Tendinopathy is a condition that affects the tendons, which are the tough, fibrous tissues that attach muscle to bone. Unlike tendonitis, which refers specifically to inflammation of the tendons, tendinopathy is a more general term that encompasses a range of tendon-related issues.
When tendons are subjected to repetitive stress or overuse, they can become damaged and may not function properly. This can lead to pain, swelling, and weakness in the affected area. It can occur in any body part where tendons are present, but it is most common in the shoulders, elbows, knees, and heels.
There are two main types of tendinopathy: insertional and mid-substance. Insertional affects the area where the tendon attaches to the bone, while mid-substance occurs within the tendon itself. The symptoms and treatment for these two types can vary.
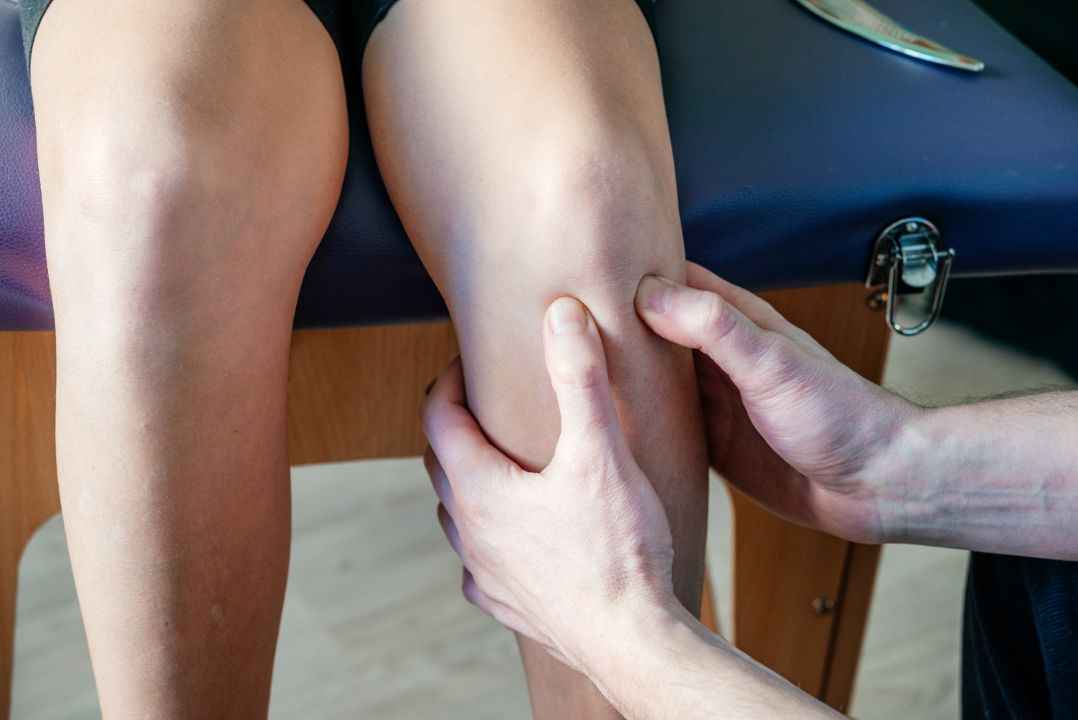
Photo Credit: Marinesea, Envato
Several factors can contribute to the development of this condition, including age, gender, underlying medical conditions, and lifestyle factors like physical activity and nutrition. The exact mechanisms by which tendon disorder develops are not yet fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of mechanical, genetic, and environmental factors.
Tendon damage is often characterised by gradual pain and discomfort in the affected area. The symptoms may worsen over time, eventually leading to a significant loss of function.
The most common symptoms of tendinopathy include:
It is important to note that not all cases of this condition present with the same symptoms, and some individuals may experience additional or different symptoms. If you suspect you may be experiencing tendinopathy, seek medical attention promptly to receive an accurate diagnosis and treatment.

Photo Credit: seleznev_photos, Envato
Tendon disorder is a condition that can develop due to a variety of causes and risk factors. While some causes are intrinsic, related to the individual’s age and gender, others are irrelevant, related to the type and intensity of physical activity.
Preventing tendinopathy is crucial to avoiding the pain and discomfort associated with the condition. You can reduce your risk of developing this condition by taking some simple steps.
Before engaging in any physical activity, it is important to warm up and stretch properly. This helps to prepare your muscles and tendons for the activity, reducing the risk of injury. Start with a gentle warm-up, such as walking or light jogging, and then perform stretches that target the muscles and tendons you will use during the activity.
Overuse of your muscles and tendons can lead to tendinopathy. Rest periods throughout the activity can help prevent overuse and reduce your risk of developing tendinopathy. Listen to your body and take breaks as needed.

Photo Credit: valeriygoncharukphoto, Envato
If you are at risk of developing tendinopathy, modifying your physical activities can help to reduce your risk. For example, if you are a runner, consider reducing your mileage or incorporating cross-training activities that are less stressful on your tendons.
Using proper technique during physical activity can also help to prevent tendon injury. Whether lifting weights or performing a specific sport, ensure that you use the correct form to avoid putting excess strain on your tendons.
Various treatment options are available for tendinopathy, ranging from conservative approaches to more advanced interventions. The treatment choice will depend on the severity of the condition, the extent of the tendon damage, and the individual’s overall health and medical history.
Conservative approaches are commonly used in treating tendinopathy. Physical therapy, for example, can help reduce pain and inflammation, improve range of motion, and strengthen the affected tendon. Depending on the extent of the injury, physical therapy may involve exercises to improve flexibility and strengthen the supporting muscles, as well as manual therapy techniques like massage and stretching.
Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and analgesics may also be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation. However, these medications may have side effects and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Alternative therapies like acupuncture, massage therapy, and chiropractic care also manage pain and improve functionality. While these therapies may not be supported by scientific evidence, some individuals find them effective in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.
More advanced interventions may be considered if conservative approaches do not provide sufficient relief. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT), for example, uses high-energy shockwaves to stimulate healing and tissue regeneration. Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) therapy, on the other hand, involves injecting a concentration of platelets into the damaged tendon to promote healing.
In more severe cases, surgery may be required. The type of surgery will depend on the tendon damage’s location, extent, and severity. Procedures like tendon debridement, which involves removing damaged tissue, and tendon transfer, which involves using a healthy tendon to replace a damaged one, may be performed.
It is important to note that while advanced interventions may provide relief, they also carry risks and may require longer recovery times. As such, they should only be considered after careful evaluation and consultation with a healthcare professional.
Rehabilitation and exercises are important components of managing tendinopathy. Treatment may involve progressive loading exercises to help strengthen the affected tendon, improve flexibility, and promote recovery. The goal of rehabilitation is to reduce pain and inflammation while restoring mobility and functionality.
Physical therapy is often the first line of treatment for tendinopathy. A physical therapist will prescribe exercises that target the affected tendon, along with other interventions such as massage, heat or cold therapy, and electrical stimulation. By working with a physical therapist, patients can benefit from a customised exercise program that considers their needs and abilities.
It is important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate type and level of exercise for each individual. Overexertion can worsen symptoms and delay healing.
In conclusion, living with tendinopathy can be challenging, but with proper management and ongoing self-care, individuals can reduce pain and maintain functionality. It is important to seek early intervention from a healthcare professional to prevent the condition from worsening.
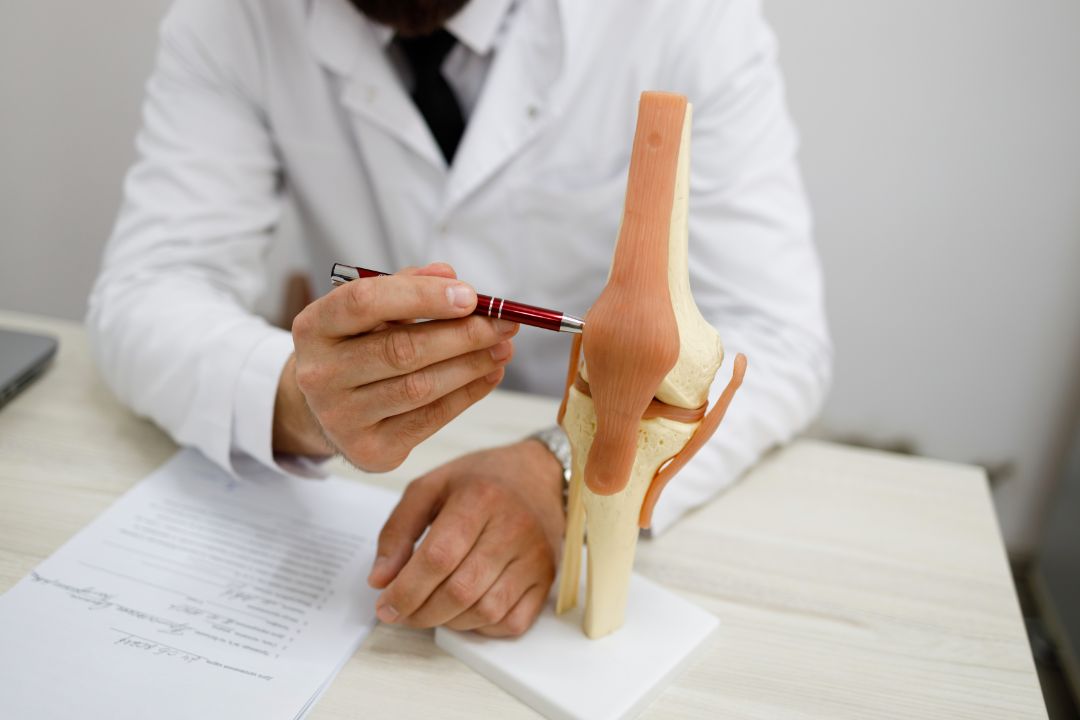
Photo Credit: borodai, Envato
Regular exercise and proper rehabilitation can also help strengthen the affected tendon and promote recovery. This may include specific exercises recommended by a physiotherapist or other healthcare professional and modifications to physical activities to reduce the risk of re-injury.
It is also crucial to practice prevention strategies, including adequate rest periods, proper warm-up and stretching techniques, and modifications to physical activities as needed. This can help reduce the risk of developing this condition in the first place or prevent it from recurring.
Living with tendinopathy requires ongoing attention and management, but with the right approach, individuals can continue to lead active and fulfilling lives.
Tendinopathy is a condition that affects the tendons, causing pain and inflammation. It is often characterised by degeneration and weakening of the tendon tissue.
While tendinopathy, tendonitis, and tendon injuries all involve the tendons, tendinopathy refers to a broader category of tendon conditions, including chronic degeneration, while tendonitis specifically refers to tendon inflammation. Tendon injuries can be acute traumas or tears.
Common tendinopathy symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and weakness in the affected tendon. Individuals may also experience difficulty performing activities that involve the affected tendon.
Various factors, including repetitive or excessive use of the tendon, improper technique during physical activities, age-related degeneration, and certain medical conditions, can cause tendinopathy.
To prevent tendinopathy, it is important to engage in proper warm-up and stretching before physical activities, take regular rest breaks, gradually increase the intensity or duration of exercises, and maintain overall physical fitness.
Treatment options for tendinopathy include physical therapy, medication, alternative therapies such as acupuncture or ultrasound, and surgery may be considered in severe cases.
Rehabilitation and exercises play a crucial role in managing tendinopathy. They can help improve the strength and flexibility of the affected tendon, promote healing, and prevent future injuries.