Gluteal tendinopathy is a common condition that affects the gluteal muscles, specifically the gluteus medius and minimus tendons. It is characterized by pain in the hip area, often referred to as lateral hip pain. Let’s discuss the underlying causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Gluteal tendinopathy refers to a degenerative condition of the gluteal tendons, which connect the gluteal muscles to the greater trochanter of the femur. This greater trochanteric pain syndrome can cause discomfort, affecting daily activities and mobility.
The exact causes of greater trochanter pain syndrome are not fully understood, but certain factors are known to contribute to its development. Overuse or repetitive movements involving the gluteal muscles, such as running or climbing stairs, can strain the tendons and lead to tendinopathy. Age-related degeneration and structural abnormalities may also play a role.
Gluteal tendinopathy is often associated with trochanteric bursitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the bursa. The trochanteric bursa is a fluid-filled sac located near the greater trochanter, which cushions and reduces friction between the tendons and bones in the hip area. Inflammation of the bursa can exacerbate the symptoms.
 Photo Credit: katemangostar, Freepik
Photo Credit: katemangostar, Freepik
The pain from gluteal tendinopathy is noticeable on the side of the hip, often described as a deep ache or sharp, stabbing sensation. The pain extends and may worsen with activities that involve the gluteal muscles, such as walking, climbing stairs, or sitting for prolonged periods.
Hip pain can radiate down the side of the thigh and may be accompanied by stiffness or limited range of motion in the hip joint. Patients may also experience muscle weakness in the gluteal area, which can contribute to gait abnormalities.
Lateral hip pain is a common complaint in individuals with gluteal tendinopathy. It typically occurs on the outside of the hip and can be aggravated by activities that require repetitive movements or prolonged standing. Lateral hip pain can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life.
Diagnosing gluteal tendinopathy involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional or a physio. They will assess the patient’s medical history, perform a physical assessment, and evaluate symptoms. Specific tests, such as the single-leg squat test and resisted hip abduction, may be conducted to assess the strength and functionality of the gluteal muscles and tendons.
Advanced imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound, can provide detailed images of the gluteal tendons and surrounding structures. These imaging modalities can help confirm the diagnosis of gluteal tendinopathy and identify other potential causes of hip pain.
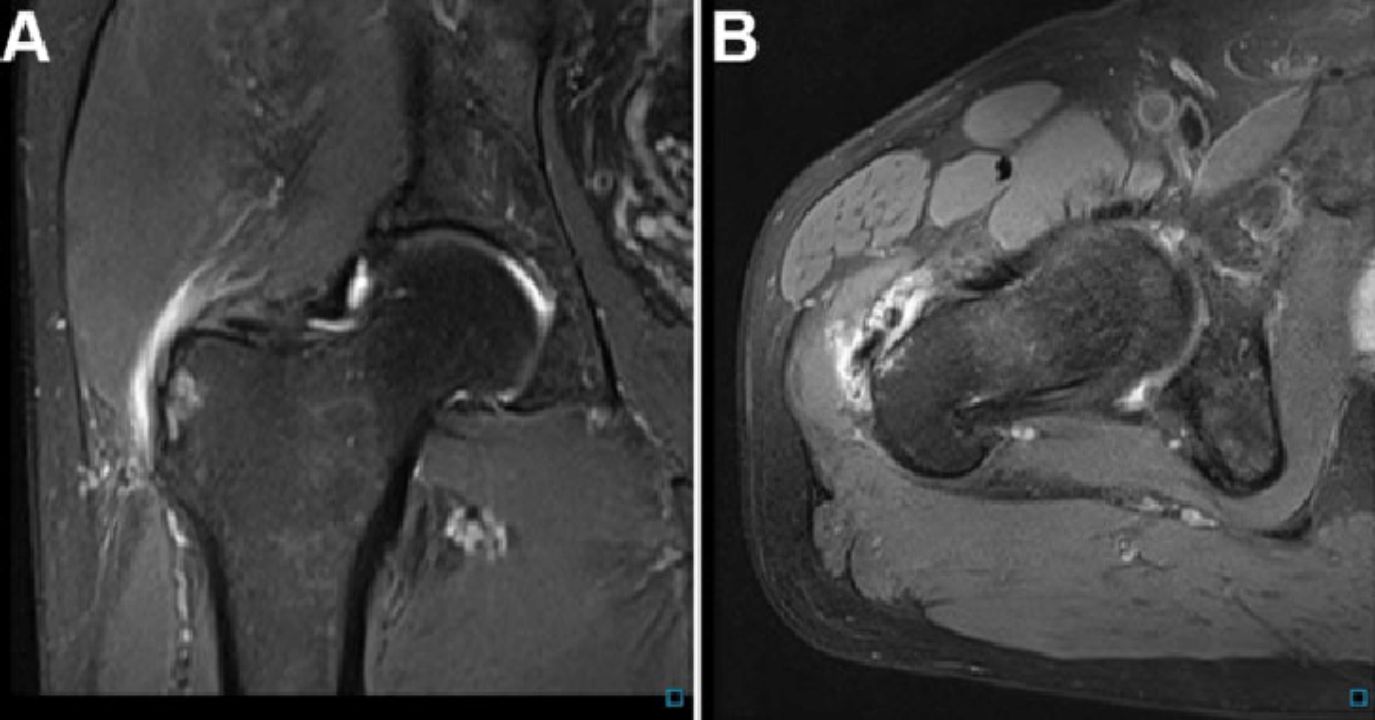 Photo Credit: Research Gate
Photo Credit: Research Gate
Assessing the greater trochanter plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of gluteal tendinopathy. Palpation can elicit tenderness, indicating inflammation or degeneration of the gluteal tendon. Imaging studies can further assess the extent of damage and provide guidance for personalized treatment plans.
In most cases, this ailment can be managed conservatively. Initial treatment of gluteal tendinopathy may involve a combination of rest, ice or heat therapy, physical therapy exercises, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation. Modifying activities that aggravate symptoms and using assistive devices such as crutches or canes may also be helpful.
In cases where conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief, corticosteroid injections may be considered. These injections are administered directly into the affected area to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. However, it is important to note that such injections should be used judiciously and as part of an overall treatment plan.
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing gluteal tendinopathy. A qualified physiotherapist can design an individualized strengthening exercise program to strengthen the gluteal muscles, improve hip stability, and enhance overall function. This may include specific exercises such as clamshells, hip abductions, and bridges, which can be tailored to each stage of the condition.
 Photo Credit: Freepik
Photo Credit: Freepik
Gluteal tendinopathy is typically categorized into three stages: reactive tendinopathy, tendon disrepair, and degenerative tendinopathy. Each stage represents a different level of tendon damage and requires a tailored approach to treatment and management.
Effective management of gluteal tendinopathy involves tailoring the treatment approach based on the stage of the condition. A conservative approach focusing on rest, exercises, and activity modification may be sufficient in the early stages. More aggressive interventions, such as injections or surgery, may be considered as the condition progresses.
Specific exercises can be prescribed for each stage of gluteal tendinopathy to promote healing, restore function, and prevent further deterioration. These exercises should be performed under the guidance of a healthcare professional or physiotherapist to ensure proper technique and progression.
Gluteal tendinopathy is typically managed with conservative treatments such as physical therapy, which focuses on strengthening the gluteal muscles and improving hip stability. Pain management strategies may include over-the-counter pain relief meds, corticosteroid injections, or the use of assistive devices like crutches or canes.
Recovery time can vary widely depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. Many people with gluteal tendinopathy see improvement with conservative treatments within a few weeks to months, but more severe cases may take longer to resolve.
Gluteal tendinopathy typically presents as pain at the side outside the hip, which may worsen with activities like walking, climbing stairs, or lying on the affected side. The pain may be sharp or dull and is often worse at night.
While walking is generally safe with gluteal tendinopathy, listening to your body and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain is important. Using a cane or crutches can help reduce stress on the hip and alleviate pain during walking.
Gluteal tendinopathy is often caused by overuse or strain of the gluteal tendons, particularly in activities that involve repetitive hip movements. Other risk factors include age, being female, and having certain biomechanical abnormalities such as hip or knee misalignment.
While not all cases of gluteal tendinopathy can be prevented, certain strategies may reduce the risk. These include maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and incorporating strength training and flexibility exercises into your routine to keep the hip and leg muscles strong and flexible. Using proper form and technique when exercising or playing sports is important to avoid overuse or strain.
The exact cause of gluteal tendinopathy is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from overuse or repetitive stress on the tendons. Other factors such as age, hormonal changes, and biomechanical abnormalities, may also contribute to the development of this condition.
Diagnosis of gluteal tendinopathy is typically based on the patient’s symptoms and a physical examination. Imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other possible causes of hip pain.