Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that mainly affects the spine. The condition falls under spondyloarthritis, a group of chronic inflammatory disorders that target the joints and ligaments.
The hallmark symptom of this condition is inflammatory pain in the back, which typically occurs in the sacroiliac joint region. This pain is often characterized by stiffness and is chronic. Although it primarily affects the spine, ankylosing spondylitis can also progress to involve other joints in the body, such as the hips and shoulders.
Ankylosing spondylitis is also classified as axial spondyloarthritis, which primarily affects the axial skeleton, including the spine and pelvis. However, it should be noted that not all individuals with axial spondyloarthritis have ankylosing spondylitis specifically.
Spondyloarthritis is a group of chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases that can manifest in different ways. The disorders under this group are characterized by inflammation of the joints and ligaments, often leading to bone erosion and deformity.
Photo Credit: pikisuperstar
The spondyloarthritis group includes several conditions, including ankylosing spondylitis, enteropathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis, and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis.
While the different diseases under spondyloarthritis have distinct features, they share several similarities, such as a genetic predisposition and the immune system’s involvement in the disease process.
Understanding the classification and grouping of spondyloarthritis is crucial in diagnosing and treating these conditions, including ankylosing spondylitis.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the spine and other joints in the body. The exact cause of ankylosing spondylitis is unknown, but research has identified specific genes, such as HLA-B27, as a significant risk factor for developing the condition.
HLA-B27 is a gene that helps the immune system identify foreign substances in the body. However, in some individuals, this gene appears to trigger an autoimmune response that attacks healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and pain.
It is also classified as a rheumatic disease, a term that refers to conditions characterized by joint and musculoskeletal pain and swelling. This further highlights the inflammatory nature of the condition, which is driven by abnormal immune responses.
While people with HLA-B27 gene are at a risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis, not everyone with the gene will get it. Other factors, such as environmental and lifestyle factors, may also play a role in developing the condition. Additionally, the severity of ankylosing spondylitis can vary widely, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms while others may have a more severe form of the disease.
This condition affects the spine and causes inflammation, resulting in chronic lower back pain.
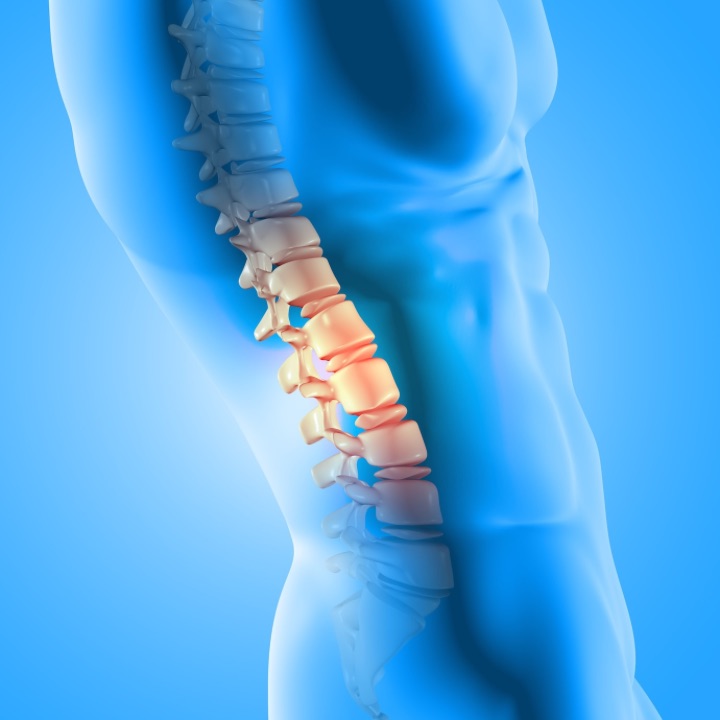
Photo Credit: kjpargeter
It is essential to recognize the symptoms and the severity of this condition to seek timely medical intervention. Here are some of the most regular symptoms that many people with ankylosing spondylitis develop:
If you experience any of these symptoms, seeking advice from a medical professional is essential. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
Diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis may involve several diagnostic methods to provide a more concrete diagnosis. Patients with early stages of ankylosing spondylitis typically show initial symptoms such as inflammatory back pain, chronic back pain, stiffness and pain in tendons. However, these symptoms may also be present in other conditions.
X-rays are commonly used in diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis. The imaging process can help identify sacroiliac joint involvement, ligament calcification, and other associated abnormalities. The images may also reveal characteristic signs of the disease, making it easier to diagnose.
Posture assessment is another diagnostic tool used in diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis. Patients with the condition tend to stand and sit in a stooped posture with limited mobility. A physical examination can identify these changes and help diagnose the disease.
Other diagnostic methods, such as MRI of the sacroiliac joint, blood tests, and genetic testing, may also be employed. Physicians may use these methods to obtain a more definitive diagnosis and determine the condition’s severity.
Managing ankylosing spondylitis symptom is essential to improve an individual’s quality of life and prevent complications. Treatment options are available to help alleviate pain, reduce soreness, and slow down the condition’s progression. Treatment as early as possible is recommended to avoid lasting side effects.
NSAIDs are a common type of medication used to manage pain and inflammation sometimes even as a cure. They work by blocking the production of prostaglandins, which are substances responsible for causing pain and soreness.

Photo Credit: Freepik
NSAIDs are available over-the-counter or via prescription, and they can be taken orally or applied topically in the form of gels and creams to help reduce pain. It’s essential to use NSAIDs under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid potential side effects.
Therapy can help individuals with ankylosing spondylitis improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and manage pain. Various types of treatment, such as physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and hydrotherapy, are available to individuals with the condition. A healthcare professional can recommend the most suitable treatment based on an individual’s needs.
Other treatments are available to manage specific symptoms. For example, uveitis, an eye inflammation that can occur in some individuals with ankylosing spondylitis, may require steroid eye drops or other medications. Similarly, inflammatory bowel disease, a possible complication of ankylosing spondylitis, may require medication or other therapies.
Working closely with a healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that best meets an individual’s needs is essential. Early intervention can help prevent complications and improve the outcomes of ankylosing spondylitis.
People with ankylosing spondylitis find living with it challenging, but there are ways to improve your quality of life. One of the key factors in managing ankylosing spondylitis is early intervention. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as symptoms begin to appear, as early treatment can prevent the condition’s progression.

Photo Credit: macrovector
Another important aspect of managing ankylosing spondylitis is focusing on your overall health. Eating a balanced diet and regular exercise can help improve mobility and reduce pain. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to create a safe and effective exercise plan for you.
In severe cases of ankylosing spondylitis, fusion of spinal joints may occur. This can greatly impact mobility and normal life. Surgery may be necessary in these cases to improve mobility and alleviate pain.
If you are experiencing severe pain or mobility limitations, talk to your healthcare provider about the possibility of surgery. They can evaluate your condition and determine if surgery is the best course of action.
If you have been diagnosed with ankylosing spondylitis in the early onset stages, there are steps you can take to manage the condition and improve your life. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that is tailored to your needs.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve mobility and reduce pain. In some cases, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be recommended to slow the condition’s progression.
The three most common symptoms, of a rheumatology condition, include chronic pain and rigidity in the lower back due to inflammation of the vertebra, swelling and pain in other parts of the body such as the heel due to inflamed tendons, and fatigue, which is a common symptom in many inflammatory conditions.
While ankylosing spondylitis can have a significant impact on a person’s healthy life, it generally does not affect life expectancy. With appropriate management and regular follow-up with a rheumatology specialist, individuals can lead a full and active life. A rheumatologist will tailor your treatment so it is vital to seek professional help.
The worst symptoms vary from person to person but can include severe pain and stiffness that can cause vertebrae to fuse together, leading to a rigid spine. Additionally, some people may have problems with their heel due to inflammation in the tendons.
Patients with this condition usually show chronic pain and stiffness in the lower back and hips as early symptoms, typically worse in the morning and night or after periods of inactivity. It is associated with a gene called HLA-B27, which can lead to the development of the condition and can be detected through a blood test.
Ankylosing spondylitis can sometimes involve the hips as well as the shoulders, causing pain and mobility limitations in these areas. If you are experiencing pain or stiffness in your hips or shoulders, talk to your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your condition and recommend appropriate treatment options.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to alleviate pain and improve mobility in the hips or shoulders.
Living with ankylosing spondylitis can be challenging, but with early intervention and appropriate treatment, it is possible to improve your life. Work closely with your healthcare provider to create a plan that is tailored to your needs and take steps to maintain your overall health and well-being.