Groin pain is a common injury that can be caused by a variety of factors, including sports-related activities, overuse, and trauma. Common types of groin pain injuries include groin strain, groin pull, adductor muscle injury, and groin hernia.
It is important to recognize the symptoms of groin pain, which may include groin contusion, muscle strain, inflammation, and discomfort. Seeking medical evaluation and imaging techniques can help diagnose the severity of the injury, with symptoms like groin tenderness, tightness, swelling, and groin ache being significant.
Treatment options for groin pain injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Rehabilitation exercises, medications, and surgery may be recommended, with specific concerns like groin soreness, groin bruise, groin trauma, and groin fracture being addressed. Additionally, actions can be taken to prevent common conditions leading to groin pain injuries, such as groin ligament injury, muscle spasm, overuse injury, and nerve compression.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options of groin pain injuries can help individuals better manage and prevent this common injury.
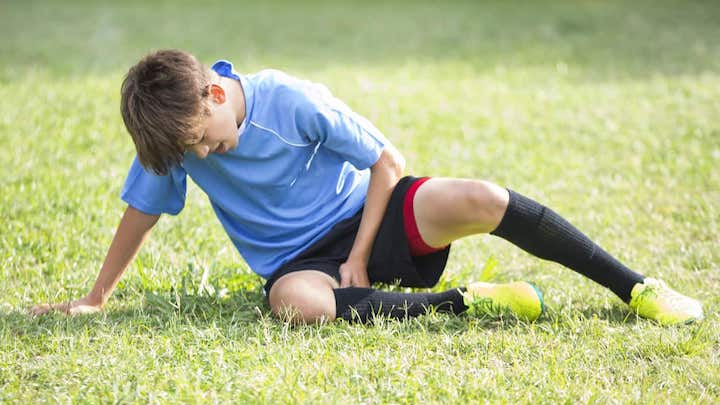

Photo Credit: SDI Productions, Getty Images
Groin pain injuries can result from a variety of causes, including sports-related activities, overuse, or trauma. Here, we examine some of the most common types of groin pain injuries and the risk factors associated with their occurrence.
A hip flexor strain occurs when the muscles that lift the thigh towards the torso are stretched beyond their capacity. This can lead to pain in the front of the hip or upper groin area and may cause difficulty with walking or bending forward. Risk factors for this type of injury include overuse, sudden movements, and poor conditioning.
Athletes who engage in sports that require quick changes of direction or kicking movements are at increased risk of experiencing sports-related groin pain. This type of injury can be caused by overuse of the adductor muscles in the groin or by a direct blow to the area. Symptoms include pain and discomfort in the groin area, which may be more noticeable during sports activities.
A groin tear, also known as a groin strain, occurs when the adductor muscles in the groin are stretched or torn. Symptoms may include sudden pain in the groin area, tenderness, swelling, and bruising. Risk factors include sudden and forceful movements, muscle fatigue, and poor flexibility.
A groin sprain, also known as a pubic bone sprain, can occur when the ligaments that connect the pubic bones become stretched or torn. This can cause pain in the groin area that may radiate to the hips or lower abdomen. This type of injury risk factor includes overuse, trauma, or pregnancy.
Understanding the common types of groin pain injuries and their associated risk factors is essential in preventing injury and maintaining proper physical health. The following section will examine the symptoms and signs of groin pain injuries.
Groin pain injuries can be debilitating and affect daily activities. It is important to recognise the symptoms and signs to get the right diagnosis and treatment promptly. Common indications of groin pain injuries vary but can be classified as follows:
A groin contusion usually occurs following a direct blow to the muscles in the groin area, resulting in bruising and swelling. Symptoms of a groin contusion include pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area. The pain may be more intense when walking or moving the leg.
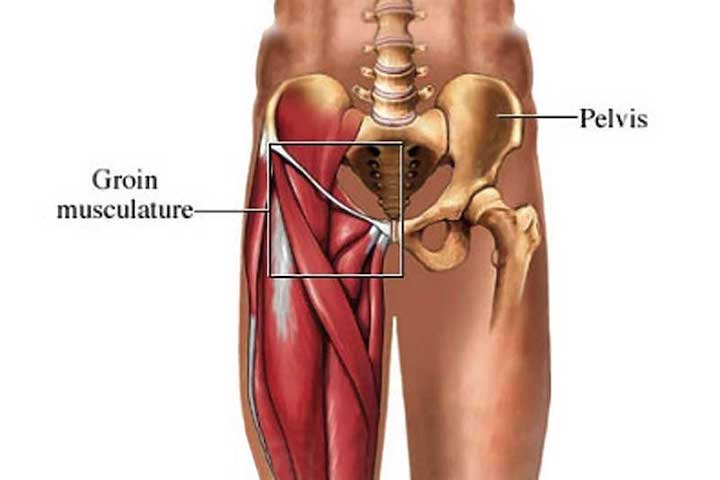
Photo Credit: Keystone Physiotherapy
A groin muscle strain is a common injury that usually occurs while participating in activities requiring quick direction changes, such as soccer or basketball. Symptoms of a groin muscle strain include pain, tenderness, and stiffness in the affected area. The pain may worsen when stretching, moving the leg, or during physical activity.
Groin inflammation, also known as osteitis pubis, occurs when there is an inflammation of the pubic symphysis joint. Symptoms of groin inflammation include pain and tenderness in the groin area, difficulty walking, and pain when moving the leg or during physical activity.
Groin discomfort can be caused by a variety of factors, including a pulled groin muscle or a hernia. Symptoms of groin discomfort include pain, tenderness, and a sensation of pressure in the groin area. The pain may worsen when moving the leg or during physical activity.
If you are experiencing groin pain, it’s essential to seek a medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. The diagnostic process may involve a physical examination and various imaging techniques.
Your doctor will begin by examining the affected area, looking out for signs of swelling, redness, and tenderness. They may ask about your medical history, including any previous injuries or medical conditions contributing to your groin pain.
During the medical evaluation, your doctor may also test your range of motion and perform strength assessments to determine the severity of the injury.
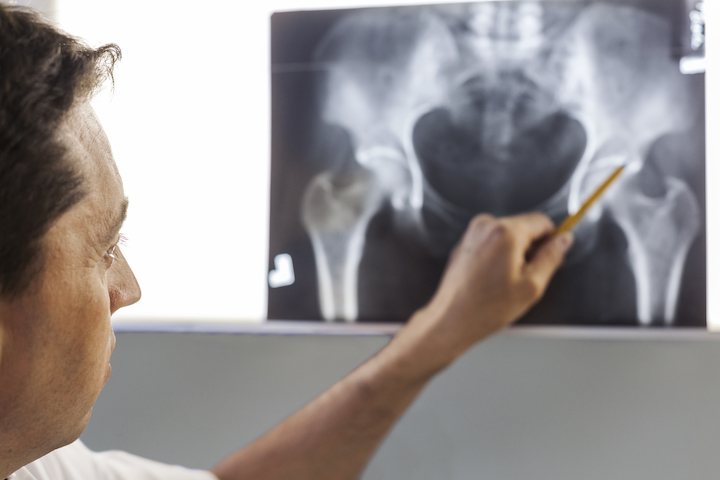
Photo Credit: WestEnd61, Envato Elements
In addition to a physical examination, imaging techniques may also be used to diagnose the underlying cause of your groin pain. The most common types of imaging include:
Your doctor will determine the type of imaging required based on the symptoms you are experiencing and the severity of the injury.
It’s important to note that diagnosing groin pain can be complex, as the symptoms may mimic other conditions. Therefore, seeking medical attention is crucial to ensure an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment plan.
Depending on the severity of the groin pain injury, different treatment options can range from rehabilitation exercises to medications to surgical interventions. The treatment plan will be determined by the type and extent of the injury, as well as the patient’s medical history and current physical condition.
Rehabilitation exercises are often the first line of treatment for groin pain injuries. These exercises are designed to help strengthen the affected muscles, improve flexibility and range of motion, and reduce pain and inflammation. Common rehabilitation exercises for groin pain injuries include:
It is important to note that rehabilitation exercises should be performed under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
Medications can be prescribed to manage the pain and inflammation associated with groin pain injuries. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen are often used to reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide short-term pain relief.
Surgery may be necessary in cases where the groin pain injury is severe. Surgery may be recommended for injuries such as a groin fracture or hernia causing significant pain or discomfort. The type of surgical intervention will vary depending on the specific injury.
Groin pain injuries can present with specific concerns that must be addressed in the treatment plan. Some of these concerns include:
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate course of treatment for these specific concerns.

Photo Credit: Cliff Booth, Pexels
Groin pain injuries can be debilitating and may take considerable time to heal, so it is important to take steps to prevent them from occurring in the first place. Here are some practical tips and strategies to help minimise the risk of groin pain:
Before any physical activity, it is essential to warm up properly. This can include light aerobic exercise and dynamic stretching. Warming up increases blood flow to the muscles and prepares them for physical activity. Stretching after exercise is equally important to help improve flexibility and prevent muscle strains.
If you are new to a specific sport or activity, it is essential to progress the intensity and duration gradually. Overexerting yourself can increase the risk of groin injuries, such as muscle strains and tears.
Proper technique is critical when performing any physical activity, particularly those involving the lower body. Incorrect technique can place additional stress on the muscles and increase the chance of injury. Consulting with a coach or trainer can help ensure you are using the proper form.
Rest and recovery are just as important as exercise and physical activity. Giving your body adequate time to recover between workouts can prevent overuse injuries, such as groin overuse injury and muscle spasms.
Using the proper equipment can help prevent groin injuries. For example, wearing supportive footwear can help improve balance and reduce the risk of falls and other accidents contributing to groin trauma. Additionally, wearing protective gear like groin guards can help prevent injuries while playing contact sports.
Finally, it is essential to listen to your body. If you experience any pain or discomfort in the groin area, taking a break and allowing your body time to heal is important. Continuing to exercise or play through the pain can exacerbate existing injuries and increase the risk of further damage.
Following these tips and strategies can help prevent groin pain injuries and stay healthy and active.
A: Groin pain injuries can be caused by various factors, including groin strain, groin pull, adductor muscle injury, and groin hernia.
A: Symptoms of groin pain injuries may include groin contusion, groin muscle strain, groin inflammation, and groin discomfort.
A: Groin pain injuries can be diagnosed through medical evaluations and imaging techniques. Medical professionals may assess symptoms such as groin tenderness, groin tightness, groin swelling, and groin aches.
A: Treatment options for groin pain injuries may involve rehabilitation exercises, medications, and, in some cases, surgical interventions. Depending on the severity of the injury, specific concerns like groin soreness, groin bruise, groin trauma, and groin fracture may be addressed.
A: To prevent groin pain injuries, it is recommended to take precautions against conditions such as groin ligament injury, groin muscle spasm, groin overuse injury, and groin nerve compression. Implementing proper strategies and following guidelines can help minimise the risk of future injuries.