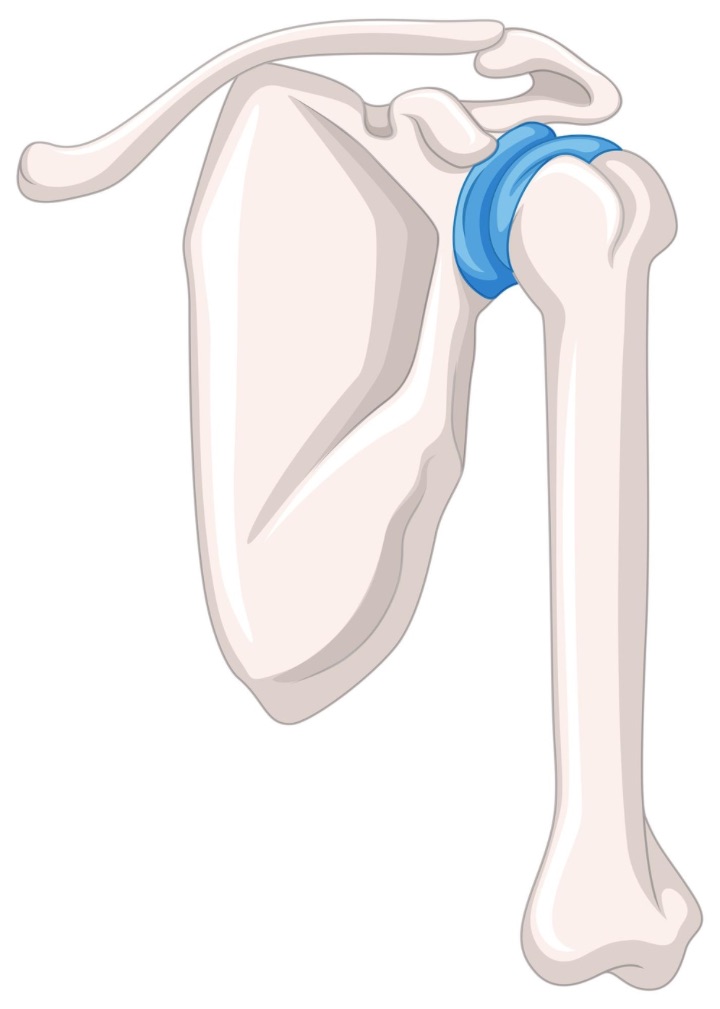
Photo Credit: brgfx
As with any medical condition, early diagnosis and treatment of a rotator cuff tear can help to prevent further damage and improve outcomes.
Multiple factors, including both acute injuries and chronic conditions can cause rotator cuff tears.
Acute injuries are sudden traumatic events that cause immediate pain and damage to the rotator cuff. Examples of acute injuries include falling on an outstretched arm, lifting a heavy object, or a direct blow to the shoulder. These injuries can cause partial or complete tears in the rotator cuff.
Chronic conditions are long-term conditions that worsen over time, resulting in progressive damage to the rotator cuff. These conditions are often related to overuse, degeneration, or age-related changes in the shoulder joint. Common chronic conditions contributing to rotator cuff tears include tendinitis, bursitis, and degenerative changes in the rotator cuff tendons.
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing a rotator cuff tear:
While not all rotator cuff tears can be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience rotator cuff tear symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and improve outcomes.
Photo Credit: prostooleh
Rotator cuff tears can be treated with a variety of options depending on the severity of the tear. Some mild or moderate tears can be treated conservatively, while severe or complete tears may require surgery. Here are some of the treatment options that may be recommended:
If the rotator cuff tear is mild or moderate, the doctor may recommend conservative treatment options, which include:
If conservative treatment options are not effective or the rotator cuff tear is severe, the doctor may recommend surgical treatment options, which include:
After rotator cuff tear treatment, rehabilitation and aftercare are crucial for regaining strength and normal function in the affected shoulder. Rehabilitation usually begins after any surgery or after the pain and swelling have reduced to an acceptable level. Rehabilitation may include:
Note: It’s important to follow the treatment plan recommended by the doctor and to attend all follow-up appointments in order to ensure a full recovery and avoid further complications.
Photo Credit: Freepik
Recovering from a rotator cuff tear can be a long and challenging process. However, with the right rehabilitation techniques and exercises, it is possible to regain strength and function in the affected shoulder.
Physical therapy is an essential aspect of rotator cuff tear recovery. Your physiotherapist will work with you to develop a personalized rehabilitation program that is tailored to your specific needs and goals.
During your physical therapy sessions, you will be guided through a series of exercises designed to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in your shoulder. Your therapist may also use various modalities, such as heat or ice, to help reduce pain and inflammation.
In addition to attending regular physical therapy sessions, performing rotator cuff tear exercises at home is important to help speed up recovery. Here are a few exercises that may be included in your rehabilitation program:
Note that it’s important to start with light weights and gradually increase the resistance as your shoulder gets stronger.
The recovery process for a rotator cuff tear can be challenging, but staying committed to your rehabilitation program is important. With the right exercises and techniques, you can regain strength and function in your shoulder and get back to your normal activities.
Always consult with your doctor or physiotherapist before starting any new exercise program, and be sure to follow their guidance closely to ensure a safe and effective recovery.
Recovering from a rotator cuff tear can take time and patience, and it’s natural to have questions about the process. Here are some frequently asked questions about rotator cuff tears and their treatment:
Recovery time can vary depending on the severity of the tear and the chosen treatment plan. Generally speaking, a full recovery can take several weeks to several months. It’s important to follow your doctor’s recommended treatment plan and to be patient with your body’s healing process.
Surgery may be necessary if conservative treatments, such as physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises, do not improve the condition. Surgery may also be recommended for larger or more severe tears, or if the injury causes significant pain or loss of function. Your doctor can help determine if surgery is necessary in your particular case.
Physical therapy is often prescribed as part of the treatment plan for a rotator cuff tear. It can help improve range of motion, reduce pain and inflammation, and strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected shoulder. Your physiotherapist can work with you to develop a tailored exercise program that meets your specific needs.
Small tears may be able to heal on their own with rest and conservative treatment, while larger tears may require surgery or other interventions. It’s important to consult your doctor to determine the best course of action for your injury.
Like any surgery, rotator cuff tear surgery carries risks. These may include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, or repair failure. However, with proper care and monitoring, complications are rare. Your surgeon can discuss surgery’s potential risks and benefits with you.
Your physiotherapist can recommend specific exercises to help you regain strength and range of motion in your affected shoulder. Some common exercises for rotator cuff tears may include range-of-motion exercises, stretching, and resistance training. It’s important to follow your physiotherapist’s recommendations and avoid overexerting yourself during rehabilitation.
You can improve your chances of a successful recovery by recognising the signs of a rotator cuff tear and seeking prompt treatment. Don’t hesitate to consult with your doctor or physiotherapist if you have any questions or concerns about your injury and its treatment.