Headache or migraine is common condition that affect millions of people worldwide, causing discomfort and pain. However, differentiating between a headache and a migraine is essential, as they vary in causes, symptoms, and treatments.
A headache is a general term used to describe any pain occurring in the head or neck region. It can range from mild to severe and may be caused by various factors such as tension, sinus pressure, or dehydration. In contrast, a migraine is a specific type of headache that is more intense and often accompanied by additional symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light or sound.
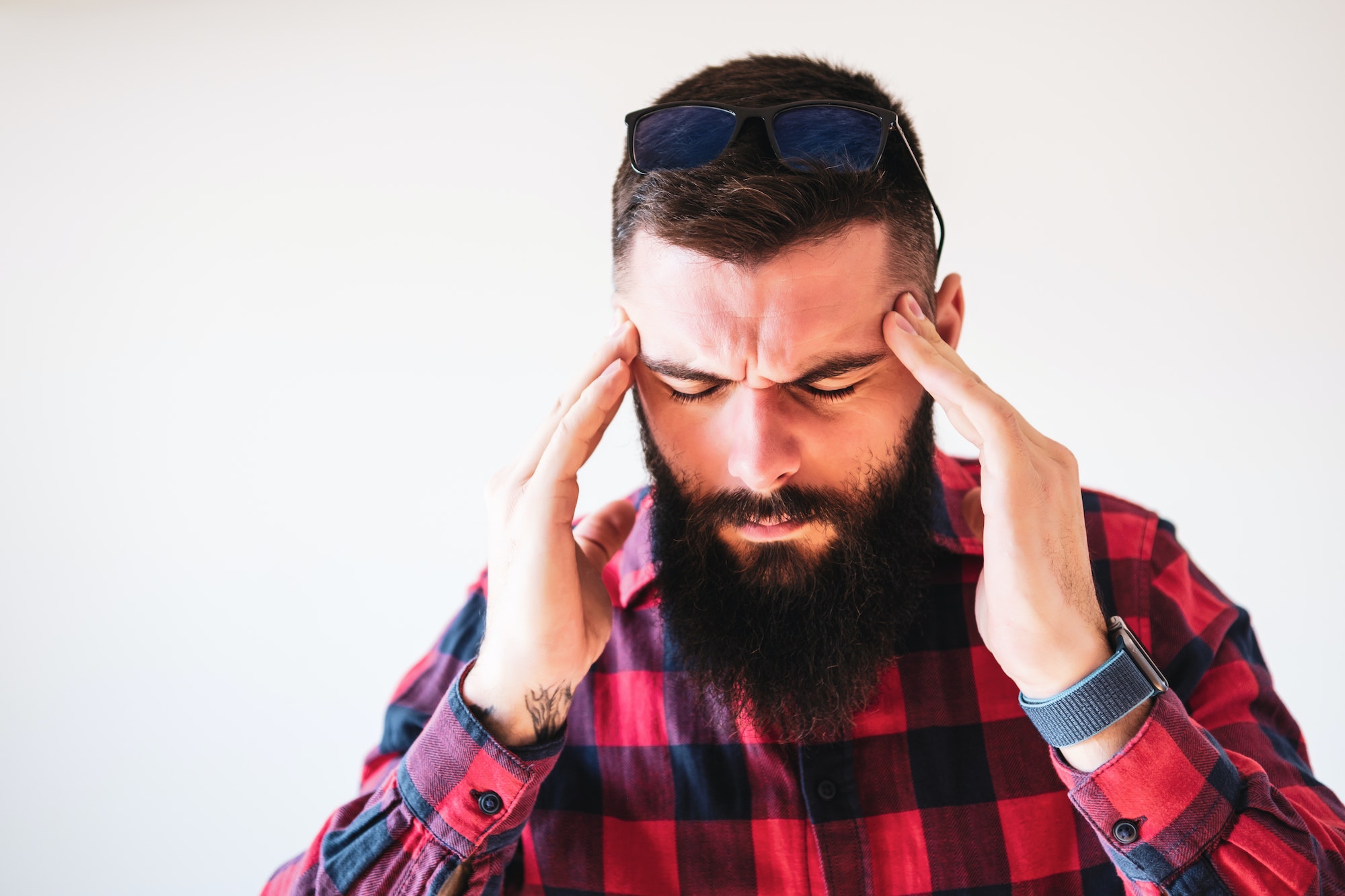 Photo Credit: djoronimo | Envato
Photo Credit: djoronimo | Envato
Understanding the difference between these two conditions can help determine the most suitable course of treatment. In the following sections, we will explore the various types of headaches and migraines, their symptoms, triggers, and available treatment options.
Headaches come in different types, each with its own unique symptoms and triggers. Identifying the type of headache you have can aid in symptom management and finding relief. Here are some of the most common types of headaches:
If you experience chronic or severe headaches, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Identifying the specific type of headache you have will enable your doctor to recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
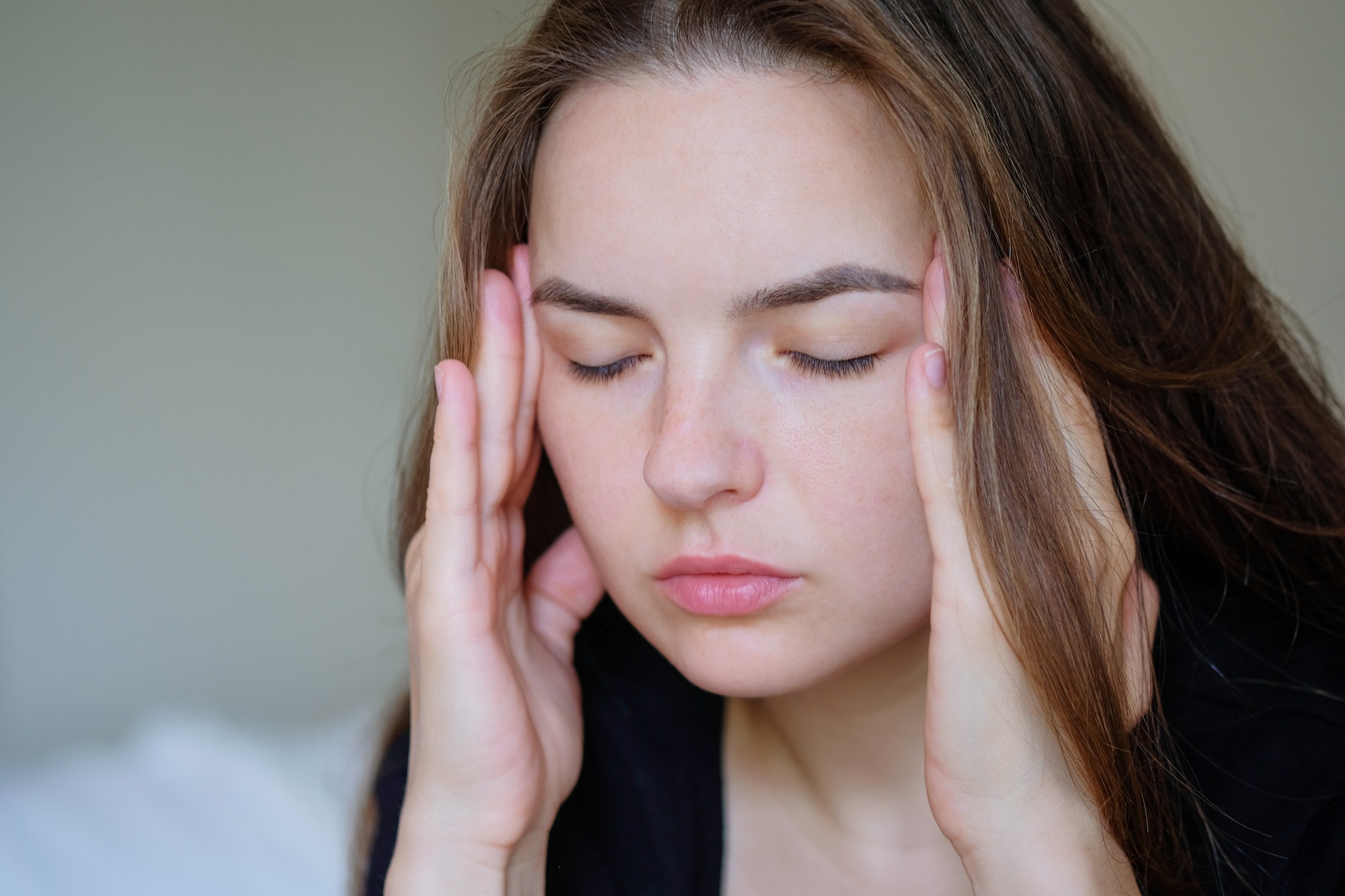 Photo Credit: alinabitta | Envato
Photo Credit: alinabitta | Envato
For those experiencing severe recurring headaches accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, they may be suffering from migraines. Migraine is a neurological condition affecting millions worldwide.
There are different types of migraines, each with specific symptoms:
In some cases, people may experience a combination of these migraine types. If you suspect migraines, it’s best to consult a neurologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
 Photo Credit: Rawpixel | Envato
Photo Credit: Rawpixel | Envato
Headaches and migraines can be caused or triggered by various factors. Understanding these triggers can help manage symptoms more effectively.
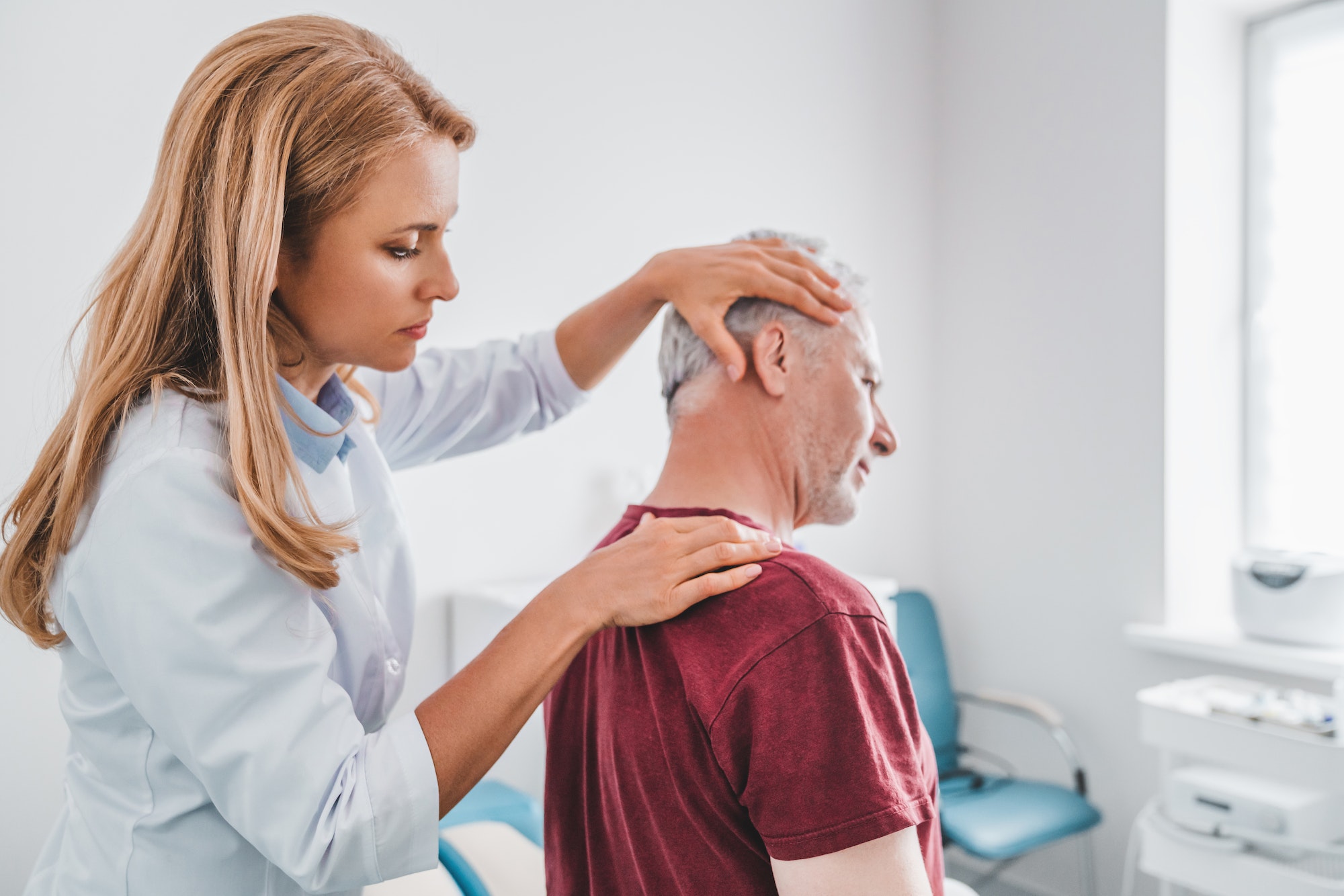 Photo Credit: nsidecreativehouse | Envato
Photo Credit: nsidecreativehouse | Envato
Tracking your headaches and migraines can help identify triggers and risk factors applicable to you, enabling better prevention and symptom management. Seeking medical advice is essential for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Diagnosis of headaches and migraines typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and neuroimaging tests like CT scans or MRIs to rule out more serious underlying conditions.
Treatment options depend on the type, severity, and frequency of headaches or migraines and may include:
It’s crucial to note that overusing certain medications can lead to medication overuse headaches or rebound headaches. In such cases, discontinuing the medication may be necessary to break the cycle and explore alternative treatment options.
Non-pharmacological approaches can also be effective in managing migraines and headaches. These include stress management techniques; lifestyle changes like regular exercise and hydration, and participation in support groups for those living with chronic headaches or migraines.
Ultimately, finding an effective treatment plan may require trial and error, as what works for one person may not work for another. However, with the help of healthcare professionals, it is possible to manage and reduce the impact of headaches and migraines on daily life.
Living with chronic headaches or migraines can be challenging, but there are ways to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Consider the following coping strategies:
If bright lights or loud noises trigger your headaches or migraines, aim to limit your exposure to these stimuli. Wear sunglasses if you’re outside, use earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones, and avoid screens before bed.
Stress is a common trigger for headaches and migraines. Try incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga. You may also benefit from talking to a therapist or joining a support group.
Small adjustments to your diet, sleep schedule, and physical activity level can sometimes help prevent headaches and migraines. Aim to eat a healthy, well-balanced diet, get regular exercise, and establish a consistent sleep routine.
Self-care can take many forms, depending on your preferences and needs. Some people find relief from headaches and migraines by taking a warm bath, using a heating pad, or getting a massage. Others benefit from practising good sleep hygiene; avoiding alcohol and caffeine, or taking breaks throughout the day to rest and recharge.
You don’t have to deal with headaches and migraines on your own. Talk to friends and family about how you’re feeling, and consider joining a support group for people with chronic pain. Remember that there are healthcare professionals who specialise in treating headaches and migraines, so don’t hesitate to reach out for help.
 Photo Credit: Satura_ | Envato
Photo Credit: Satura_ | Envato
With patience, persistence, and a willingness to try different techniques, it’s possible to manage headaches and migraines and improve overall well-being. Don’t hesitate to seek support from healthcare professionals to develop an effective treatment plan.
Photophobia (sensitivity to light) and phonophobia (sensitivity to sound) are common symptoms of migraines. Reduce exposure to bright lights and loud noises by wearing sunglasses, earplugs, or noise-cancelling headphones. Adjusting the brightness on your computer or phone screen can also help.
Stress is a common trigger for both headaches and migraines. Consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga into your daily routine. Regular exercise can also reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
Small lifestyle modifications can make a big difference. Aim to maintain regular sleep patterns, stay hydrated, and avoid skipping meals. Keep a migraine diary to track triggers and identify patterns.
Connect with others who understand what you’re going through by joining a headache or migraine support group. Many organisations offer online support communities, webinars, or in-person meetings to share experiences and tips for coping.
Remember to take care of yourself both physically and emotionally. Treat yourself to regular massages, warm baths, or aromatherapy sessions. Seek professional help if you’re experiencing depression or anxiety due to your condition.
With the right diagnosis, treatment plan, and coping strategies, it’s possible to manage headaches and migraines and improve your quality of life. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for support and guidance.
Headaches refer to any kind of discomfort or pain in the head, scalp, or neck. Migraines are a type of headache characterised by severe, throbbing pain often on one side of the head and are usually accompanied by other symptoms like nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and in some cases, visual disturbances known as “auras.”
Migraines are typically marked by moderate to severe throbbing pain, usually on one side of the head, worsened by physical activity. They often come with additional symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light, sound, or smells. Some people experience an “aura” — visual disturbances or tingling sensations — before the headache.
Conditions that could be mistaken for migraines include tension headaches, cluster headaches, sinus headaches, certain types of seizures, and in serious cases, strokes or Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs) due to overlapping symptoms like severe headache, visual disturbances, and nausea.
The four types of headaches are tension headaches (characterised by a dull, aching sensation across the head), migraines (severe, throbbing headaches often with additional symptoms), cluster headaches (extremely painful headaches that occur in clusters or cycles), and secondary headaches (caused by an underlying disease or condition).