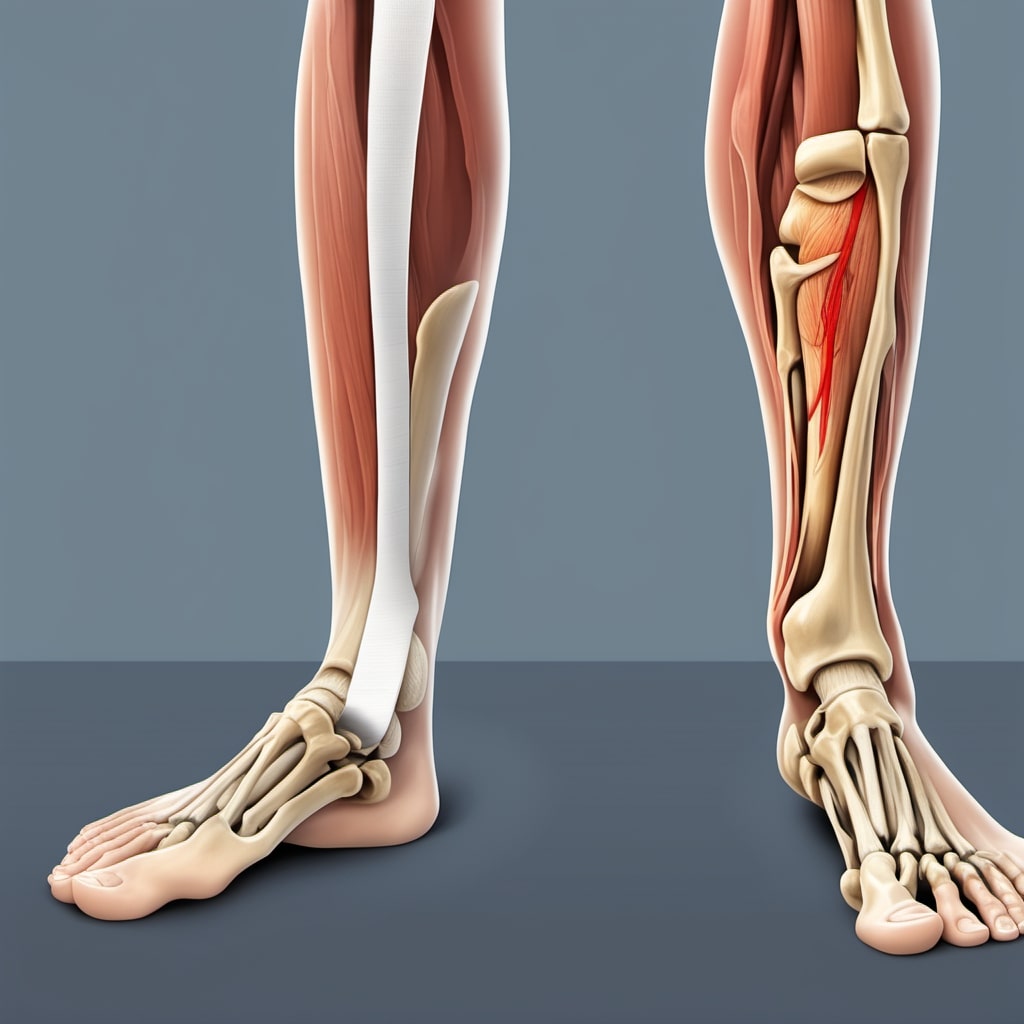
Anterior shin splints, also known as anterior tibial stress syndrome, refer to lower leg pain in the front outside the shin bone.
Injury associated with exercise-induced leg pain is a frequent issue among athletes and those who regularly participate in physical activity.
Anterior shin splints, also known as anterior tibial stress syndrome, refer to the pain and inflammation on the lower leg’s front (anterior) part, specifically the shinbone (tibia). Unlike other shin splints, anterior shin splints occur outside the shinbone and can be felt as dull, aching pain.
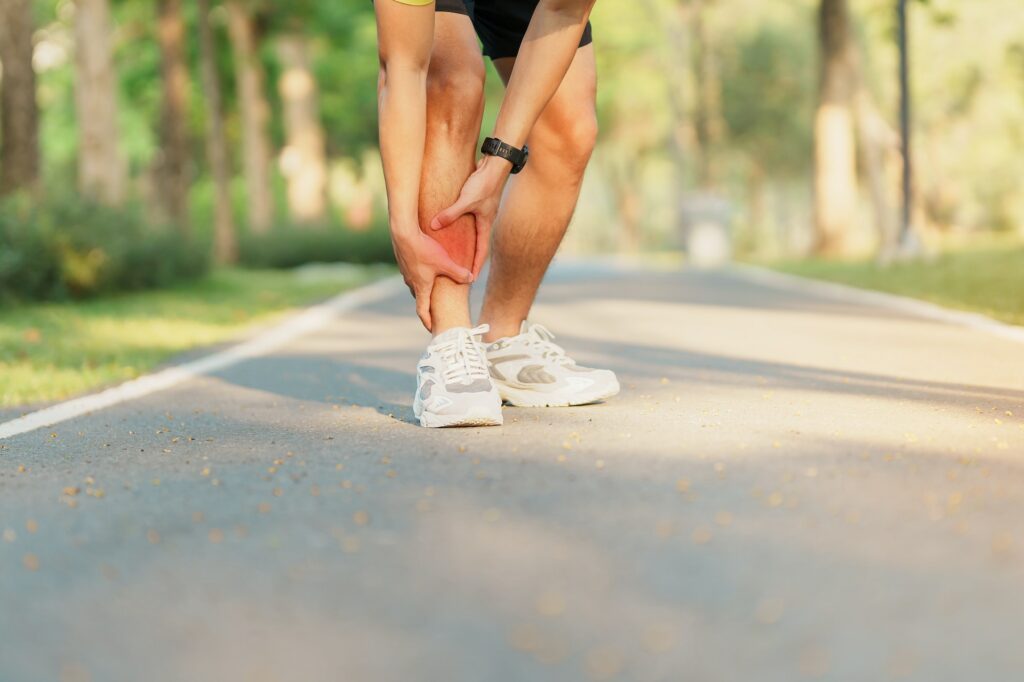

The cause of anterior shin splints is repetitive stress on the shinbone and the connective tissue surrounding it, resulting from activities such as running, jumping, or dancing. This repetitive stress can lead to microtears in the muscle tissue and inflammation of the connective tissue, resulting in pain and discomfort.
Diagnosing anterior shin splints typically involves a physical examination and medical history. X-rays and other imaging tests may be used to rule out other possible causes of lower leg pain, such as stress fractures or tendonitis.
Anterior shin splints differ from other types in location and symptoms. Anterior shin splints occur on the lower leg’s front (anterior) part and can be felt as a dull, aching pain. Posterior shin splints occur on the lower leg’s inside (medial) part and can be felt as a sharp, stabbing pain. Medial tibial stress syndrome refers to pain along the entire length of the shinbone and is often associated with swelling.
While all types of shin splints can be caused by repetitive stress on the shinbone, the location and severity of pain can vary. It is important to correctly diagnose the type of shin splints to determine the most effective treatment.
If you have anterior shin splints, you typically experience pain in the front of your lower leg, between your knee and ankle. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent.
Other common symptoms of anterior shin splints include:
You may also experience small bumps or lumps along your shin bone in severe cases. This is a sign that your anterior tibial muscle has been pulled away from the bone, which can cause significant pain and discomfort.
The duration of the symptoms of anterior shin splints can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Sometimes, the symptoms may disappear within a few days with rest and proper treatment. However, more severe injuries can take several weeks or even months to heal fully.
Repetitive stress on the muscles and tendons of the lower leg typically causes anterior shin splints. Specifically, stress on the tibia bone and the muscles and tendons that attach to it often cause them to deteriorate. Several different factors can cause this stress.

Overuse is the most common cause of anterior shin splints. This occurs when the muscles and tendons of the lower leg are subjected to repetitive stress over a prolonged period. This is often seen in runners and other athletes who engage in activities that require a great deal of running, jumping, or other high-impact movements.
Wearing improper footwear is another common cause of anterior shin splints. Shoes that do not provide adequate support or cushioning can place added stress on the muscles and tendons of the lower leg, leading to injury over time. This is particularly common in athletes who wear worn-out shoes or shoes that are designed for something other than the specific activity they are performing.
Various anatomical factors can also contribute to developing anterior shin splints. For example, people with flat feet or high arches may be more prone to developing this condition, as these foot types can place added stress on the lower leg muscles and tendons. Similarly, people with tight calf muscles or weak shin muscles may also be at increased risk for anterior shin splints.
Regardless of the specific cause of anterior shin splints, it is important to address the issue promptly to avoid further injury and promote proper healing.
While anyone can develop anterior shin splints, certain factors can increase your risk of experiencing this condition.
Overuse is a common cause of anterior shin splints and can occur when you increase the frequency or intensity of your workouts too quickly. To prevent anterior shin splints from occurring, gradually increasing your activity level over time is important.
People with flat feet are more prone to experiencing anterior shin splints. This is because their feet do not properly absorb shock, which can lead to increased stress on the lower leg. If you have flat feet, wearing shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning is important.
Imbalances in the lower leg muscles can also increase your risk of developing anterior shin splints. Certain muscles can become overworked and tired, while others must be more utilised. To prevent muscle imbalances, it is important to perform exercises targeting all of the lower leg muscles.
Running with poor form can increase your risk of developing anterior shin splints. The improper form can stress lower leg muscles and bones. To prevent the injury caused by poor running form, it is important to work with a coach or trainer to correct your form.
Certain conditions, such as anterior tibial stress syndrome, can increase your risk of developing anterior shin splints. If you have a pre-existing condition affecting your lower legs, taking proper precautions to prevent further injury is important.
By understanding the risk factors associated with anterior shin splints, you can take steps to prevent this condition from occurring.
If you suspect you have anterior shin splints, seeing a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment is important. They will perform a physical exam and inquire about your symptoms, medical history, and activities that may contribute to the injury. They may also order imaging tests such as X-rays and MRIs to rule out other potential causes of lower leg pain.
Initial treatment for the injury typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). This will help reduce inflammation and pain in the affected area. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen may also be recommended.
If the symptoms persist, your healthcare professional may suggest physical therapy to help restore flexibility and strength to the affected area. They may also recommend orthotics or shoe inserts to provide support and reduce stress on the shins.
Surgery may be necessary in severe cases to correct any structural issues in the lower leg.
While undergoing treatment, it’s important to manage the symptoms of anterior shin splints to prevent further damage. This may involve modifying your activities to reduce stress on the shins, such as avoiding high-impact exercises and gradually increasing your training intensity. It’s also important to wear appropriate footwear and ensure they fit properly.
Stretching and foam rolling may also help alleviate tightness in the lower leg muscles. Your healthcare professional or physical therapist can guide specific exercises to incorporate into your routine.
Most people with anterior shin splints can fully recover and return to regular activities with proper diagnosis, treatment, and management.
Recovery exercises are essential to the treatment process for anterior shin splints. By helping to strengthen the muscles in the lower leg, they can help prevent the condition from recurring.
Calf stretches are an important part of recovery exercise for those with anterior shin splints. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and lean forward to perform a calf stretch. Keep your heels firmly on the ground and hold the stretch for 30 seconds. Repeat this stretch three times.
To perform toe raises, stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Slowly lift your heels off the ground, rising onto the balls of your feet. Hold the position for a few seconds before slowly lowering your heels back to the ground. Repeat this exercise for 10 repetitions.
Ankle rotations can help strengthen the lower leg muscles and improve flexibility. To perform ankle rotations, sit down and rotate your ankle in a circular motion. Perform 10 rotations in one direction before switching to the opposite direction.
Resistance band exercises can be a helpful way to strengthen the muscles in the lower leg. Place a resistance band around your ankles and walk forward straight. Repeat this exercise for 10 repetitions.

It’s important to perform recovery exercises for injuries consistently and correctly. Stop immediately and consult your healthcare provider if you experience any pain or discomfort while performing these exercises.
Prevention is always better than cure, especially regarding anterior shin splints. Here are some practical steps you can take to minimise your risk of developing this painful condition:
Wearing the wrong type of shoes can increase your chances of developing anterior shin splints. Ensure you invest in supportive footwear appropriate for your activity level. High-impact exercises require shoes with extra cushioning, whereas low-impact activities like yoga require less support.
Overuse is a common cause of anterior shin splints. Make sure you gradually increase the intensity and duration of your exercise routine to avoid putting too much strain on your lower legs. Listen to your body and take breaks when necessary.
Warming up before exercising and cooling down afterwards can help prevent anterior shin splints. Start with some light stretching to warm your muscles up before you begin your workout, and finish with some gentle stretches to help your muscles recover.
Weaker leg muscles can increase your risk of developing anterior shin splints. Incorporate strength training exercises into your workout routine to help build up the muscles in your lower legs and make them more resilient to injury.
Improper technique can put undue strain on your lower legs, leading to anterior shin splints. Ensure you use the correct form when performing exercises and seek professional guidance if necessary.
By taking these steps to prevent injuries, you can ensure that you stay healthy and pain-free while pursuing your fitness goals.