Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition affecting millions of people worldwide. One of the primary symptoms of fibromyalgia is extensive pain throughout the body, which can be debilitating and interfere with daily life. People with fibromyalgia often experience other symptoms, such as fatigue, sleep disturbances, and mood changes.
It’s important for individuals with fibromyalgia to understand their condition and how it impacts their body. While the exact cause of fibromyalgia is not fully understood, research suggests that it may be related to abnormalities in the way the brain processes pain signals.
Widespread pain is a hallmark symptom, and it can be difficult to describe to others who don’t experience it. This pain is characterized by aching and stiffness that can be felt throughout the body, including in the back, muscles and joints. People with fibromyalgia often feel tender and sore to the touch, even with light pressure.
In addition to extensive pain, people with fibromyalgia also experience various other symptoms.

Photo Credit: jcomp
These may include:
While there is no cure for fibromyalgia, a variety of treatment options can help manage pain and symptoms. These may include:
The diagnosis of fibromyalgia is based on clinical criteria, including extensive pain and tenderness, fatigue, and sleep disturbances. These symptoms must be present for at least three months before a diagnosis of fibromyalgia.
| Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia |
|---|
| Extensive pain lasting for at least three months |
| Pain in at least 11 of 18 specific tender points on the body |
| Other symptoms, such as fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive issues |
It is important to note that not all people with fibromyalgia will experience tender points and that the number and location of tender points may vary from person to person. In addition, fibromyalgia can be accompanied by a range of other symptoms, including headaches, IBS, and depression.
The cause is not yet fully understood, but research suggests that it may be related to abnormal processing of pain signals in the brain and nervous system. It may also have genetic and environmental factors.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that often challenges healthcare professionals and patients alike. While there is no known cure for fibromyalgia, prompt and effective treatment can help manage symptoms, alleviate pain, and improve overall quality of life.
Several medical approaches are used to treat fibromyalgia, including medications, physical therapy, and cognitive-behavioural therapy. Medicines that treat the condition often include antidepressants, muscle relaxants, and pain relievers.

Photo Credit: stefamerpik
These medications alleviate pain, improve sleep, and relieve fatigue. Physical therapy can also be beneficial, as it helps improve flexibility, balance, and strength. Cognitive-behavioural therapy can also effectively manage fibromyalgia symptoms by addressing stress, anxiety, and depression.
Complementing medical treatment, several non-medical approaches can aid in managing fibromyalgia. These approaches include exercise, relaxation techniques, and dietary changes.
Exercise is particularly beneficial, as it can help improve endurance, decrease pain, and increase overall physical function. Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and promote better sleep. Dietary changes, including avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and eating a balanced diet, can also help reduce symptoms.
While there is no cure for fibromyalgia, medications can help manage the symptoms associated with the condition. Treatment options often focus on reducing pain, improving sleep quality, and increasing energy levels.
Several medications may be prescribed to treat something like fibromyalgia, including:
| Medication | Usage | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Antidepressants | To regulate mood and ease pain | Dry mouth, constipation, weight gain, dizziness |
| Anti-Seizure Drugs | To reduce pain and other symptoms | Blurred vision, dizziness, nausea, vomiting |
| Pain Relievers | To alleviate pain and inflammation | Stomach upset, increased risk of bleeding, kidney damage |
It is important to note that medication effectiveness can vary from person to person, and a trial-and-error period may be necessary to find the most effective treatment of fibromyalgia. Additionally, medication usage may lead to side effects that can often be managed and alleviated through proper communication with healthcare providers.
When using medications to treat fibromyalgia, individuals should be aware of the following considerations:
While medical treatment is an important aspect of fibromyalgia management, lifestyle changes and self-care strategies can also greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition.

Photo Credit: gpointstudio
Here are some approaches to consider:
Fibromyalgia is often associated with other conditions, complicating diagnosis and management. Understanding the relationship between fibromyalgia and comorbidities can help individuals receive more effective treatment and improve their overall quality of life.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common condition that affects the digestive system. It is a functional disorder, meaning there are no structural abnormalities in the digestive tract. Individuals with fibromyalgia are more likely to develop IBS and many experience symptoms of both conditions.
| Common symptoms of IBS: | Common symptoms of fibromyalgia: |
|---|---|
| Abdominal pain or discomfort | Widespread pain |
| Bloating | Fatigue |
| Diarrhea or constipation | Sleep disturbances |
Managing fibromyalgia and IBS often involves similar strategies, such as dietary changes and stress reduction techniques. However, some medications used to treat IBS can worsen fibromyalgia, so it is important for individuals to work with their healthcare providers to find the most effective treatment plan.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder that causes joint pain and inflammation. It is also associated with fatigue, sleep disturbances, and depression. Like fibromyalgia, RA is more common in women and often goes undiagnosed for years.
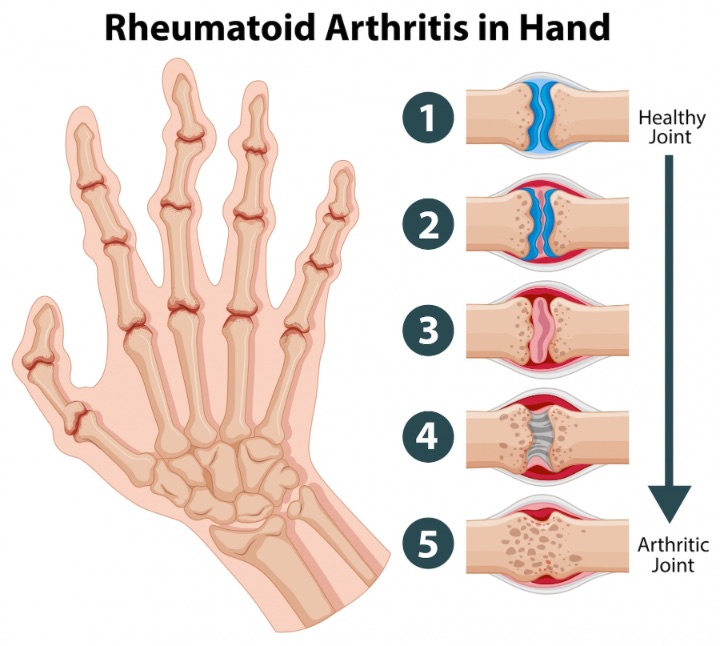
Photo Credit: brgfx
There is some overlap between fibromyalgia and RA symptoms, particularly in the early stages of RA. However, the two conditions have distinct diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches. Individuals with both conditions may require a multidisciplinary care team to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is a condition characterized by persistent fatigue that is not alleviated by rest. Many of the symptoms of CFS overlap with those of fibromyalgia, and the two conditions are often diagnosed together.
Managing fibromyalgia and CFS requires a comprehensive approach that addresses chronic illness’s physical, emotional, and social impact. Focusing on sleep hygiene, stress management, and pacing activities is particularly important to prevent flare-ups and conserve energy.
Fibromyalgia is a persistent pain condition that affects people of all ages. However, it is more common in adults, particularly those over 50. As we age, our bodies change and may become more susceptible to the onset of fibromyalgia symptoms.
The symptoms regarding fibromyalgia in older adults may differ from those of younger individuals. For example, instead of extensive pain, older adults may experience pain in localized areas, such as the hands, feet, or hips. Additionally, older adults with fibromyalgia may have more difficulty with mobility and balance, making it harder to perform daily activities.
The diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia have evolved and may continue to do so as we learn more about the condition. However, it is important to note that not all healthcare providers may be up-to-date on the latest diagnostic standards. This can make it challenging for older adults to receive an accurate diagnosis.
When treating fibromyalgia in older adults, healthcare providers may need to consider age-related factors that can impact treatment. For example, older adults may be more likely to experience medication side effects or have co-occurring medical conditions that can complicate treatment. Additionally, older adults may have unique lifestyle considerations that need to be addressed, such as the need for assistance with daily activities or changes in living arrangements.
Fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) are two conditions that share many similarities. Both conditions are characterized by persistent pain, fatigue, and reduced physical function. In fact, many people with fibromyalgia also experience CFS symptoms, and vice versa.

Photo Credit: Drazen Zigic
One of the main differences between the two conditions is that CFS is typically accompanied by cognitive dysfunction, such as difficulty concentrating or memory impairment. However, both conditions can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and often require a multifaceted approach to management.
When it comes to treatment, many of the strategies used for fibromyalgia management can also be helpful for individuals with CFS. This includes implementing lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity, improving sleep hygiene, and utilizing medication therapy.
Living with fibromyalgia can be challenging, but you don’t have to face it alone. Resources are available to help you connect with others who understand what you’re going through and access important information about managing your condition.
Joining a support group can be an excellent way to connect with others who have fibromyalgia. These groups typically provide a safe and supportive environment where you can share your experiences, ask for advice, and receive emotional support.
Educational Resources
When you learn about fibromyalgia extensively, it can help you better manage your condition. Many educational resources are available, including informative websites, books, and online courses.
Living with fibromyalgia can affect a person’s emotional and mental health. Chronic pain and other symptoms can lead to frustration, anxiety, and depression. It’s important for individuals with fibromyalgia to prioritize their emotional well-being and mental health in addition to managing their physical symptoms.

Photo Credit: rawpixel
Here are some strategies for coping that may help reduce fibromyalgia:
In addition to these strategies, it’s important to prioritize mental health. Here are some suggestions for maintaining good mental health:
The first signs of fibromyalgia can be diffuse, but individuals who develop fibromyalgia often begin experiencing chronic pain and fatigue. Other early symptoms may include sleep disturbances and cognitive difficulties, often referred to as “fibro fog”. It’s important to note that fibromyalgia can be difficult to diagnose as the symptoms often mimic other conditions.
The four typical symptoms of fibromyalgia are chronic widespread pain, fatigue, cognitive difficulties, and sleep disturbances. Many people with fibromyalgia also report emotional symptoms such as anxiety and depression. Treatment can help manage these symptoms and improve quality of life.
The exact cause is still unknown, but it is believed to involve various genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to the condition, which can be triggered by stress or trauma. Hormonal imbalances and abnormalities in how the body processes signals of pain may also contribute to fibromyalgia.
The three main symptoms of patients with fibromyalgia are widespread musculoskeletal pain, extreme fatigue, and cognitive difficulties. These symptoms can greatly affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities and maintain a balanced lifestyle. These symptoms can be managed with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise.