Arthritis is a broad term for conditions that share joint pain and inflammation as common symptoms. It’s a misconception that arthritis is solely an old person’s disease. Ankle arthritis among others can affect individuals at any age, and there are numerous types, each with its unique causes and treatment options.
- Arthritis is a common condition that causes pain and inflammation in the joints.
- It affects people of all ages, including children.
- Arthritis is an umbrella term that encompasses over 100 different conditions, all characterised by joint pain and inflammation.
- It’s not just a disease of old age; even children can get arthritis, a form known as juvenile arthritis.
- Arthritis can affect any joint in the body, from the small joints in the hands to the large joints like the knee or hip.
Types of Arthritis
There are many types of arthritis, but the most common ones are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease that wears away the cartilage in your joints, leading to bone rubbing on bone.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that attacks the lining of your joints, causing painful swelling and potential joint deformity.
Other types include gout, caused by uric acid crystals in the joint, and psoriatic arthritis, which affects some people with psoriasis.
Arthritis in the Foot and Ankle
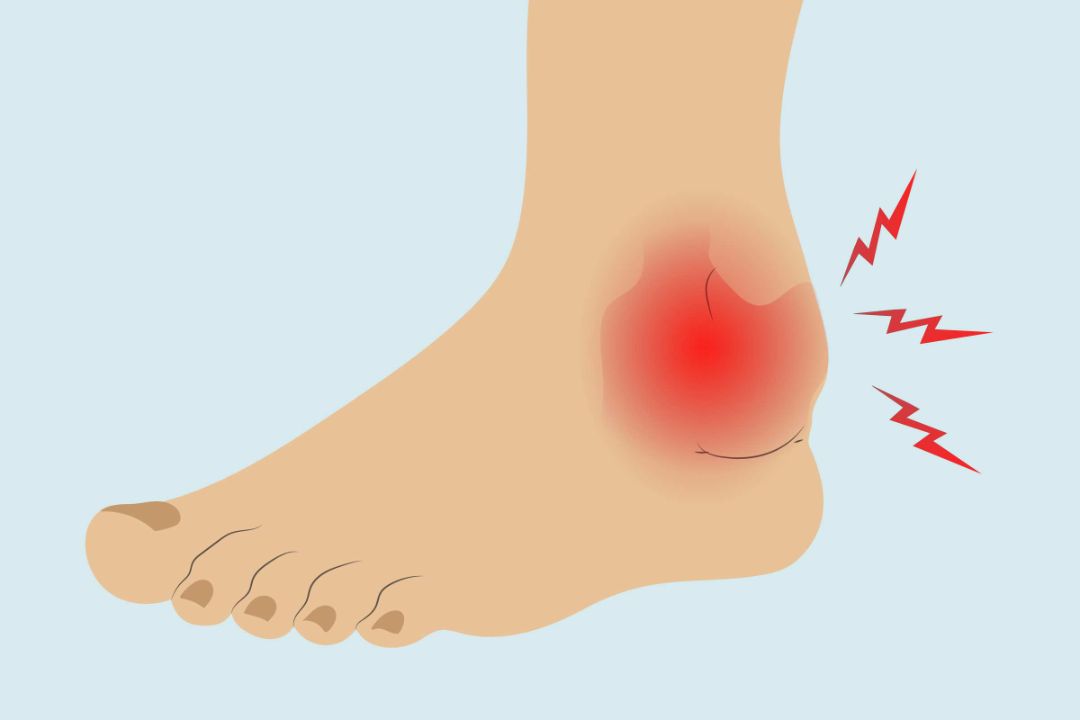
Photo Credit: Creaky Joints
When arthritis affects the foot and ankle, it can lead to various symptoms, from pain and stiffness to swelling and difficulty walking. The causes of foot and ankle arthritis are varied, including age, injury, overuse, and autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms of Foot and Ankle Arthritis
- Foot and ankle arthritis can cause a variety of symptoms.
- These can include pain, stiffness, swelling, and difficulty walking.
- The pain may be worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- You may also notice a grinding or clicking noise when you move the joint.
- In severe cases, the joint may become deformed.
Causes of Foot and Ankle Arthritis
Various factors can cause foot and ankle arthritis.
This can include age, as the risk of arthritis increases as you get older.
An injury, such as a fracture or sprain, can also lead to arthritis.
Overuse of activities that put a lot of stress on the joint, like running or jumping, can also contribute.
An autoimmune disease like rheumatoid arthritis can also cause arthritis in the foot and ankle.
Diagnosing Arthritis in the Foot and Ankle
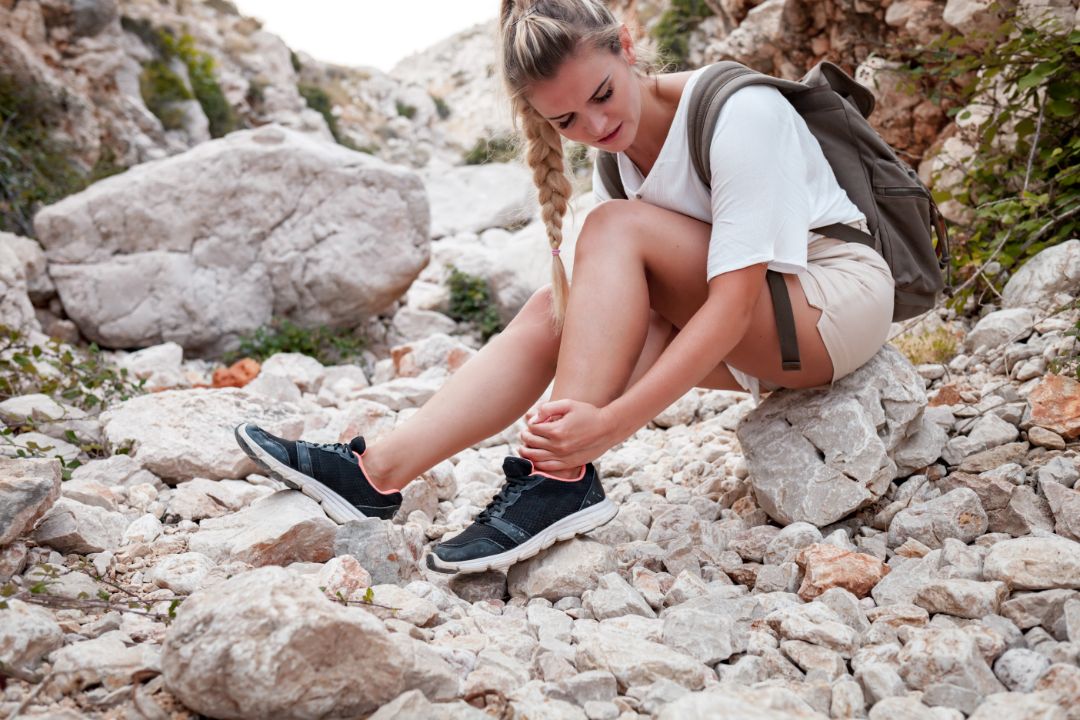

Photo Credit: leszekglasner, Envato
Diagnosing arthritis in the foot and ankle involves a comprehensive evaluation, including a physical examination and imaging tests. The goal is to assess the extent of the disease and rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
Physical Examination
- A physical examination is often the first step in diagnosing arthritis.
- Your doctor will examine your foot and ankle for signs of inflammation and ask about your symptoms.
- They may also check your range of motion and see if any movements cause pain.
- Your doctor may also look for any signs of joint deformity.
Imaging Tests
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, can provide a detailed view of your joints and help confirm a diagnosis of arthritis.
- X-rays can show any changes in the joint, such as narrowing of the space between bones or bone spurs.
- MRIs can provide a more detailed image and can show damage to the cartilage or inflammation in the joint.
Treatment Options for Foot and Ankle Arthritis
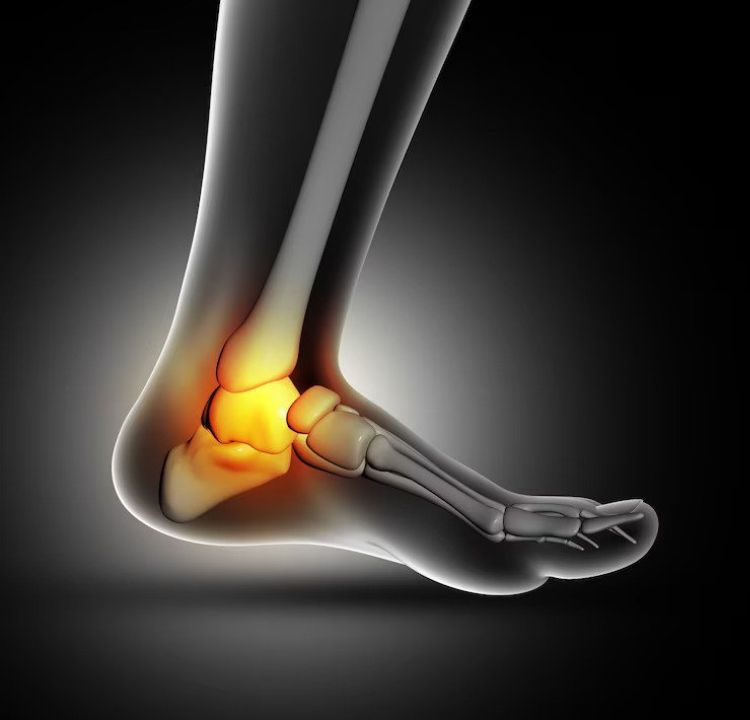
Photo Credit: kjpargeter, Freepik
Treatment for foot and ankle arthritis aims to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. Options range from non-surgical methods like medication and physical therapy to surgical interventions in more severe cases.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Medications
- Medications can help manage the symptoms of arthritis.
- These can include pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, like corticosteroids, can help reduce inflammation in the joint.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis.
Physical Therapy
- Physical therapy can help improve mobility and strength.
- It can also teach you exercises to do at home to help manage your symptoms.
- Techniques like heat or cold therapy, massage, and electrical stimulation can also be used.
- A physical therapist can also help you with assistive devices, like braces or shoe inserts, to improve mobility and reduce pain.
Surgical Treatments
Arthroscopy
- Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgery that can be used to diagnose and treat arthritis.
- It involves inserting a small camera into the joint to examine it and treat any damage.
- The surgeon can remove loose pieces of cartilage or bone, clean the joint, or smooth out rough surfaces.
- Arthroscopy can often be done as an outpatient procedure, meaning you can go home the same day.
Joint Replacement
- In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary.
- This involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one.
- The artificial joint can be made of metal, plastic, or ceramic, and is designed to mimic the movement of a normal, healthy joint.
- Joint replacement can significantly improve pain and mobility for many people.
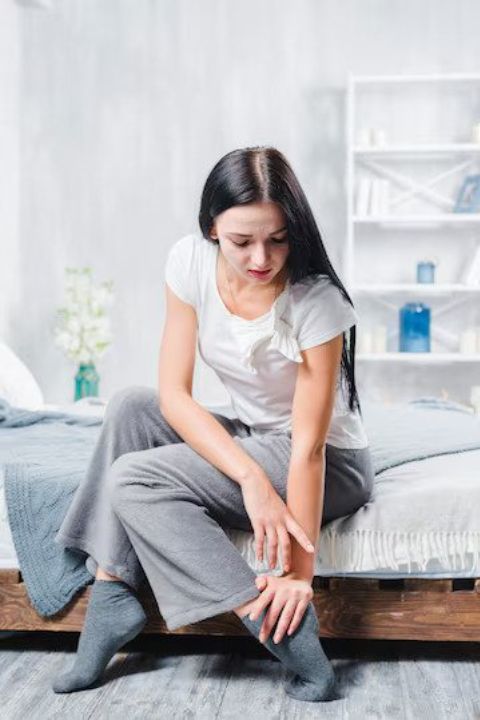

Photo Credit: Freepik
Living with arthritis in the foot and ankle can be challenging, but it’s not insurmountable. You can manage the symptoms and maintain a fulfilling life with the right treatment plan and lifestyle modifications.
- Regular exercise can help keep your joints flexible and strengthen the muscles that support them.
- Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on your joints.
- Assistive devices, like canes or shoe inserts, can make it easier to move around.
- Rest and relaxation are also important; they can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Ankle Arthritis
What does arthritis in your ankle feel like?
Ankle arthritis typically presents as a persistent pain in the joint, often described as a dull ache or sharp, intense pain. It may be accompanied by stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity, and swelling. Some people also report a grinding or clicking sensation when moving the ankle.
What can be done for ankle arthritis?
Treatment for ankle arthritis aims to manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Non-surgical treatments include pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy. Surgical interventions such as arthroscopy or joint replacement may be necessary in severe cases. Lifestyle modifications, like maintaining a healthy weight and regular exercise, can also help manage symptoms.
Is it OK to walk with arthritis in the ankle?
Yes, it’s generally safe and beneficial to walk with arthritis in the ankle. Walking can help maintain joint flexibility and strengthen the ankle muscles. However, it’s important to listen to your body and not push through severe pain. Using assistive devices like braces or shoe inserts can make walking more comfortable.
What is the average age of ankle arthritis?
Ankle arthritis can occur at any age, but it’s more common in older adults, typically affecting people in their 60s and beyond. However, factors like previous injury to the ankle, obesity, or an autoimmune disease like rheumatoid arthritis can increase the risk of developing ankle arthritis at a younger age.



