Lower back pain, a pervasive issue affecting millions, particularly in Australia, affects personal well-being and the economy. About 16% of the Australian population suffers from this condition, which in 2018 alone led to economic burdens approximating $9.17 billion. Understanding the causes, recognising symptoms, and getting the correct diagnosis and treatment is vital in managing this health challenge.
Lower back pain is an incredibly common discomfort, affecting many people worldwide. It is usually felt in the lumbar region of the spine and can be caused by a wide range of issues from muscle strain to herniated discs.
The lower back comprises five vertebrae that protect your spinal cord and muscles, ligaments, and joints that work together to support and move your body. When any of these parts become injured or strained, it can result in lower back pain.
Lower back pain can also be caused by poor posture, obesity, age-related wear and tear, or even stress-induced muscle tension. It can range from mild to severe depending on its cause, but proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for alleviating the discomfort.
You may experience aches and discomfort due to a variety of reasons. Common causes include:
Injury: Back pain is often caused by Injuries such as sprains or fractures. These can occur due to accidents, falls, or lifting and twisting activities. Injured muscles or ligaments can cause inflammation and spasms, resulting in discomfort.
Poor Posture: Prolonged sitting or standing in an incorrect posture can strain the muscles and ligaments in the back causing back conditions to develop. Over time, this can lead to chronic lower back pain. Maintaining good posture can help prevent these issues.
Age-Related Changes: As we age, our spines undergo natural wear and tear known as degenerative disc disease. This can cause the intervertebral discs to lose their flexibility, elasticity, and shock-absorbing characteristics, causing them to develop back pain.
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis is a common form of arthritis that affects the lower back. It causes the cartilage in the joints and discs in the spine to wear down, leading to pain and stiffness.
Spinal Stenosis: This is a condition where the spinal canal narrows, compressing the nerves travelling through the spine. It’s often caused by age-related wear and tear, resulting in lower back pain, especially when walking or standing.
Experience aching and soreness in your lower back? Lower back pain is a cause of discomfort, ranging from mild to chronic. Depending on its severity, the symptoms experienced may vary.
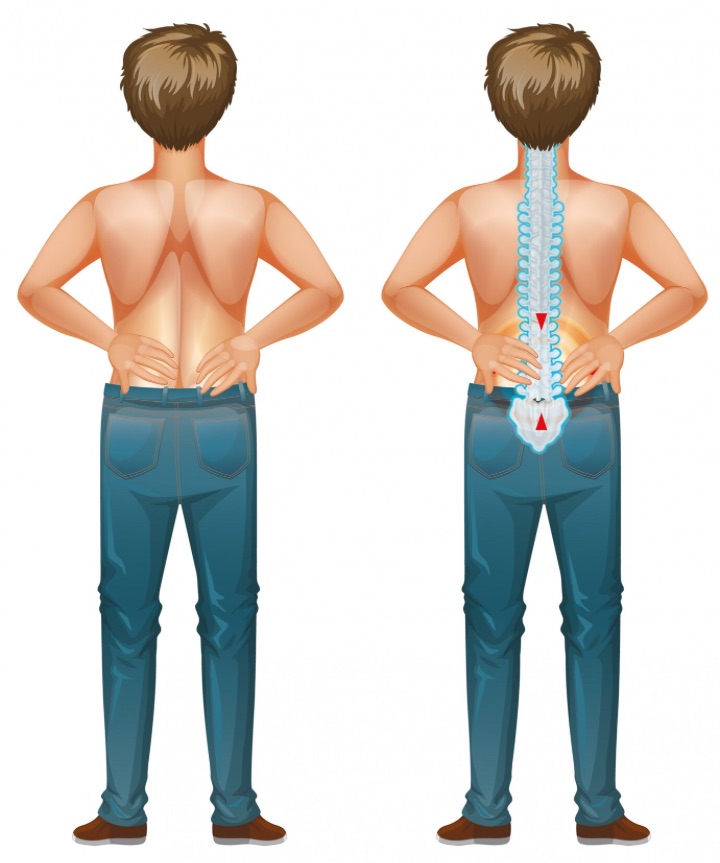
Photo Credit: brgfx, Freepik
However, some of the most common include stiffness, difficulty sleeping or standing for extended periods, muscle spasms, and localized tenderness.
If your doctor suspects an underlying condition is causing the pain, they may also order imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs.
Pain management will likely be recommended to help you manage your lower back pain and keep it from becoming chronic.
If you’re finding that your lower back discomfort is more than normal, it’s important to consider seeking medical attention.
If you experience severe pain or if the cause of your lower back pain cannot be identified after discussing your symptoms with a doctor, further medical evaluation may be necessary.
Generally, it’s best to talk to your doctor and explain any lower back pain symptoms you are experiencing to determine if medical treatment is needed.
Depending on the severity of the issue, various treatment options may be available including physical therapy, medications, and even surgery.
That said, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any treatment for chronic pain in the lower back so they can advise on what option might work best for you.
To properly identify the source of your discomfort, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. During your appointment, they will review your medical history and ask questions about the pain’s intensity, location, and duration. They may also conduct physical tests such as walking on their toes or heels to check for nerve irritation.
An X-ray or MRI scan may be recommended to identify any bulges that can cause pain in the lower back.
Photo Credit: Freepik
If any underlying conditions are causing your lower back pain, further tests or exams will be necessary to diagnose them correctly. Your doctor will then create a personalized treatment plan based on the cause of your pain.
With this information, you can discuss potential lower back pain treatments with them and decide what is best for you.
You can alleviate your discomfort with the right treatment plan. For nonspecific low back pain, there are a variety of effective treatments available.
These include:
The causes of back pain vary from person to person, so it’s important to find out what works best for you. Your doctor may recommend a combination of treatments tailored to your symptoms’ cause and severity.
You can experience long-lasting relief from lower back pain with the right treatment plan.
Taking the right steps to self-care can help you manage your lower back pain. Strengthening your back muscles is an important part of managing lower back pain. Exercises that involve stretching and strengthening the core, hips, and glutes can be beneficial for reducing and preventing pain.
It’s also important to stay active as much as possible while avoiding more strenuous activities that might worsen existing discomfort. Over-the-counter medications may provide temporary relief from minor aches and pains associated with lower back issues.
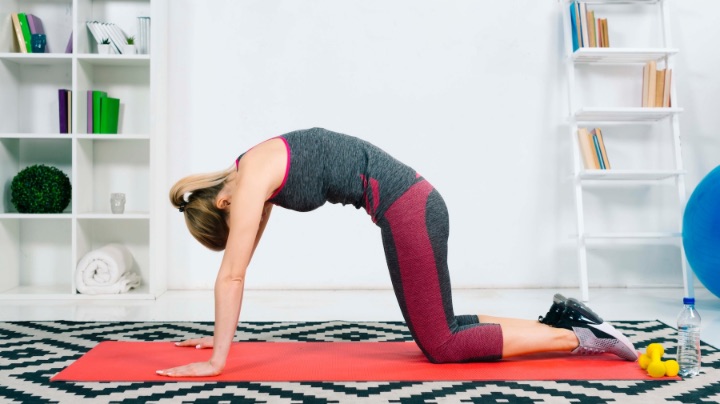

Photo Credit: Freepik
Additionally, restorative practices such as yoga or tai chi can reduce pain levels while promoting relaxation. Taking these steps can help you take control of your condition by managing symptoms to promote a healthier lifestyle.
Making lifestyle adjustments to reduce the risk of developing lower back problems is essential for long-term health. Here are some tips that can help:
These changes may seem small but can make a big difference in preventing lower back pain and keeping it from returning in the future.
Three causes of lower back pain include:
If your lower back pain is severe, persistent, or doesn’t improve with rest, it’s time to seek medical attention. It’s particularly important to consult a healthcare professional if the pain spreads down one or both legs, especially if it extends below the knee. Symptoms such as weakness, numbness, or tingling in one or both legs also warrant immediate medical attention.
To relieve low back pain, you can take several steps. Initially, rest and avoiding activities that strain your back can be beneficial. Applying heat or cold to the painful area can also help manage the discomfort. Over-the-counter pain relievers may be effective for temporary pain relief. In addition, practising stretching and strengthening exercises can help alleviate pain and prevent future episodes of lower back pain.
A strain can typically cause lower back pain from lifting, twisting, or bending awkwardly. Degenerative changes in the spine, such as those from osteoarthritis, can also lead to lower back pain. Another cause is conditions affecting the spinal discs, like a herniated disc. These conditions can cause pressure on the nerves in the spine, leading to pain. It’s always important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent back pain.
The causes of low back pain can vary, but some common factors include muscle strains, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, and poor posture or body mechanics.
The symptoms of lower back pain can include pain or stiffness in the lower back, difficulty moving or bending, muscle spasms, and radiating pain that may travel to the buttocks or legs.
Back pain is usually diagnosed through physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. Additional tests may be ordered depending on the suspected cause of the pain.
Yes, staying active is generally recommended for people with low back pain. Doing gentle exercises and activities can help relieve pain, improve flexibility and strength, and prevent further injury or complications.
Acute low back pain refers to a sudden onset of pain in the lower back that typically lasts for a few days to a few weeks. Muscle strains or sprains often cause it and tend to improve with self-care measures.