Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy is a condition that affects the shoulder joint. It is characterised by the formation of calcium deposits in the rotator cuff tendons, causing pain and discomfort for the patient.
Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy can be a challenging condition to manage, but it can be effectively treated with the right knowledge and approach. The following paragraphs will provide a comprehensive overview of this condition, including its underlying mechanisms and the latest treatment options available.
Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy, also known as calcific tendonitis, is a medical condition that occurs when calcium deposits build up in the shoulder joint. It affects the rotator cuff tendons, which stabilise the shoulder and enable proper movement.
Calcific tendonitis is a common cause of shoulder pain and tends to affect individuals over 30 years old. In some cases, the calcium deposits may dissipate on their own, but in other cases, they may cause chronic pain and discomfort.

Photo Credit: leungchopan, Envato
“Calcific tendonitis is a condition that can cause significant pain and disability, but it can usually be managed effectively with conservative treatments,” says Dr. John Smith, an orthopedic specialist at St. Mary’s Hospital.
The calcium deposits can cause irritation and inflammation of the tendons, leading to stiffness and loss of range of motion. The condition can worsen without proper treatment, making it increasingly difficult to perform everyday activities.
The exact cause of calcific tendonitis is not yet fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of factors such as age, trauma to the shoulder, genetics, and repetitive motion. Over time, these factors can lead to the formation of tiny calcium deposits in the shoulder joint.
As these deposits grow in size, they can irritate the surrounding tendons and cause inflammation. This inflammation can result in pain and discomfort in the shoulder, especially when it is being used to lift or move heavy objects or engage in repetitive activities like throwing a ball or swimming.
Calcific tendonitis can occur in any of the tendons in the shoulder, but it most commonly affects the rotator cuff tendons. These tendons lift the shoulder and rotate the arm, making them particularly susceptible to injury and inflammation.
Several factors may increase an individual’s risk of developing rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy. These include:
If you are experiencing rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy symptoms, seeking proper medical attention is essential. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and help you return to your normal activities without pain or discomfort.
Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy is a condition that causes calcium deposits to form in the tendons of the rotator cuff in the shoulder. This can lead to a variety of unpleasant symptoms that can affect daily activities and quality of life.
Common symptoms associated with rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy include:
It is important to note that not everyone with rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy experiences all of these symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, speaking with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment is important.

Photo Credit: microgen, Envato
Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy can occur due to various factors, including age, repetitive motion, and other risk factors. Here are some of the potential causes of this condition:
While these factors can increase the likelihood of developing rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy, it is not always possible to determine the exact cause.
If you are experiencing persistent shoulder pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion, your doctor may suspect rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy. To diagnose this condition, your doctor will perform a physical examination and may order imaging tests or other diagnostic procedures.
During a physical examination, your doctor will assess your shoulder for signs of inflammation and tenderness. They may also ask you to perform various arm and shoulder movements to evaluate your range of motion and pinpoint the location of your pain. Your doctor may also use imaging tests to look for calcium deposits in your shoulder joint.
Imaging tests allow doctors to get a better look at your shoulder joint and identify any calcific deposits. Your doctor may order an X-ray, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. X-rays are particularly useful for detecting calcific deposits, while MRI scans provide detailed images of the soft tissues in and around the shoulder joint.
Sometimes, your doctor may recommend additional tests to confirm a rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy diagnosis. For example, they may use a needle to aspirate fluid from your shoulder joint for lab testing. This fluid can provide valuable information about the underlying cause of your symptoms.
Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy is a condition that can cause significant discomfort and mobility issues. Fortunately, there are several treatment options available to manage its symptoms. Treatment plans may vary depending on the severity of the condition, the location of the calcium deposits, and the individual’s overall health. Before beginning treatment, it is important to properly diagnose the condition, and work with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action.
In many cases, conservative treatments are the first line of defense against rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy. These treatments may include:

Photo Credit: svitnalah, Envato
In some cases, healthcare professionals may recommend medications to manage rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy symptoms. These may include:
In rare cases, surgery may be required to remove the calcium deposits and repair the affected tendons. This type of intervention may be necessary when individuals have significant pain and reduced mobility, or if conservative treatments and medications have been unsuccessful.
It is important to note that surgery is typically considered a last resort, and healthcare professionals will typically explore other options before recommending this type of intervention.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation can play an important role in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy. A physical therapist can work with individuals to regain range of motion, improve strength and flexibility, and develop an exercise program to prevent future injuries.
Recovery times can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment utilized. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized treatment plan that meets your specific needs and goals.
In addition to medical treatment, specific exercises and stretches can help manage and alleviate rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy symptoms. Here are some of the most effective exercises to consider:
This stretch can help loosen up your shoulder joint and improve mobility. To perform the pendulum stretch, follow these steps:
Strengthening the muscles that support the rotator cuff can help alleviate symptoms of calcific tendinopathy. Try this external rotation exercise:
Improving your shoulder blade (scapula) positioning can help reduce pain and improve function in your shoulder joint. Give this scapular squeeze exercise a try:
Note: It’s essential to consult with a qualified physiotherapist or healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have a known medical condition or injury.
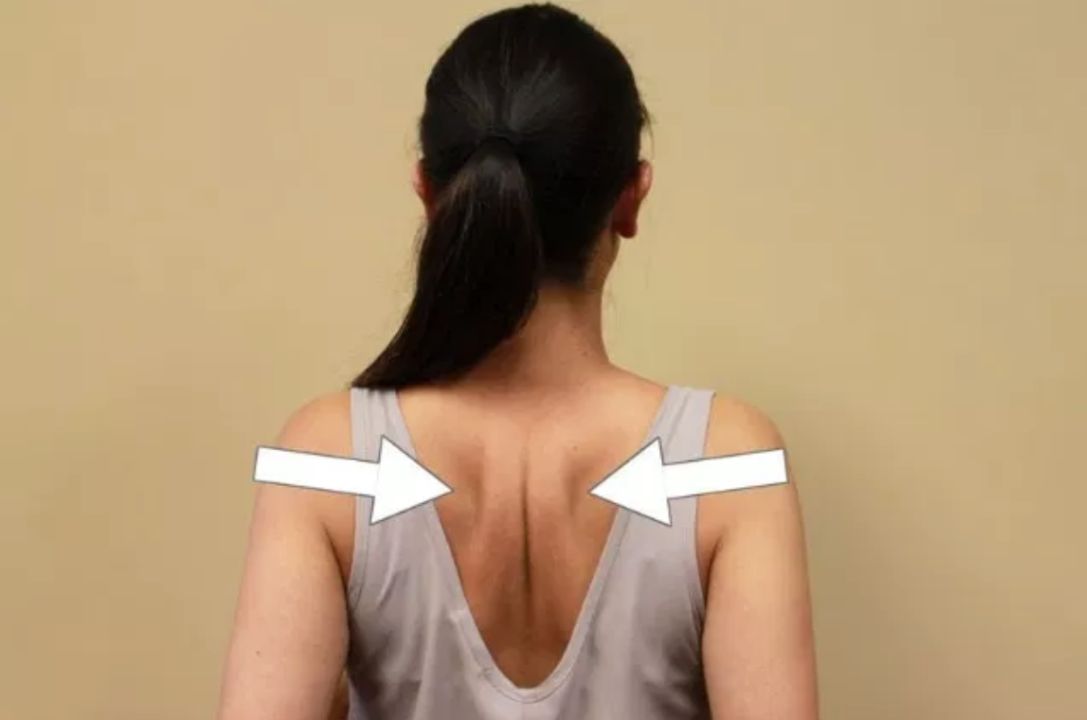
Photo Credit: Park Sports Physical Therapy
These exercises can be done at home but should be performed under the guidance of a qualified physiotherapist or healthcare professional. Doing these exercises regularly can significantly improve the symptoms of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy. However, be sure not to push yourself too hard, as this can further damage the shoulder joint.
Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy can be a painful and frustrating condition, and it’s natural to have questions about it. Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand this condition and its treatment.
Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy is a condition in which calcium deposits build up in the tendons of the rotator cuff, causing pain and stiffness in the shoulder joint.
The most common rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy symptoms include shoulder pain, limited range of motion, and stiffness. The pain may be worse at night or when reaching overhead, and can also be associated with weakness in the affected arm.
The exact cause of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy is not known, but it is thought to be related to a combination of factors including age, repetitive motion, and other risk factors such as diabetes or thyroid disease.
Diagnosis of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy typically involves a physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or an MRI, and sometimes other diagnostic procedures such as ultrasound-guided needle aspiration or arthroscopy.
Treatment for rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy can include conservative measures such as rest, ice, physical therapy, and medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Yes, specific exercises and stretches can be beneficial in managing and alleviating symptoms associated with rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy. Your healthcare provider or physical therapist can recommend exercises tailored to your needs.
In some cases, calcific deposits can eventually dissolve on their own, but in other cases, they may persist and cause ongoing symptoms. However, many people can manage their symptoms and maintain good shoulder function successfully with appropriate treatment and management.