Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome (SLJ) is a condition that can cause knee pain in adolescents. It occurs when there is inflammation in the patellar tendon, the cord-like structure that connects the kneecap to the shinbone.
This inflammation can make it painful for young people to participate in physical activities such as sports or even everyday movements like walking or climbing stairs.
The cause of SLJ is repetitive stress on the patellar tendon, which can occur in young athletes who participate in activities such as basketball, soccer, gymnastics, and track and field.
During these activities, the patellar tendon can experience too much pulling or rubbing against the knee joint, leading to inflammation and pain.
Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome (SLJ) is a condition that results in knee pain, particularly among young athletes. It is a type of patellar tendonitis that affects the growth plate at the bottom of the kneecap. SLJ mainly affects teenagers who engage in high-impact sports involving jumping, running, and other activities that stress the knee.
SLJ is often confused with patellofemoral pain syndrome, a condition that causes pain at the front of the knee. However, SLJ is characterised by pain and swelling below the knee cap. It is important to differentiate between these two conditions, as the treatment varies depending on the specific diagnosis.
SLJ is most commonly observed in young athletes who participate in sports that involve repeated strains on the patellar tendon. It is estimated that up to 14% of young athletes develop SLJ, with the highest incidence rate among boys aged 12 to 14 years old.

Athletes who play sports that involve jumping, such as basketball and volleyball, are at a higher risk of developing SLJ. Other high-impact sports such as football, soccer, and gymnastics can also increase the risk of SLJ.
Furthermore, SLJ is more common in children who experience growth spurts, as the bones and muscles grow at different rates, increasing tension and strain on the patellar tendon.
The exact cause of SLJ is not known. However, it is believed to be caused by repetitive stress and overuse of the patellar tendon, which can lead to inflammation and microtrauma to the growth plate. In addition, anatomical factors such as tight or weak quadriceps muscles, flat feet, and leg-length differences may contribute to the development of SLJ.
Genetic factors may also play a role, as SLJ tends to run in families. Moreover, SLJ may be linked to other conditions such as Osgood-Schlatter disease, a growth-related condition that affects the knee.
The mainstay of SLJ treatment is conservative measures such as rest, ice, and physical therapy. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and pain management techniques such as massage and ultrasound therapy may also be prescribed in some cases to alleviate pain and inflammation.
More intensive treatments such as corticosteroid injections may be considered if these measures do not provide relief. In addition, exercises that target quadriceps tendonitis and jumper’s knee may help to strengthen the patellar tendon and improve knee stability.
It is important to avoid activities that exacerbate pain and to gradually return to physical activity with guidance from a healthcare professional.
As with many conditions, treatment for Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome (SLJ) typically begins with conservative measures. These may include:
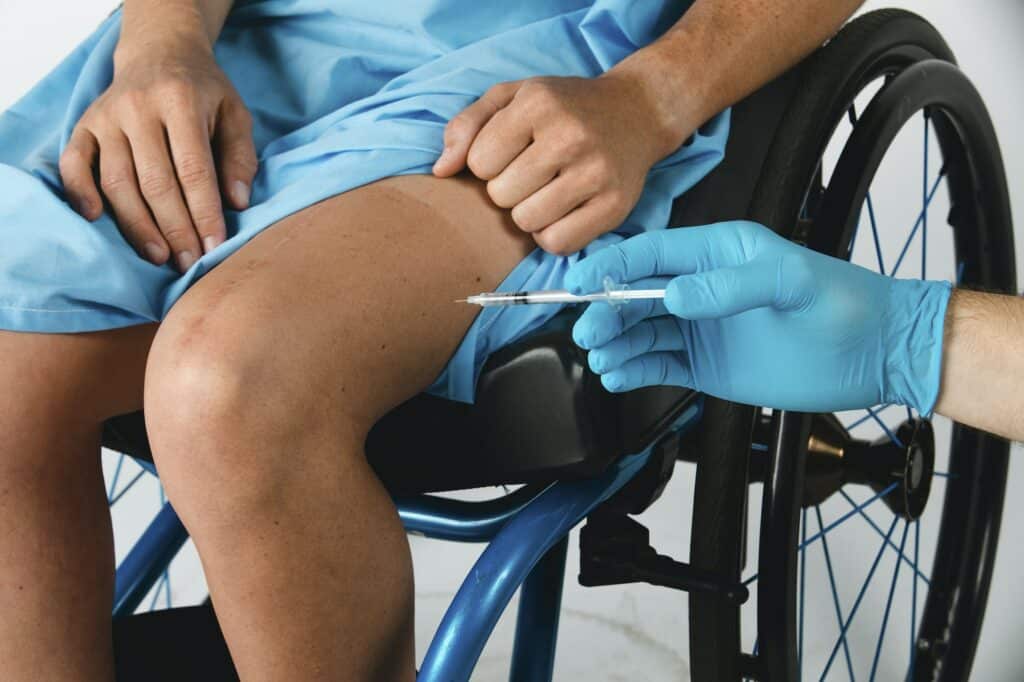
More aggressive treatment options may be considered for individuals with more severe or persistent symptoms. These may include:
It’s worth noting that SLJ is closely related to other knee conditions such as quadriceps tendonitis and jumper’s knee, and treating these underlying conditions may help to alleviate SLJ symptoms.
Various treatment options are available to individuals suffering from Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome (SLJ). Treatment approaches may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s age and activity level.
Conservative measures are often the first line of treatment for SLJ. These methods focus on managing pain and inflammation while healing the affected area. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may also be recommended.
Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve strength and flexibility surrounding the knee joint. Modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation may be used to promote healing and reduce pain.
Exercises targeting the quadriceps and patellar tendons may be incorporated into a physical therapy programme to alleviate SLJ symptoms. These exercises may include leg extensions, step-ups, and lunges. Additionally, exercises that target the jumper’s knee, such as eccentric heel drops, may also be beneficial.
Surgery may be considered in rare cases where conservative measures fail to alleviate SLJ symptoms. Surgical options may include a patellar tendon release or removal of the affected osteophyte. However, surgery is typically a last resort and is only recommended after all other treatment options have been exhausted.
It is important to note that individuals suffering from SLJ should always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for their specific condition.
Prevention and proper management of Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome (SLJ) is crucial, especially in young athletes who are at a higher risk of developing this condition. Here are some essential strategies to consider:
By implementing these strategies, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing SLJ and improve their overall knee health. Working with healthcare professionals to manage SLJ properly and reduce the risk of long-term damage to the knee joint is crucial.
If you are experiencing knee pain that persists for several weeks or worsens with activity, it is important to seek medical advice. While Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome (SLJ) is a relatively common condition among adolescents, proper diagnosis and treatment require the expertise of a healthcare professional.
If you or your child experiences knee pain that interferes with daily activities, it is important to seek medical attention. In some cases, knee pain may be a sign of a more serious condition that requires immediate treatment. Seek emergency care if fever, chills, or severe swelling accompany knee pain.
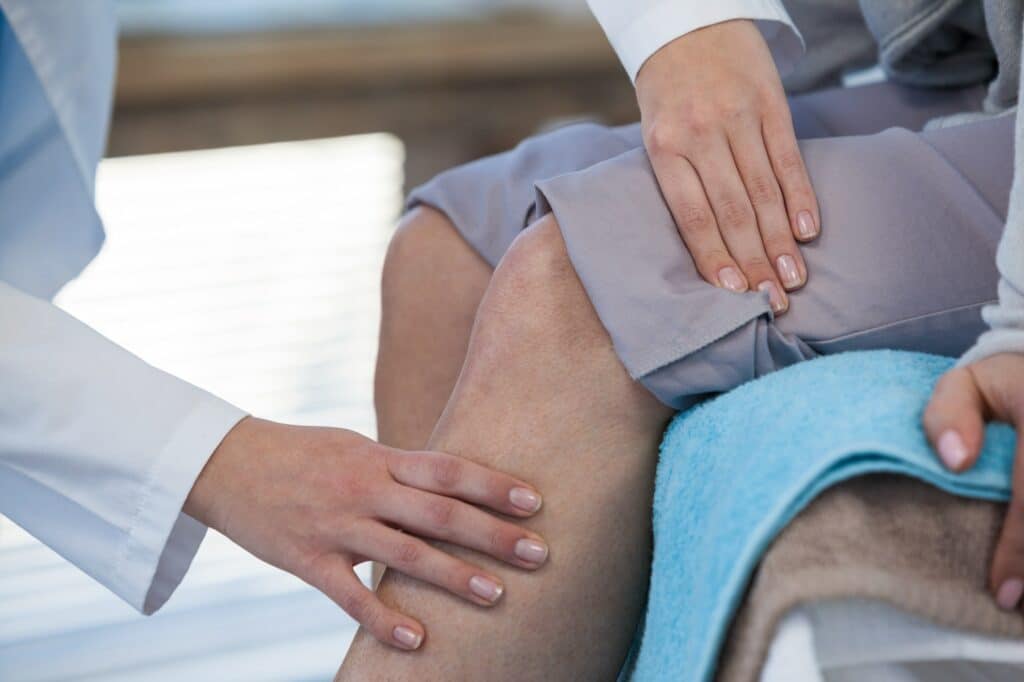
For non-emergency cases, schedule an appointment with a healthcare professional with experience diagnosing and treating SLJ. This may include a primary care doctor, a paediatrician, or a sports medicine specialist.
Before your appointment, make a list of any symptoms you or your child has been experiencing. Include details such as the location and intensity of the pain, when it first began, and what activities exacerbated the pain.
It may also be helpful to bring any relevant medical records and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. This can help your healthcare provider make an accurate diagnosis and establish an appropriate treatment plan.
During your appointment, do not hesitate to ask questions to help you better understand SLJ and its treatment options. Consider asking your healthcare provider: