Stress fractures are small cracks in the bone that are common injuries that can occur from repetitive stress, and early detection is key for effective management.
Stress fractures are tiny cracks in bones that can occur due to repetitive trauma or overuse. These cracks can be difficult to detect and may not show up on X-rays initially. However, they can cause significant pain and discomfort, especially when left untreated.
The most common symptom is localised pain at the site of the injury. This pain may worsen during physical activity and lessen during rest. Other symptoms may include:
If you experience any of these symptoms, seeking medical attention is essential. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and expedite recovery.
Photo Credit: pressfoto
These fractures typically occur due to repeated stress on the bones, causing them to weaken over time. However, various other causes contribute to the development of stress fractures.
One of the primary causes of this fracture is making errors during training. This can include increasing intensity or duration too quickly, failing to rest adequately between workouts, or using improper form during exercises, such as running with improper shoes or on uneven surfaces.
Another cause of stress fractures is sudden changes in physical activity, such as starting a new exercise program or drastically increasing the frequency or duration of an existing program. This places undue stress on bones that are not yet accustomed to such levels of activity, leading to the development of this condition.
Inadequate intake of essential nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D can also contribute to this condition. These nutrients are vital for maintaining healthy bones and allowing them to withstand stress and strain.
Additional factors contributing to fractures include hormonal imbalances, medical conditions affecting bone health, and certain medications that can weaken bones. Women, in particular, are at a higher risk of developing stress fractures due to factors such as osteoporosis and hormonal imbalances.

Photo Credit: chevanon
By understanding the various causes of this condition, individuals can take necessary precautions to prevent them. This includes wearing appropriate footwear, gradually increasing activity levels, maintaining a balanced diet, and seeking medical attention if experiencing persistent pain or discomfort.
When it comes to treating stress fractures, several options are available, depending on the severity of the fracture and the affected area. Here are some of the most common and effective treatments:
The first line of treatment for stress fractures is to rest the affected area and immobilise it, which often involves wearing a cast, brace or using crutches to avoid putting weight on the bone. This allows the bone to heal and recover.
Once the bone has started to heal, physical therapy may be necessary to help improve flexibility, strength, and balance. Physical therapy exercises help reduce the risk of future fractures by addressing the underlying factors contributing to the fracture.
In severe cases where the fracture has not healed or is at risk of further damage, surgery may be necessary to ensure proper healing. This usually involves stabilising the fracture with pins, screws or plates to promote healing.
Returning to physical activity gradually is crucial to avoid re-injury. Your healthcare professional may recommend a gradual return to weight-bearing activities over several weeks, depending on the location and severity of the fracture.
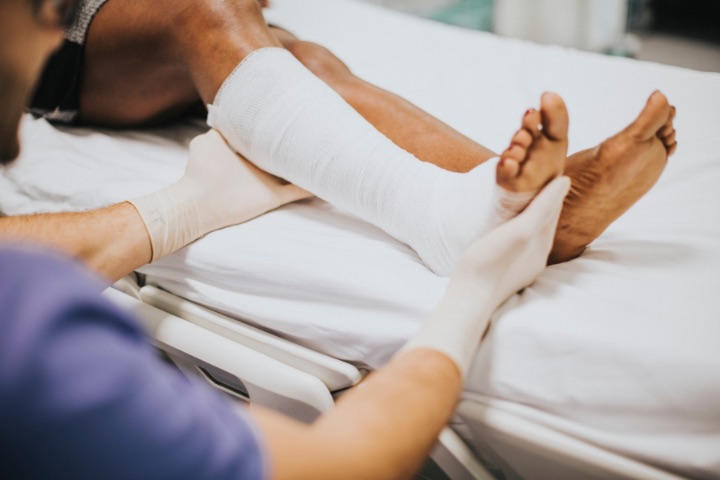
Photo Credit: rawpixel
No matter which treatment approach is used, it is essential to follow it strictly to ensure proper healing and a full recovery. Speak to your healthcare professional about the best course of treatment for your fracture.
Stress fractures can be a significant source of pain and frustration, especially for athletes and individuals with an active lifestyle. Here are some frequently asked questions about stress fractures that can help you understand the condition better.
Depending on the location and severity of the stress fracture, certain exercises can help strengthen the surrounding muscles and promote healing. Non-weight-bearing exercises such as swimming, cycling, and yoga can be an excellent way to maintain fitness and support recovery. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise program.
Proper footwear and equipment are essential in preventing stress fractures during physical activities. Ensure that your shoes have adequate arch support and cushioning, and replace them regularly. Gradually increase your training intensity and duration and vary your workouts to avoid repetitive stress on specific bones.
The healing time for a stress fracture can vary depending on the location and severity of the injury. Generally, a stress fracture takes six to eight weeks to heal completely. However, it can take longer, and in some cases, conservative treatment may not be sufficient. Always follow your healthcare professional’s advice regarding your recovery and return to physical activity.
Incorporating proper warm-up and cool-down routines before and after physical activities can help prevent stress fractures. Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activity, using proper equipment, and maintaining a balanced diet with adequate calcium and vitamin D intake can also reduce the risk of this condition.
Healthcare professionals diagnose through a thorough physical examination and diagnostic imaging tests. X-rays and MRIs are the most common imaging modalities to identify stress fractures.
Your healthcare professional may also ask about your medical history, physical activities, and symptoms to determine an appropriate treatment plan.
Understanding and taking necessary precautions can help prevent and manage the condition effectively. Always consult a healthcare professional to ensure proper diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.