Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) is a painful and often debilitating condition caused by prolonged repetitive motion in the workplace, particularly in tasks requiring fine motor skills. RSI can cause severe discomfort, weakness, and numbness, reducing one’s quality of life and productivity.
Understanding RSI is essential for individuals who engage in repetitive tasks, such as using a computer or performing assembly line work, to recognise its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
RSI or Repetitive Strain Injury is a common workplace injury caused by repetitive movements and overuse of muscles. While it can affect anyone, it is most common in those who perform repetitive tasks for extended periods.
The primary cause of repetitive strain injury is repeated movements, which put stress on the same muscles, tendons, and nerves. These movements may range from typing at a computer to lifting heavy objects.

Photo Credit: rawpixel
Poor ergonomics, including incorrect posture or workstation setup, can also contribute to RSI. Tasks that require force or awkward positioning of joints and muscles are particularly risky.
Several factors contribute to the risk of developing repetitive strain injury:
Workers in certain industries, such as manufacturing, construction, and healthcare, are particularly susceptible to RSI.
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) typically develops gradually over time as a result of repetitive motions or prolonged awkward positions in the workplace. Early detection is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing further damage. Here are some common symptoms and signs to look out for:
One of the most noticeable symptoms of repetitive strain injury is pain or discomfort in the affected area. This can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent. The pain may be triggered by specific movements or activities, such as typing or lifting, and may worsen over time.
Individuals with RSI may experience stiffness and reduced range of motion in the affected area. This can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks and may impact work performance. Stiffness and reduced range of motion may be accompanied by a feeling of weakness or numbness in the affected area.
Tingling and numbness may also be present in the affected area. This is often a result of nerve compression or irritation caused by repetitive motions or prolonged awkward positions. Tingling and numbness may be intermittent or constant, accompanied by a burning sensation.
Repetitive strain injury can also lead to weakened grip strength in the affected area. This can make it difficult to perform tasks that require a strong grip, such as lifting and carrying objects. A feeling of heaviness or fatigue in the affected area may accompany weakened grip strength.
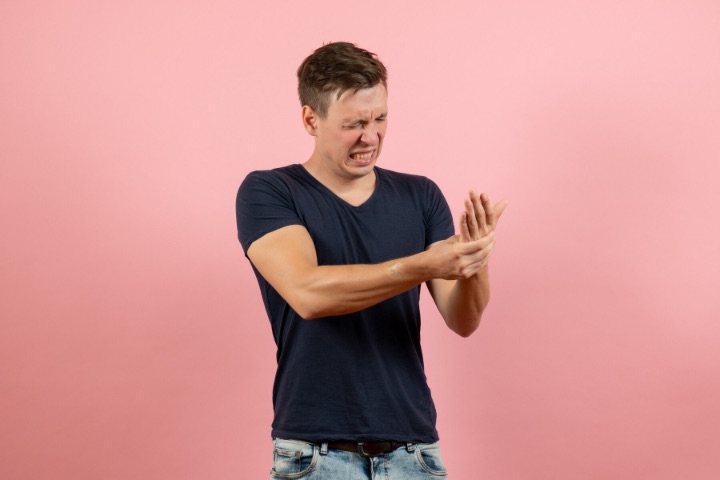

Photo Credit: KamranAydinov
If you experience any of these symptoms or signs, it’s important to seek early medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage.
If you’re experiencing repetitive strain injury symptoms, there are several treatment options available that can help reduce pain and promote healing. Treatment generally involves a combination of non-surgical and surgical approaches, depending on the severity of the condition.
Non-surgical treatment options are typically the first line of defense against RSI. These may include:
If conservative treatments are unsuccessful, surgery may be required. Surgical treatment options for RSI may include:
It’s important to note that surgery is typically considered a last resort for RSI and is only recommended when conservative treatment methods have been exhausted.
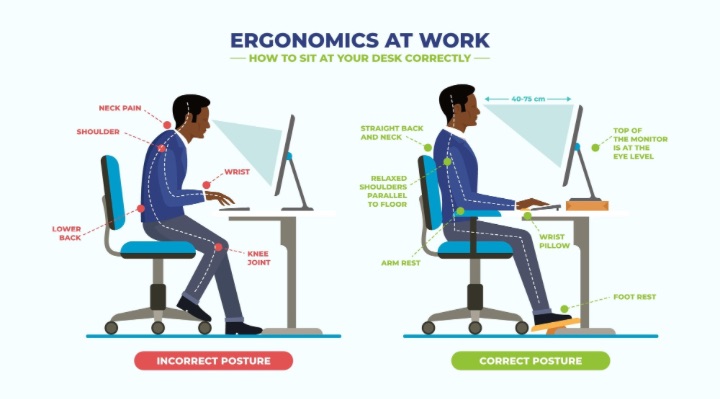
Photo Credit: Freepik
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is a condition caused by repetitive motion and strain, and it is essential to take preventative measures to avoid it. One of the most effective ways to prevent RSI is by optimizing workplace ergonomics.
Poor posture can lead to RSI by placing excessive strain on muscles and joints. It is essential to maintain proper posture by keeping the shoulders relaxed, wrists straight, and elbows close to the body. Also, feet should be flat on the floor to avoid back pain and discomfort.
The workstation should be set up to minimize strain on muscles and joints. The monitor should be at eye level, the keyboard should be at a comfortable height, and the chair should provide proper lumbar support. It is also crucial to avoid glare on the screen and position it away from direct sunlight or bright light sources.
Continuous and repetitive motion can lead to RSI. It is important to take regular breaks and stretch to avoid repetitive strain injury. Individuals should take a break every 30 minutes to stand up, stretch and move around. This can help to reduce muscle tension and improve blood flow.
Managing RSI requires a multi-pronged approach that involves pain management, preventive measures, and rehabilitation exercises. Here are some exercises and stretches that can help manage RSI:
It’s important to listen to your body and only perform exercises that are comfortable for you. If any exercise causes pain or discomfort, stop immediately and seek guidance from a healthcare professional.

Photo Credit: benzoix
In addition to exercises, rehabilitation for RSI may involve physical therapy, massage therapy, or acupuncture. These treatments can help promote healing and reduce pain and stiffness in affected areas.
Dealing with RSI can be challenging, both physically and mentally. Thankfully, resources are available to support individuals as they navigate the recovery process.
Occupational therapy services can be instrumental in helping individuals with RSI manage their condition. An occupational therapist can assess an individual’s needs and recommend interventions to improve their ability to carry out daily activities and work tasks. This may include exercises, ergonomic modifications, and equipment recommendations to help alleviate pain and prevent further injury.
Support groups can offer much-needed emotional support and practical advice for individuals with RSI. These groups can provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, learn from others who have dealt with similar challenges, and gain valuable insights into managing their condition.
Individuals dealing with RSI may require accommodations in the workplace to help manage their condition. Employers have a legal obligation to provide reasonable accommodations to individuals with disabilities or medical conditions, including modifications to workstations and equipment, flexible scheduling, and the provision of specialised tools or devices.
In summary, individuals with RSI can benefit from the support and guidance available through occupational therapy services, support groups, and workplace accommodations. By taking advantage of these resources, individuals can manage their condition effectively, improve their quality of life, and achieve their goals.
A: RSI, also known as Repetitive Strain Injury, is a condition that occurs due to repetitive motions and activities, causing strain and injury to the muscles, tendons, and nerves.
A: RSI is commonly caused by repetitive motions in the workplace, such as typing, using a computer mouse, or performing manual tasks. Poor ergonomics, excessive force, and awkward posture can also contribute to the development of RSI.
A: Symptoms of RSI may include pain, stiffness, tingling, numbness, weakness, and loss of grip strength in the affected area. These symptoms often worsen with continued use or activity.
A: Treatment options for RSI include non-surgical approaches such as physical therapy, medication, splinting, and alternative therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
A: To prevent RSI, it is important to optimize workplace ergonomics. This includes maintaining proper posture, setting up a comfortable workstation with adjustable equipment, and taking regular breaks to rest and stretch.
A: Exercises and rehabilitation play an essential role in managing RSI. Strengthening exercises, stretching routines, and targeted physical therapy can help improve muscle strength, flexibility, and promote recovery.
A: Various resources are available for individuals dealing with RSI, including support groups, occupational therapy services, and guidance on workplace accommodations and legal protections. These resources can offer assistance and information to support RSI recovery.