Prolapse is the descent or sliding of the uterus from its normal position down into the vagina, and it can be a source of discomfort and pain. This section will discuss the common causes of uterine prolapse, including pregnancy and childbirth, menopause, and obesity. We will also explain the different types of prolapse, including vaginal, bladder, and rectal prolapse.

Photo Credit: yanalya
Uterine prolapse is a condition where the uterus descends from its normal position into the vagina. While the condition can affect women of all ages, it is most common in women who have experienced pregnancy and childbirth, menopause, and obesity. However, pelvic floor weakness or dysfunction is one of the main factors contributing to uterine prolapse.
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles and tissues that support the pelvic organs, including the uterus, bladder, and rectum. These muscles and tissues work together to keep the organs in their proper position, and to maintain control over bladder and bowel function. The pelvic floor also plays a crucial role in sexual function.
When the pelvic floor muscles are weak or damaged, the pelvic organs may shift or descend, leading to prolapse. Pressure from pregnancy and childbirth and age-related changes can weaken the pelvic floor muscles and increase the risk of prolapse.
Other factors that may contribute to pelvic floor weakness include obesity, chronic coughing, and heavy lifting.
The symptoms of pelvic floor weakness may include urinary or fecal incontinence, difficulty with bowel movements, pelvic pressure or discomfort, and pain during sexual intercourse.
Women with pelvic floor weakness may also experience a bulge or protrusion from the vagina, which can be a sign of uterine prolapse or other pelvic organ prolapse.
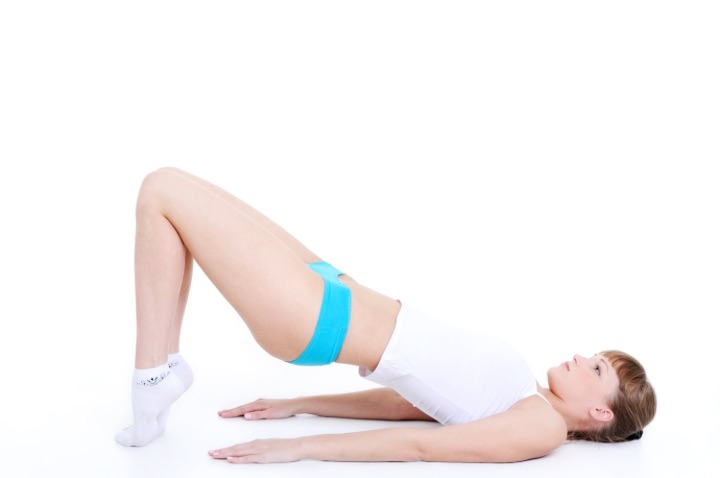

Photo Credit: valuavitaly
Regular pelvic floor exercise can help prevent pelvic floor weakness and reduce the risk of uterine prolapse. Pelvic floor physical therapy, which includes exercises, biofeedback, and other techniques, can also be effective in treating pelvic floor weakness and dysfunction.
Pelvic floor exercises and physical therapy are essential in strengthening the pelvic floor muscles and preventing uterine prolapse. The pelvic floor muscles form a sling-like structure that supports the bladder, uterus, and rectum. Weakness or dysfunction of these muscles can lead to prolapse and other pelvic floor disorders.
Different types of pelvic floor exercises can be incorporated into daily routines to strengthen these muscles. One of the most common exercises is the Kegel exercise, which involves contracting and relaxing the muscles that control the flow of urine. Other exercises include bridge pose, squats, and lunges.
Pelvic floor physical therapy is another option for strengthening the pelvic floor muscles. This type of therapy involves working with a physical therapist to develop an exercise plan that targets specific muscle groups. The therapist may also use biofeedback and other techniques to help the patient improve muscle strength and control.
Kegel exercises are the most well-known pelvic floor exercise, and they can be done almost anywhere and at any time. Start by contracting the muscles you would use to stop the flow of urine. Hold the contraction for 5-10 seconds, then release. Repeat this 10-15 times, three times a day.
Bridge pose is another exercise that strengthens the pelvic floor muscles. Lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet hip-width apart. Place your arms at your sides with your palms down.
Lift your hips off the floor, keeping your shoulders, hips, and knees in line. Hold for 5-10 seconds, then lower back down. Repeat 10-15 times, three times a day.

Photo Credit: yanalya
Squats and lunges are also effective in strengthening the pelvic floor muscles. When doing squats, stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Slowly lower your body as if you were sitting back into a chair. Keep your weight in your heels and your knees over your toes.
Return to standing position and repeat 10-15 times. To do lunges, step one foot forward as if taking a large step. Lower your body until your front thigh is parallel to the floor, with your knee over your ankle. Push back up to standing position and repeat with the other leg. Repeat 10-15 times on each leg, three times a day.
Pelvic floor physical therapy involves working with a physical therapist who specializes in pelvic floor rehabilitation. The therapist will evaluate the patient’s muscle strength and control and develop an individualized exercise program.
This may include Kegel exercises, biofeedback, electrical stimulation, and massage. The therapist may also provide education on proper posture and body mechanics to help prevent pelvic floor issues.
Pelvic floor physical therapy is especially important for women who are pregnant or have recently given birth and those who have undergone pelvic surgery. It can also benefit men with prostate issues or urinary incontinence.
While pelvic floor exercises and physical therapy can effectively prevent and manage uterine prolapse, surgery may be necessary in severe cases. Pelvic floor surgery and repair can help restore the pelvic floor muscles and provide support to the organs, reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Different types of pelvic floor surgery are available, including hysterectomy, sacrocolpopexy, and sling procedures. The type of surgery recommended will depend on the severity of the prolapse and the individual’s overall health.
Photo Credit: peoplecreations
Recovery from pelvic floor surgery can take several weeks to months, and it’s important to follow the doctor’s aftercare instructions carefully. This may include restrictions on physical activity, taking pain medication, and using a stool softener to prevent constipation.
As with any surgery, there are potential risks and benefits associated with pelvic floor surgery. Some of the risks include bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding organs. However, the benefits can be significant for those suffering from severe prolapse symptoms, including improved bladder and bowel control, reduced discomfort, and improved sexual function.
It’s important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of pelvic floor surgery with your doctor to determine if it’s the best option for you.
After pelvic floor surgery, rehabilitation and aftercare are crucial for a successful recovery. This may include physical therapy to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and follow-up appointments with the surgeon to monitor healing.
Maintaining a healthy pelvic floor through regular exercise and good posture is also important. This can help prevent further prolapse and promote overall pelvic health.
For those who suffer from uterine prolapse, pelvic floor support devices can be a great option for managing the condition. These devices work by providing added support to the pelvic floor muscles, which can help reduce prolapse symptoms and improve quality of life.
Several types of pelvic floor support devices are available, including pessaries and support garments. Pessaries are small, flexible devices inserted into the vagina to support the pelvic organs. Support garments, on the other hand, are designed to be worn like regular underwear and provide added support to the pelvic floor muscles.

Photo Credit: master1305
When used properly, pelvic floor support devices can provide a number of benefits for those with uterine prolapse. They can help to reduce discomfort and pain, improve bladder and bowel function, and improve overall quality of life. However, it’s important to remember that these devices are not a cure for prolapse and should be used with other treatment options, such as pelvic floor exercise and physical therapy.
Pelvic floor assessment is a crucial tool for identifying uterine prolapse and other pelvic floor disorders. It involves a physical examination of the pelvic floor muscles and may also include imaging tests, such as ultrasound, MRI, or X-ray studies. Pelvic floor assessment can help diagnose the severity of the prolapse and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Physical examination is the most common method used for pelvic floor assessment. This involves an internal examination of the pelvic floor muscles while the patient is lying down. The examiner will assess the strength and tone of the muscles, as well as the degree of descent of the pelvic organs. A gynecologist or urogynecologist usually performs the examination.
In some cases, imaging tests may also be used to assess the pelvic floor muscles. Ultrasound, MRI, and X-rays are all useful tools for evaluating the anatomy and function of the pelvic floor. These tests can help identify the underlying cause of the prolapse and determine the best course of treatment.
Pelvic floor assessment is an important part of maintaining pelvic floor health, but it is just one part of the equation. Pelvic floor training and awareness are also essential for preventing prolapse and other pelvic floor disorders. Regular exercise of the pelvic floor muscles can help strengthen the muscles and prevent them from becoming weak or lax. It is also important to be aware of the factors that can contribute to pelvic organ descent, such as pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and obesity.
Pelvic floor awareness refers to an understanding of the anatomy and function of the pelvic floor muscles, and the factors that can impact their strength and support. By promoting pelvic floor awareness, individuals can take steps to prevent uterine prolapse and maintain optimal pelvic health.
Pelvic organ support is crucial to maintaining the position and function of organs such as the uterus, bladder, and rectum. When the pelvic floor muscles weaken or become damaged, the organs can descend or bulge, leading to conditions like uterine prolapse.
Factors that may impact pelvic organ support and displacement include pregnancy and childbirth, menopause, obesity, chronic coughing, and heavy lifting. By being aware of these factors and taking steps to minimize their impact, individuals can promote healthy pelvic organ support and reduce their risk of developing uterine prolapse.
Pelvic floor dysfunction can lead to a range of complications and discomfort, including urinary and fecal incontinence, chronic pain, and sexual dysfunction. By becoming familiar with the symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction and seeking treatment when necessary, individuals can prevent these complications and improve their quality of life.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the pelvic floor muscles is an important aspect of pelvic floor awareness. The pelvic floor muscles stretch like a hammock from the pubic bone to the tailbone, supporting the pelvic organs and helping to control urinary and bowel function. By learning about the pelvic floor muscles and how to keep them strong, individuals can promote healthy pelvic organ support and reduce their risk of developing uterine prolapse.
Uterine prolapse is the sliding or descent of the uterus from its normal position in the pelvis down into the vagina. This can happen when the muscles and ligaments that support the uterus become weak or damaged.
The symptoms of uterine prolapse can vary, but may include a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the pelvis, difficulty urinating or having a bowel movement, and pain during sex. In severe cases, the uterus may protrude from the vagina.
Uterine prolapse can be caused by a number of factors, including pregnancy and childbirth, menopause, obesity, and chronic coughing or straining. Other factors that can contribute to pelvic floor weakness, such as aging and genetics, may also play a role.
Uterine prolapse can be diagnosed through a physical examination, which may include a pelvic exam and imaging tests such as an ultrasound or MRI. A pelvic floor assessment may also be performed to determine the strength and function of the pelvic floor muscles.