Discoid meniscus is a rare knee condition that can have a significant impact on daily life and mobility. It is caused by an abnormality in the knee anatomy, where the meniscus is shaped like a disc instead of the typical crescent shape. This abnormality can lead to knee pain, meniscus tears, and knee injuries, and it may require orthopedic care, knee surgery, and knee rehabilitation to manage properly.
The knee is one of the largest and most complex joints in the body, and it is composed of several components, including bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. The menisci are two cartilage pieces that cushion and stabilise the knee joint. A discoid meniscus is an abnormally shaped meniscus that is thicker and more substantial than a standard crescent-shaped meniscus.
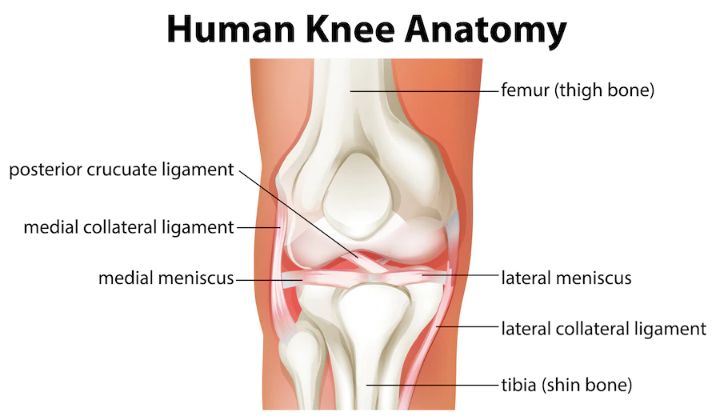
Photo Credit: brgfx
A discoid meniscus can impact knee health in various ways. It can cause knee pain, especially when moving or bearing weight on the affected knee. It can also lead to ongoing instability, increasing the risk of falls, knee injuries, and additional meniscus tears. Moreover, if left untreated, a discoid meniscus can lead to degenerative knee disorders, such as osteoarthritis.
Although discoid meniscus is a rare condition, it is essential to understand its impact on knee health to facilitate a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Discoid meniscus can cause a variety of symptoms that can affect an individual’s ability to perform daily activities. Recognising these symptoms to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment is important. The following are some common symptoms associated with discoid meniscus:
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. A doctor or orthopaedic specialist can perform a thorough examination and order imaging tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of discoid meniscus typically begins with a comprehensive physical examination by an orthopedic specialist. The doctor will ask about the patient’s medical history and symptoms, perform a visual inspection of the knee, and assess the joint’s range of motion and stability.
If discoid meniscus is suspected, the doctor may order imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most commonly used imaging test to diagnose discoid meniscus. This test provides detailed images of the knee joint and can detect abnormalities in the shape and position of the meniscus.
If the results of the physical examination and imaging tests are inconclusive, the doctor may recommend arthroscopy. This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small camera called an arthroscope into the knee joint through a small incision. The camera allows the doctor to visualise the meniscus and other structures in the knee joint and diagnose any abnormalities.

Photo Credit: vector4stock
Arthroscopy is also used as a diagnostic tool to confirm discoid meniscus and identify any other knee injuries that may be present. If a discoid meniscus is confirmed, the doctor may perform arthroscopic surgery to remove or repair the abnormal meniscus.
Treatment options can vary depending on the severity and type of discoid meniscus. Conservative approaches may be suitable in some cases, while others may require surgical intervention. It is important to consult with an orthopedic specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
In some cases, surgery may be required to treat discoid meniscus. The type of surgery performed will depend on the severity and location of the meniscus tear and the patient’s age and activity level.
During an arthroscopic meniscectomy, a small camera is inserted into the knee joint through a small incision. The surgeon then uses small instruments to remove the damaged portion of the meniscus. This procedure is typically performed on younger patients with smaller, isolated tears.
During a meniscus repair, the torn meniscus is stitched back together using sutures. This procedure is typically performed on younger patients with a larger, more complex tear located in the meniscus’s outer edge, where blood flow is higher and healing is more likely to occur.
Following surgery for discoid meniscus, rehabilitation is essential to ensure a successful recovery and prevent further injury. Rehabilitation typically involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and a gradual return to activity and exercise under the guidance of a medical professional.
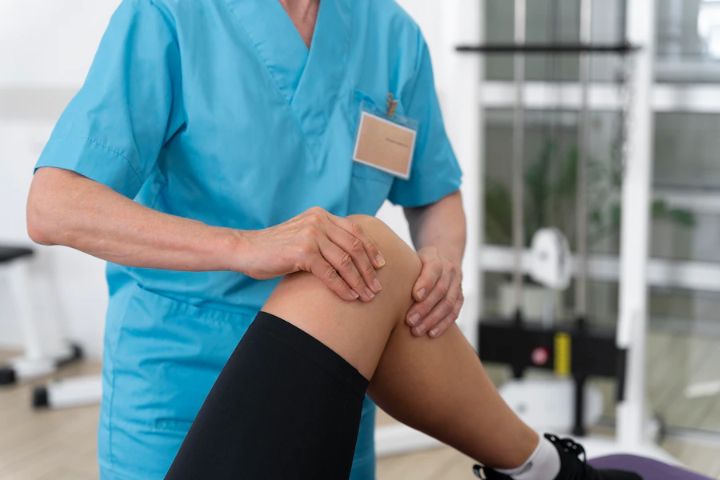

Photo Credit: Freepik
Following surgery for discoid meniscus, it is crucial to engage in proper rehabilitation to facilitate recovery and restore knee function. The rehabilitation goals include reducing pain and swelling, improving strength and flexibility, and returning to regular activities.
Recovery time can vary depending on the extent of the surgery and the individual’s overall health. Generally, patients can expect to use crutches for a few days post-surgery to avoid putting weight on the affected knee. Physical therapy typically begins within a week or two of the surgery and continues for several months. It may take up to six months to achieve full recovery.

Photo Credit: wayhomestudio
Living with discoid meniscus can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can manage your symptoms and maintain mobility. Here are some tips:
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining knee health. Aim for low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling. These activities will keep your knees strong and flexible while minimising the risk of further injury.
Poor posture can put extra strain on your knees. Make sure to stand up straight, with your shoulders back and your weight evenly distributed. Keep your feet flat on the ground and your knees at 90-degree angles when sitting.
If you experience pain or instability, consider using assistive devices such as knee braces, crutches, or canes. These tools can support and take pressure off your knees, making it easier to move around.
Proper nutrition is important for maintaining overall health, including knee health. Be sure to include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your diet. This will help to reduce inflammation in your joints and promote healing.
If you experience pain or discomfort, listening to your body and taking a break is important. Overdoing it can exacerbate your symptoms and lead to further injury. Rest when you need to, and always follow your doctor’s advice.
Living with a knee condition can be frustrating, but maintaining a positive attitude can help. Focus on what you can do rather than what you can’t. Seek support from family, friends, or a support group if needed.
Following these tips, you can manage your discoid meniscus symptoms and maintain mobility. Always consult your doctor before making any changes to your treatment plan.
Discoid meniscus is a knee condition where the meniscus, a C-shaped cartilage located in the knee joint, is abnormally shaped and can be thicker than usual. It can affect knee health and lead to complications such as knee pain, meniscus tear, and knee injuries.
Common symptoms of discoid meniscus include knee pain, knee instability, locking of the knee, and limited range of motion. Recognising these symptoms for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment is important.
Discoid meniscus can be diagnosed through physical examinations, imaging tests such as MRI scans, and arthroscopy. An accurate diagnosis is crucial to determine the most suitable treatment approach for the individual.
Treatment options for discoid meniscus in Australia include conservative approaches like rest, physical therapy, pain management, and surgical interventions such as arthroscopic meniscectomy or meniscus repair. The recommended treatment will depend on the severity of the condition and individual circumstances.
Rehabilitation is an important part of recovery after discoid meniscus surgery. It involves specific exercises to improve the knee’s range of motion, strength, and stability. The timeline for recovery may vary, and it is essential to follow healthcare professionals’ guidance during this period.
Managing daily life and mobility with discoid meniscus involves managing knee pain, preventing further injuries, and maintaining overall knee health. Regular exercise, proper nutrition, and following medical guidance are important for optimal functioning.