Adductor tendinopathy is characterised by inflammation and damage to the tendons that attach the adductor muscles to the pelvis and thigh bone. Adductor tendinopathy can be caused by repetitive strain or overuse and sudden trauma or injury.
Adductor tendinopathy is typically caused by repetitive overload of the adductor tendons, resulting in micro-tears and degeneration. It is commonly seen in sports requiring repetitive kicking or cutting movements, such as soccer and ice hockey.
Other contributing factors include poor biomechanics, muscle imbalances, and inadequate warm-up or stretching routines.
Photo Credit: kjpargeter
Individuals with adductor tendinopathy usually experience pain and tenderness in the groin area, which can worsen during activity. Symptoms may also include stiffness, weakness, and difficulty with certain movements, such as running, jumping, or squatting.
Adductor tendinopathy can lead to chronic pain, decreased mobility, and reduced athletic performance if left untreated. Seeking prompt medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms is essential.
Diagnosing adductor tendinopathy involves a thorough medical assessment by a healthcare professional. The diagnosis is usually made based on the individual’s medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies.
The medical history of the individual is essential in diagnosing adductor tendinopathy. The healthcare professional will ask about the individual’s symptoms, such as pain, swelling, or tenderness in the adductor muscles. They will also enquire about the duration and severity of the symptoms and any previous injuries to the area.
Photo Credit: korshka_nastya
During the physical examination, the healthcare professional will assess the individual’s range of motion, muscle strength, and flexibility. They will also palpate the adductor muscles to check for any tenderness or swelling. The assessment may include a gait analysis to identify any abnormalities in the individual’s walking pattern.
Imaging studies are useful in diagnosing adductor tendinopathy. An ultrasound scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect any damage, inflammation or tears in the adductor muscles or tendons. These diagnostic tests help to provide a clear view of the affected area and determine the extent of the damage.
Overall, an accurate diagnosis of adductor tendinopathy is crucial for effective treatment. It is recommended to seek medical attention if experiencing any symptoms or discomfort in the adductor muscles.
Effective treatment for adductor tendinopathy depends on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. Sometimes, a combination of treatments may be necessary to achieve the best results. The following are some of the most effective treatment options for adductor tendinopathy:
Rehabilitation exercises are an essential part of treating adductor tendinopathy. These exercises are designed to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion, which can help reduce pain and prevent further injury. Physical therapists can develop an exercise program tailored to individual needs. Exercises may include stretching, foam rolling, and resistance training.
Strengthening exercises can improve the strength of the adductor muscles and help prevent future injury.
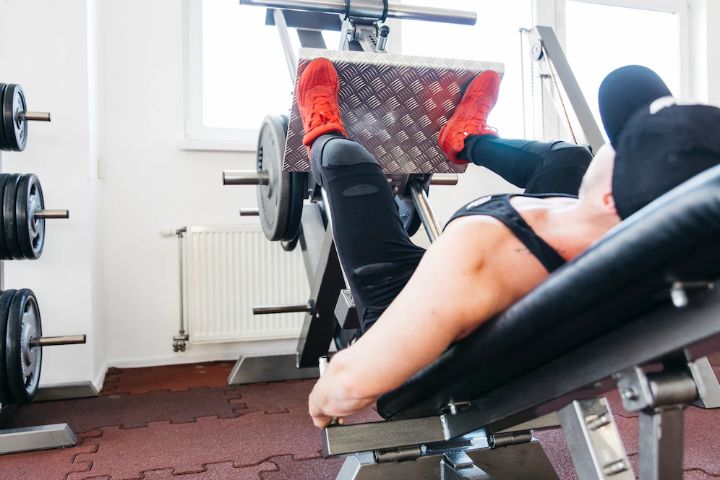

Photo Credit: Freepik
These exercises may include leg presses, squats, lunges, and single-leg deadlifts. A physical therapist can provide guidance on how to perform these exercises correctly and safely.
Cold therapy can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with this condition. Applying an ice pack or cold compress to the affected area for 20-30 minutes at a time, several times a day, can help reduce swelling and pain.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with adductor tendinopathy. These medications are available over-the-counter or by prescription, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s medical history. However, speaking with a healthcare provider before taking any medication is important.
Rest and recovery are essential components of treating this condition. Avoiding activities aggravating the condition and getting enough rest can help reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapists may also recommend the use of braces or supports to help support the affected area during rest or activity.
Overall, effective treatment for adductor tendinopathy requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the condition’s underlying cause and reduces pain and inflammation. Working with a healthcare provider, such as a physical therapist, can help individuals develop an individualized treatment plan that meets their specific needs and goals.
While adductor tendinopathy can be effectively treated with the right interventions, prevention is always better than cure. Individuals at risk of developing this condition or those with a history of adductor muscle injuries should take proactive measures to avoid further damage and ensure long-term management of their condition.
Before engaging in any physical activity, it is crucial to perform warm-up exercises to prepare the body for movement and reduce the risk of injury.

Photo Credit: standret
These exercises can include jogging, jumping jacks, and stretching. Similarly, cooling down exercises such as walking and stretching after a workout can also aid in muscular recovery and reduce injury risk.
Individuals should gradually increase the intensity and duration of their physical activity, allowing their body to adjust to the new demands. This process prevents overuse injuries and promotes optimal muscle functioning.
Using proper technique and form during physical activity can reduce the risk of injury and improve muscle functioning. It is essential to consult with a trainer or coach to learn proper techniques for weightlifting, running, and other activities that place strain on adductor muscles.
Rest and recovery are crucial components of the long-term management of adductor tendinopathy. Adequate rest allows muscles to recover and repair, while sleep promotes overall physical and mental wellness. Individuals should also consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation and massage into their routines to aid in recovery.
Proper nutrition and hydration are vital for overall health and muscle function. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein can aid in muscle recovery and repair. Staying hydrated by drinking enough water throughout the day can improve muscle function and prevent injury.
By incorporating these tips into their routine, individuals can reduce the risk of developing adductor tendinopathy or aggravating pre-existing injuries. Consulting with a healthcare professional or trainer is always advised for personalised advice and guidance.
A: Common symptoms of adductor tendinopathy include pain and tenderness in the groin area, difficulty with activities that involve hip movement or sudden changes in direction, swelling, and a sensation of weakness in the groin or inner thigh.
A: Adductor tendinopathy can be caused by repetitive stress or overuse of the adductor muscles, sudden or forceful movements that strain the adductor muscles, poor conditioning or muscle imbalances, and direct trauma or injury to the groin area.
A: Adductor tendinopathy is diagnosed through a combination of physical examinations, imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI scans, and other tests to assess the strength and flexibility of the adductor muscles.
A: Treatment for adductor tendinopathy typically involves a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy exercises to improve strength and flexibility, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, corticosteroid injections or surgical intervention.
A: To prevent adductor tendinopathy, individuals can engage in proper warm-up and cool-down exercises, maintain good overall fitness and muscle balance, gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activity, use proper technique and equipment, and listen to their body for any signs of discomfort or pain.