A meniscus tear is a common knee injury that can happen to anyone, but it’s more common in athletes and older adults. The meniscus is a rubbery, C-shaped disc that cushions your knee and helps distribute weight and absorb shock. A meniscus tear occurs when the meniscus is torn or damaged, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
There are several causes of meniscus tears, including direct impact, twisting or rotating your knee while bearing weight, and degenerative changes due to aging. The severity of a meniscus tear can range from minor to severe, and the treatment options vary based on the extent of the injury.
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage located in the knee joint. It acts as a shock absorber and helps to distribute weight evenly across the joint. A meniscus tear occurs when this cartilage is damaged or torn due to sudden twisting or turning of the knee, or from impact during physical activities such as sports.
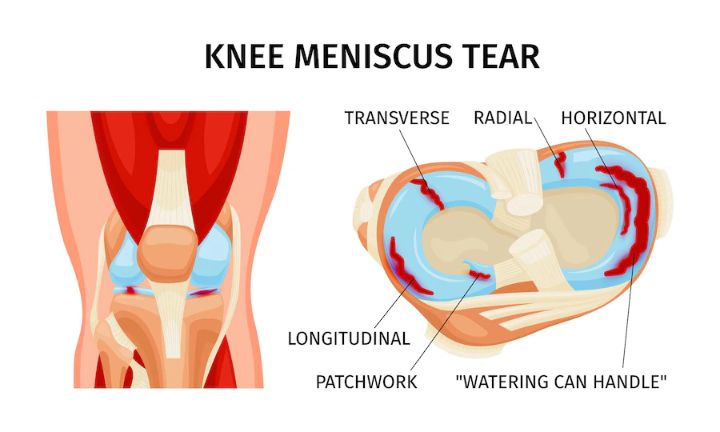
Photo Credit: macrovector
There are two types of meniscus tears: traumatic and degenerative. Traumatic tears often occur due to sudden movements or impact, while degenerative tears develop over time due to wear and tear on the knee joint. The severity of a meniscus tear is classified as either minor, moderate, or severe, depending on the size and location of the tear.
Minor tears may heal on their own with rest and conservative treatments, while moderate to severe tears may require medical intervention. Understanding the type and severity of a meniscus tear is important for determining the most appropriate course of treatment.
A meniscus tear can cause various signs and symptoms, depending on the extent and location of the injury. Some of the common indications of a meniscus tear include:
It’s essential to note that not all meniscus tears present with significant symptoms. Sometimes, a small tear may not cause noticeable discomfort or require medical intervention. However, more extensive tears can lead to persistent pain and joint dysfunction that can interfere with daily activities.
Diagnosing a meniscus tear typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. Your healthcare provider will first ask about your symptoms and medical history, then physically examine the affected knee. This may include tests to evaluate the joint’s range of motion, stability, and tenderness.

Photo Credit: Freepik
If a tear is suspected, imaging tests such as x-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. An MRI is usually the preferred imaging test as it can provide detailed images of the soft tissue structures in the knee, including the meniscus.
Sometimes, your healthcare provider may recommend an arthroscopy to diagnose a meniscus tear. This minimally invasive surgical procedure involves inserting a small camera (arthroscope) into the knee joint to visualise the area. This allows the healthcare provider to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the extent of the injury more accurately.
It is essential to seek medical attention if you suspect a meniscus issue, as early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and prevent further damage to the knee joint.
When it comes to treating meniscus tears, surgery is not always necessary. Non-surgical treatment options are available to help manage symptoms and promote healing.
Rest is crucial in the early stages of a meniscus tear. It is recommended to limit activities that aggravate the injury and to avoid putting weight on the affected knee as much as possible. Crutches may be necessary to assist with mobility.
Cold therapy is an effective way to reduce pain and swelling. Applying an ice pack to the affected knee for 15 to 20 minutes at a time, several times a day, can help alleviate symptoms.
Compression and elevation can also help reduce swelling and promote healing. Wearing a compression bandage or sleeve on the affected knee and keeping it elevated above heart level can aid in recovery.
Physical therapy exercises can help improve strength and flexibility in the affected knee. Specific exercises may include quad sets, straight-leg raises, and hamstring curls.
Rehabilitation is an important part of non-surgical treatment for meniscus tears. It may involve a combination of rest, cold therapy, compression and elevation, physical therapy exercises, and supportive devices such as knee braces.
By following these non-surgical treatment options, meniscus tears can often heal on their own. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action based on the severity of the injury.
Photo Credit: stefamerpik
If non-surgical treatments are unsuccessful, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery is typically recommended for larger or complex tears that cause significant knee instability or for those experiencing persistent knee pain and limited mobility.
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical method that is commonly used to repair a torn meniscus. During this procedure, a small camera is inserted into the knee joint, allowing the surgeon to see and assess the tear.
They will then use specialised instruments to repair the tear by sewing the torn edges together. This type of surgery is typically recommended for younger patients with acute tears in the outer portion of the meniscus.
Partial meniscectomy involves the removal of the torn portion of the meniscus. This type of surgery is more commonly recommended for older patients or those with complex tears that cannot be repaired.
This surgery aims to remove the damaged portion of the meniscus while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible, to maintain joint stability and reduce the risk of future complications.
As with any surgery, there are risks associated with a meniscus tear repair. These can include infection, blood clots, and nerve damage.
Recovery time will vary depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s overall health but typically involves rest, physical therapy, and rehabilitation exercises to restore strength and mobility to the knee joint.
Recovering from meniscus tear surgery can be lengthy, but the right rehabilitation plan can help you get back to normal activities sooner. Here’s what you need to know:
Photo Credit: fxquadro
After surgery, you will likely need to use crutches for some time to keep weight off the affected knee. Your doctor will also prescribe pain medication to help manage discomfort during the initial recovery period. Following all post-operative instructions carefully is essential to ensure the best possible outcome.
Physical therapy is a crucial component of meniscus tear surgery recovery. Your physiotherapist will create a tailored rehabilitation plan to help you regain strength, increase your range of motion, and reduce pain. This may include exercises such as straight leg raises, hamstring curls and calf raises. Gradually increasing the intensity and frequency of these exercises will help you recover more quickly.
Recovery times can vary, but most people can resume light activities within a few weeks of surgery. It may take several months to regain full strength and mobility, and some activities may need to be avoided for an extended period. Your physiotherapist will discuss your expected timeline for recovery and help you set realistic goals.
It’s important to remember that everyone’s recovery experience is different. Some people may have a faster or slower recovery time, depending on factors such as age, overall health, and the severity of the injury.
It’s essential to communicate openly with your doctor and physiotherapist and to ask questions about any concerns or expectations you may have.
While meniscus tears can occur unexpectedly, there are certain steps you can take to reduce your risk of a knee injury. To prevent meniscus tears, it is important to maintain proper knee health and protect your knees during physical activities. Here are some tips to consider:

Photo Credit: Freepik
When participating in high-impact activities, such as contact sports, wearing appropriate protective gear, such as knee pads or braces is important. These can help to reduce the risk of injury and provide added support during physical activity.
Excess weight can stress the knees, increasing the risk of a meniscus tear. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help to reduce your risk of injury.
Regular exercise can help strengthen the muscles supporting your knees, making them more injury-resistant. Incorporating low-impact activities, such as swimming or cycling, can provide the same benefits while reducing the stress on your knees.
Remember, if you do experience a knee injury, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the chances of a successful recovery and reduce the risk of complications.
In conclusion, meniscus tears can cause significant pain and discomfort, but treatment options are available. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can make informed decisions about your healthcare.
Taking preventative measures and seeking prompt medical attention for knee injuries can help to reduce your risk of a meniscus tear and promote overall knee health.
A meniscus tear can be caused by sudden twisting or rotating of the knee joint, often during sports or other physical activities. It can also occur due to age-related degeneration or wear and tear on the meniscus.
Common meniscus tear symptoms include pain, swelling, tenderness, and difficulty moving the affected knee. There may also be a popping sensation at the time of injury.
A meniscus tear is typically diagnosed through physical examinations and imaging tests, such as an MRI. In some cases, arthroscopy may be performed to assess the extent of the tear directly visually.
Non-surgical treatment options for a meniscus tear may include rest, ice, compression, elevation, physical therapy, and specific exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles and promote healing.
Surgical treatment for a meniscus tear may be necessary in cases where conservative approaches are ineffective or if the tear is severe. Procedures such as arthroscopic meniscus repair or partial meniscectomy may be performed.
A: The recovery process after meniscus tear surgery involves a period of rest, followed by physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises to regain strength and flexibility in the knee. The recovery duration can vary depending on the individual and the extent of the tear.
Meniscus tears can be prevented by practising proper knee protection techniques, such as knee pads or braces, during physical activities. Maintaining overall knee health through regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight is also important.