Osteitis Pubis, commonly known as pubic bone inflammation, is a condition that causes pelvic pain and is often associated with sports-related groin injuries. It is also known by the name of pubalgia. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of Osteitis Pubis, including its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Osteitis pubis is a painful condition that involves inflammation of the pubic bone. It is often associated with sports-related groin injuries and can cause significant pelvic pain. Understanding the pelvis’s mechanics can help comprehend the underlying causes of this condition. The pelvic girdle transfers forces between the upper and lower extremities and provides stability and support for the spine.
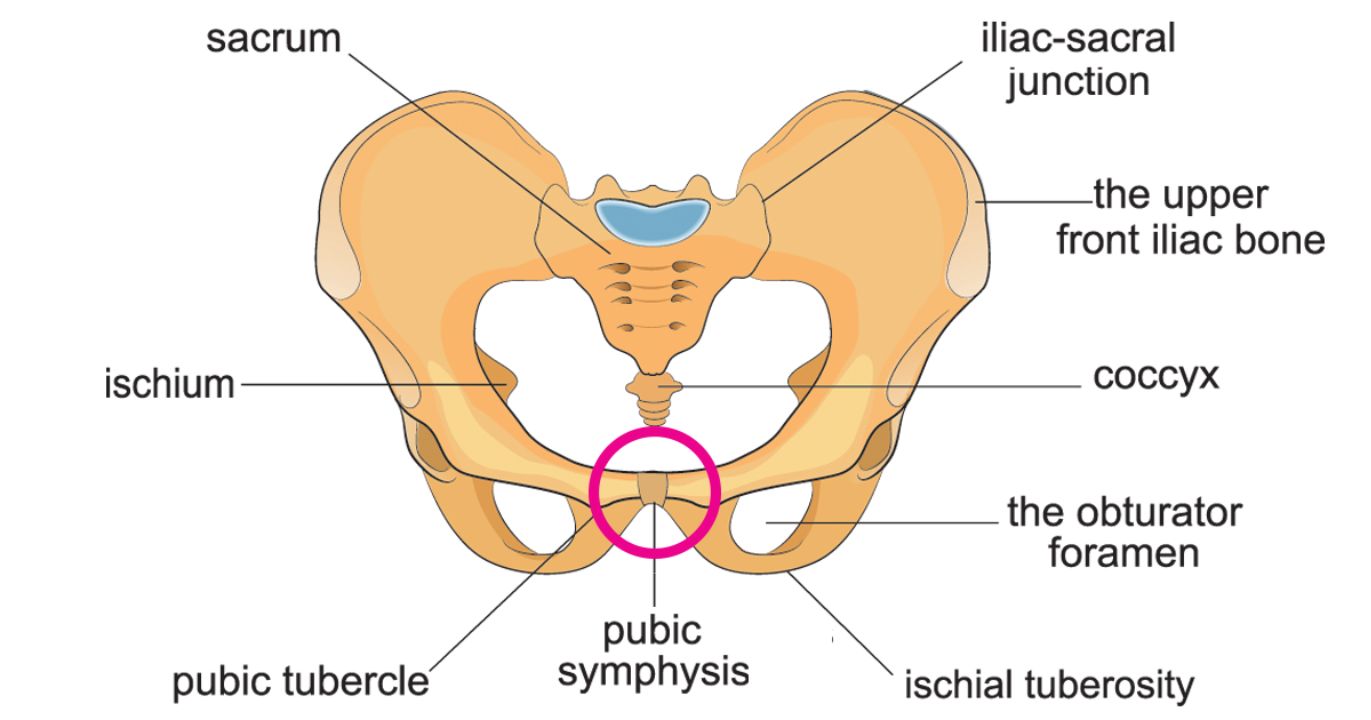
Photo Credit: Dreams Time
The pubic joint is the point where the two halves of the pelvis meet at the front of the body. It is a synovial joint, meaning that it is lubricated with fluid and surrounded by a capsule that allows for movement and flexibility. The pubic bone is protected by cartilage and fibrocartilage, which help to absorb shock and reduce friction during movement. When the pubic joint becomes inflamed, it can cause pain and discomfort in the pelvic region.
Several factors can contribute to inflammation of the pubic joint. Overuse or repeated stress on the joint can lead to microtrauma and subsequent inflammation. Sports that involve sudden changes in direction, such as football or soccer, can place significant stress on the pelvic girdle and lead to injury. Muscular imbalances, poor biomechanics, and weakness in the pelvic floor or hip muscles can also contribute to the development of osteitis pubis.
While the exact cause of osteitis pubis is not always clear, it is thought that this condition may be related to an underlying mechanical issue, such as the way that the pelvis is aligned during movement. This can result in excessive wear and tear on the pubic joint and contribute to the development of this condition.
It is typically caused by repeated stress or trauma to the pelvic area, resulting in inflammation of the pubic bone and surrounding muscles. While the condition can affect anyone, it is most commonly seen in athletes who participate in sports that involve repetitive movements, such as soccer, hockey, and running.
A sports-related groin injury, also known as pubalgia, is a common cause of osteitis pubis. This type of injury can occur when there is stress or strain on the muscles and tendons that attach to the pubic bone. The resulting pain can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, depending on the severity of the injury.
In some cases, this may be a result of an underlying medical condition, such as arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease. It may also occur as a complication following surgery or trauma to the pelvic area.
While the exact cause of osteitis pubis may vary from person to person, it is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing pelvic pain or discomfort. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and improve your chances of a full recovery.
Osteitis pubis is characterized by several symptoms, including pelvic pain, hip pain, and lower abdominal pain. The discomfort can range from mild to severe and may be aggravated by activities such as running, twisting, or kicking.
If you are experiencing these symptoms, seeking a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional is essential. A doctor will perform a physical examination, including palpation of the pelvic area, to identify areas of tenderness and pain.
Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may also be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as a hernia or stress fracture.
It is important to note that the diagnosis of osteitis pubis can be challenging due to the nonspecific nature of its symptoms. Therefore, consulting with a healthcare professional who can accurately diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options is crucial.

Photo Credit: stevanovicigor, Envato
Osteitis pubis can be a debilitating condition, but various treatment options are available to manage and alleviate symptoms. Treatment may depend on the severity of the condition, the underlying cause, and the individual’s overall health and medical history.
It is important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for individual cases of osteitis pubis. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and improve overall outcomes.
Managing this condition involves a combination of approaches, including medical treatment, physical therapy and lifestyle changes. Here are some tips to help manage osteitis pubis:
For those with osteitis pubis, taking a break from activities that cause pain or discomfort is important. This may include modifying exercise routines, such as avoiding sudden change of direction or high-impact activities. Adequate rest and activity modification can help the body heal and prevent further damage.
Physical therapy can help manage osteitis pubis by improving strength, flexibility, and mobility in the affected area. A physical therapist can design a specific exercise program tailored to an individual’s needs and condition. This may include exercises for stabilising the pelvis and strengthening the core, glutes, and hip muscles.
Ice and heat therapy can be used to reduce inflammation and pain. Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help. Heat can be applied to the area to promote blood flow and loosen muscles.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with this condition. Over-the-counter pain medications like acetaminophen can be used to manage pain, but it is important to follow the recommended dosage.
Specific exercises can help alleviate symptoms and prevent future occurrences. These exercises may include pelvic tilt, clamshell, and bridges. Stretching exercises targeting the hip flexors, quadriceps, and adductors can also be beneficial. It’s important to consult with a physical therapist before starting any exercise program.
Preventive measures can be taken to reduce the risk of developing osteitis pubis. This may include adequate warm-up and cool-down routines before and after physical activity, wearing appropriate footwear, and gradual progression of activity level. Maintaining good posture and engaging in strength training to maintain core stability can also help prevent the condition from occurring.
Recovery from osteitis pubis can be a slow and gradual process, and it is important to allow the body enough time to heal properly. Rest is key in the initial stages of recovery, and individuals with osteitis pubis should avoid activities that aggravate their symptoms.
Once symptoms improve, a gradual return to physical activity can begin. This should be under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a qualified physical therapist to ensure that the individual does not push themselves too hard and cause a relapse.
Physical therapy is an important part of the recovery process for individuals with osteitis pubis. A physical therapist can provide exercises and stretches that can help alleviate symptoms and improve flexibility and strength in the pelvic area.
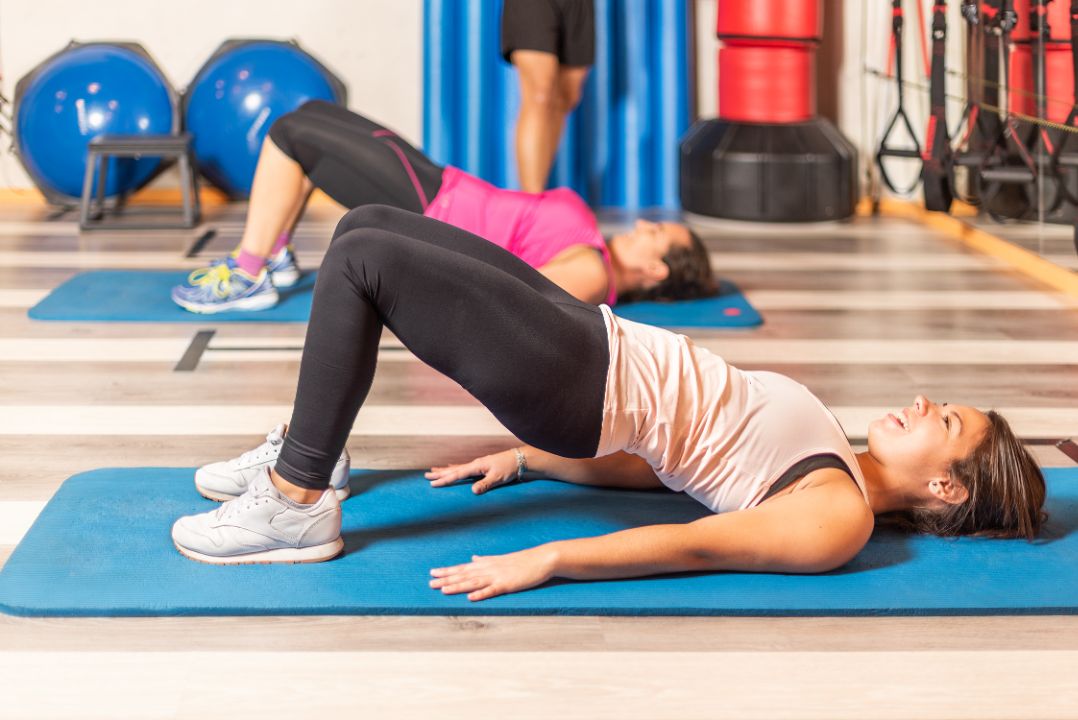

Photo Credit: ivanmorenosl, Envato
A healthcare professional may also prescribe pain-relieving medication to help manage symptoms.
In some cases, more invasive treatments, such as corticosteroid injections or surgery, may be necessary to address severe or unresolved cases of osteitis pubis. However, these treatments are typically reserved for cases where conservative management has been unsuccessful.
Exercise can be an effective tool in managing osteitis pubis symptoms. It is important to work with a qualified physical therapist to develop a personalised exercise program that is tailored to an individual’s specific needs, and that takes the severity of their condition into account.
Some examples of exercises that may be beneficial for individuals with osteitis pubis include:
It is important to note that these exercises should only be performed under the supervision of a qualified physical therapist or healthcare professional.
Osteitis pubis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pubic bone, resulting in pelvic pain.
Osteitis pubis can be caused by sports-related groin injuries and pubalgia, among other factors.
Symptoms of osteitis pubis include pelvic pain and hip pain.
Osteitis pubis can be diagnosed through physical examinations, medical history review, and diagnostic tests or imaging.
Treatment options for osteitis pubis include conservative approaches such as physical therapy, medication, and surgical interventions in some cases.
Osteitis pubis can be managed through exercises and stretches that help alleviate symptoms and preventive measures to reduce the risk of developing the condition.
The recovery and rehabilitation process for osteitis pubis involves rest, gradual return to physical activity, and potential therapies or exercises that aid recovery.
It is important to seek medical attention for pelvic pain to receive a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment for conditions such as osteitis pubis.