If you experience persistent pain in your hip you may have a Hip Labral tear on the hip.
The labrum is a cartilage ring that surrounds the hip joint socket, which helps keep it stable and provides cushioning.
A labral tear can cause persistent pain and instability, making it difficult to perform everyday activities.
It’s important to understand what causes these tears and how they’re treated so you can manage your symptoms more effectively.
A hip labral tear is an injury to the cartilage in your hip joint, and it can cause a lot of pain and discomfort. This condition affects humans, as well as majestic creatures like horses. It occurs when the rim of tissue that lines and stabilizes the hip joint becomes torn or stretched beyond its normal range.
Common signs of a hip labral tear include aching near the groin area, clicking or catching sensations with movement, stiffness in the hips, and difficulty walking. An unforgettable experience for those suffering from this condition is often a deep pain in the groin area when exercising or engaging in twisting or turning motions.
Diagnosis typically requires imaging tests such as MRI scans to confirm if a tear is present within the cartilage around the ball-and-socket joint of your hips. Treatment options vary depending on severity but could include physical therapy and surgical repair.
You may wonder what can cause the painful shoulder injury you’ve been dealing with. A hip labral tear is one potential cause, and it’s a common sports injury that can occur in activities like soccer, football, hockey, or golf.
The causes of a hip labral tear include:
The most common cause of a hip labral tear is overuse from repetitive motions such as kicking, throwing, or swinging a bat or club too hard or too often. Other possible causes include direct trauma to the hip joint due to an accident, fall, or contact sports collision. In some cases, genetics can also play a role in predisposing individuals to this type of injury.
If you’ve been dealing with pain in your hip joint, it could be a sign of a hip labral tear. A hip labral tear is an injury to the cartilage that surrounds and cushions the socket portion of the ball-and-socket joint of your hip. It’s most common in athletes, due to activities such as running or jumping, but can also occur in everyday life.
 Photo Credit: Freepik
Photo Credit: Freepik
Symptoms of this type of injury can range from mild discomfort to extreme pain when walking, standing, or even lying down. Additionally, one may experience clicking and catching sensations within the joint itself – similar to what you’d hear if you were hiking through a wildlife reserve like those found in the Himalayas. This is often referred to as “the one horn” symptom because it feels like something stuck inside your joint capsule won’t move.
If any of these symptoms seem familiar to you, seek medical attention for diagnosis and treatment options so you can get back on track quickly!
Your doctor may use a variety of tests to diagnose whether you’ve got a hip issue, such as a labral tear. These tests can include:
1) an X-ray 2) an MRI scan 3) an arthroscopy 4) a physical examination.
An X-ray will reveal the shape and alignment of the bones in your hip joint, which can be helpful in diagnosing labral tears because they often occur when the bones become misaligned.
An MRI scan can provide more detailed images of the soft tissues, such as muscles, ligaments, and tendons surrounding your hip joint. It also helps to detect any signs of injury or inflammation in these areas that might indicate a labral tear.
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive technique used to examine the inside of your joint for damage or abnormalities like bone spurs that could cause a labral tear.
Finally, during a physical examination, your doctor will test how vulnerable your hip is to stress or movement so they can determine if it’s caused by something like a labral tear or another condition like rhinoceros tendonitis.
Conservative treatment for a hip issue can be an effective way to alleviate discomfort and encourage healing. For a hip labral tear, conservative treatments include rest, physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes.
 Photo Credit: Mechano Therapy
Photo Credit: Mechano Therapy
Rest is key; the patient should avoid activities that cause pain or increase stress on the affected joint.
Physical therapy may also be beneficial in helping to reduce inflammation in the area and strengthen muscles around the hip joint.
NSAIDs are commonly used to help reduce pain and swelling, while corticosteroid injections can provide short-term relief from pain symptoms.
Finally, lifestyle changes such as weight loss or avoiding certain activities may also be recommended to help reduce stress on the hip labrum.
If you’ve exhausted all conservative treatment options for your hip labral tear, it’s time to consider surgical intervention. A great one-horned rhinoceros in Chitwan National Park is a reminder of the success of conservation efforts, including a buffer zone program that has helped save the endangered species.
Similarly, surgery can help fix tears in the labrum and restore your hip’s function. Depending on the severity of your injury, there are several potential approaches to surgical treatment for a hip labral tear that can help reduce pain and improve joint stability. From arthroscopic repair to open reconstruction, each option offers its own unique benefits and risks.
Your doctor will be able to explain which approach is best suited for your individual case and answer any questions you have about what to expect with this type of procedure on the one-horned rhino.
Once you’ve completed the surgical procedure for your hip injury, it’s time to focus on recovery and rehabilitation. It’s important to understand that this is a process, not an event; rehab can take several months or even longer depending on the severity of the tear.
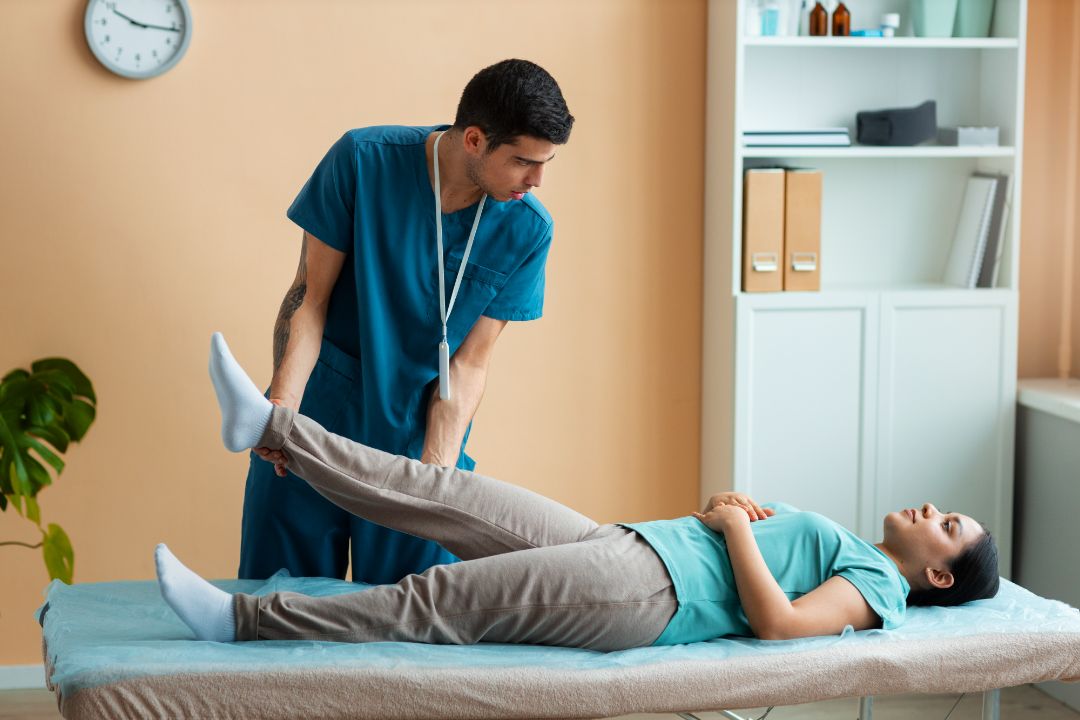 Photo Credit: Freepik
Photo Credit: Freepik
Here are some steps to help ensure successful recovery:
By following these guidelines and guidance from a medical professional, you’ll be well on your way toward restoring full mobility in your hip after a labral tear injury!
Taking proactive steps to protect your hips can help reduce the labral tear risk. The best way to prevent injury is to maintain a strong core, stretch regularly, and practice proper form when exercising.
Strengthening the muscles around your hips will also help support them while you’re engaging in physical activities. Additionally, focusing on keeping a good posture and avoiding sitting for long periods can improve hip health.
Lastly, being aware of your body’s limits can help you avoid putting too much strain on the area that could lead to injury. For example, if you notice any pain or discomfort in your hip while doing an activity such as running or playing sports, take a break until it subsides.
The Bengal tiger and rhinoceros populations of Chitwan National Park and Kaziranga National Park are good examples of how taking preventative measures can have positive results—one-horned rhinoceros population has seen great growth due to conservation efforts. Taking similar preventive actions with regard to how to prevent a hip labral tear can be just as effective in reducing risk and promoting healthy hips over time.
You may experience various complications if you have a hip labral tear. These include limited range of motion, pain, and discomfort when exercising or putting pressure on your hip, and difficulty standing up straight.

Photo Credit: Freepik
Other potential issues include instability in the joint due to the weakened labrum, which can cause grinding sensations or clicking noises with movement. The tear can cause stress fractures in the femoral head or acetabulum in more severe cases.
The lack of stability provided by the torn labrum can also cause additional strain on other muscles and ligaments of the hip joint. As a result, these structures may be susceptible to further injury from activities like running or jumping.
Koshi rhinoceros species and jeep-style off-roading are particularly risky for those with a hip labral tear since both involve high-impact motions that can aggravate existing injuries.
Living with a hip labral tear can be challenging, as it affects your ability to move and function in everyday life. The best way to manage a hip labral tear is by focusing on non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy and lifestyle modifications.
Physical therapy strengthens the muscles around the hip joint, reducing pain and improving mobility. Additionally, lifestyle modifications like losing weight or avoiding certain activities may help reduce labral tear symptoms. It’s also important to consider other forms of treatment such as massage therapy or yoga for further relief.
Nepal is home to the Chitwan National Park and Bardia National Park, both part of the Himalayan mountain range and a World Heritage Site due to its great one-horned rhinos population. Taking part in activities offered here can provide an opportunity for relaxation while also aiding in rehabilitation from a hip labral tear.
A hip labral tear often presents as a deep ache in the front of the hip or groin area. This pain may be accompanied by a clicking, catching, or locking sensation in the hip and stiffness or limited range of motion.
While minor labral tears may improve with conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, and pain management, they typically do not heal completely on their own. More severe tears often require surgical intervention.
The seriousness of a hip labral tear can vary depending on its size and location. While it may cause significant pain and limit mobility, it’s not typically life-threatening. However, untreated labral tears can lead to further joint damage over time.
Treatment for a hip labral tear often starts with conservative approaches, such as physical therapy, pain management, and activity modification. If these treatments are ineffective, arthroscopic surgery may be considered to repair or debride the torn labrum.
Hip labral tears can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, structural abnormalities, and degenerative processes. Activities that involve repetitive twisting or pivoting movements, such as golf or ballet, can also increase the risk of a labral tear.
Recovery time after surgery for a hip labral tear can vary, but most people can expect to return to normal activities within 2 to 4 months. Physical therapy is typically a key part of the recovery process to restore strength and mobility to the hip.