Popliteus syndrome is a condition primarily involving the popliteus muscle, which forms part of the complex structure at the rear of your knee joint. This particular muscle plays a significant role in unlocking and rotating your knee during certain movements such as running or deep knee flexion.
The syndrome arises when excessive strain or force is exerted on this muscle, possibly leading to muscle strains and tears in its fibres.
Cramps, discomfort and pain at the back of your leg, right down into your calf are some common markers. At times, popliteus tendonitis – inflammation of the popliteus tendon – may also be behind pain around the outer parts of your knee.
Popliteus Syndrome presents with characteristic symptoms such as pain at the back of the knee, swelling, limited range of motion, and decreased strength. Differential diagnosis is essential to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
The popliteus syndrome, also known as popliteus tendinitis, presents itself in unique ways. Here are some common symptoms:
A thorough examination of the affected knee is conducted to diagnose popliteus syndrome, followed by a review of the patient’s medical history to identify any potential causes or risk factors.
The diagnostic procedure may also include medical imaging tests like MRI or ultrasound to visualise the structure and condition of the knee joint and surrounding tissues.
Diagnosing Popliteus Syndrome starts with a thorough examination by your healthcare practitioner. They will inquire about the nature and onset of your knee pain along with other relevant details from your health history.
This is done using specific clinical tests to gauge your knee joint’s strength, flexibility, and stability – crucial factors in determining the treatment course.
Next comes diagnostic procedures like MRI or ultrasound imaging, which allow for an in-depth view into your knee joint and surrounding structures. Both these methods serve as powerful tools to distinguish Popliteus Syndrome from other conditions that may have similar symptoms.
Medical imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing knee pain associated with popliteus syndrome. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is commonly used to visualize the knee and detect musculoskeletal issues such as tears, fractures, or osteochondral defects that may be causing the pain.
It provides detailed information about the severity of a popliteus muscle tear and helps guide treatment decisions. Additionally, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) can be employed to identify any artery entrapment in Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome (PAES), which can cause similar symptoms to Popliteus syndrome.
The success of diagnosing and treating popliteus syndrome is often evaluated through outcome measures. These measures assess various aspects of the condition, such as pain reduction, improvement in knee function, and overall patient satisfaction.
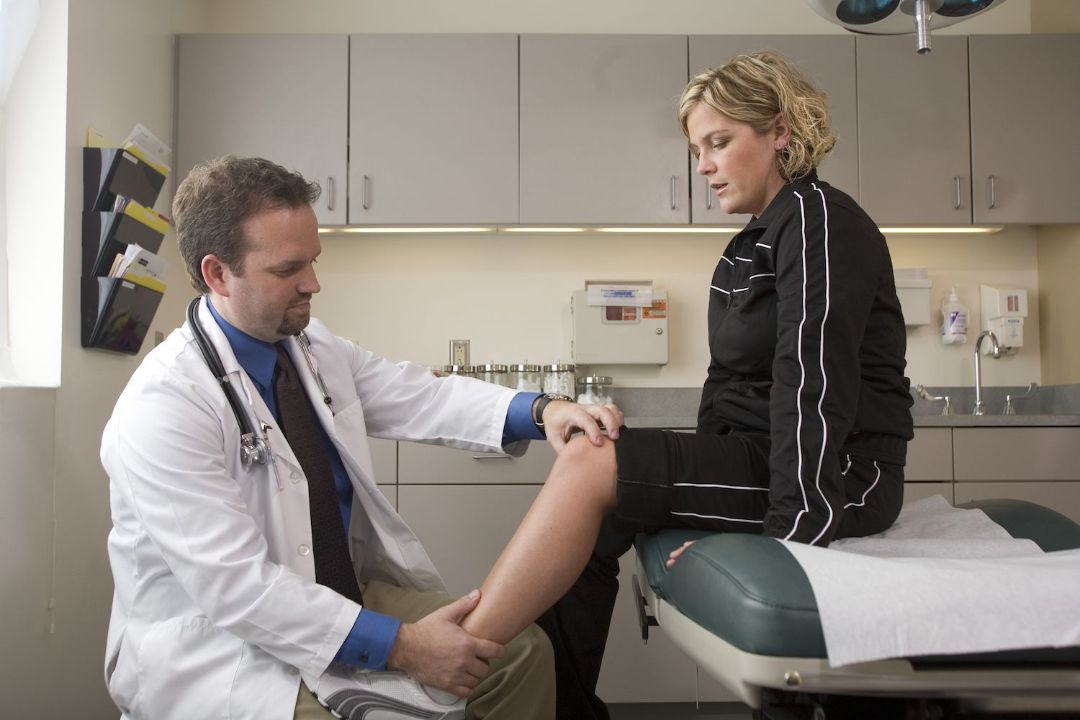
Photo Credit: Verywell Health
By tracking these outcomes, healthcare professionals can determine the effectiveness of different treatment approaches and make necessary adjustments to ensure the best possible results for individuals with popliteus syndrome.
It is important to note that further research is needed to establish standardized outcome measures and guidelines specific to this condition. However, by closely monitoring these outcomes, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans accordingly and help patients regain their comfort and mobility as quickly as possible.
Medical management for popliteus syndrome includes rest and activity modification, cold therapy and knee supports, as well as medication and massage to alleviate pain and promote healing.
Rest and activity modification are key components of managing Popliteus Syndrome to promote healing and reduce pain. By allowing the affected knee time to rest and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, individuals can give their bodies a chance to recover.
It is important to listen to your body and not push through the pain, as this can worsen the condition. Additionally, modifying daily activities may be necessary in order to prevent further strain on the knee joint.
Cold therapy and knee supports are important components of the medical management for Popliteus Syndrome. Cold therapy, which involves the application of ice or a cold pack to the affected area, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Applying ice for 10 minutes every hour after the injury is recommended in order to promote healing. Knee supports such as braces or compression sleeves can provide additional stability and support to the knee joint, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent further injury.
Medication and massage are two key components in the management of Popliteus Syndrome. Here’s how they can help:
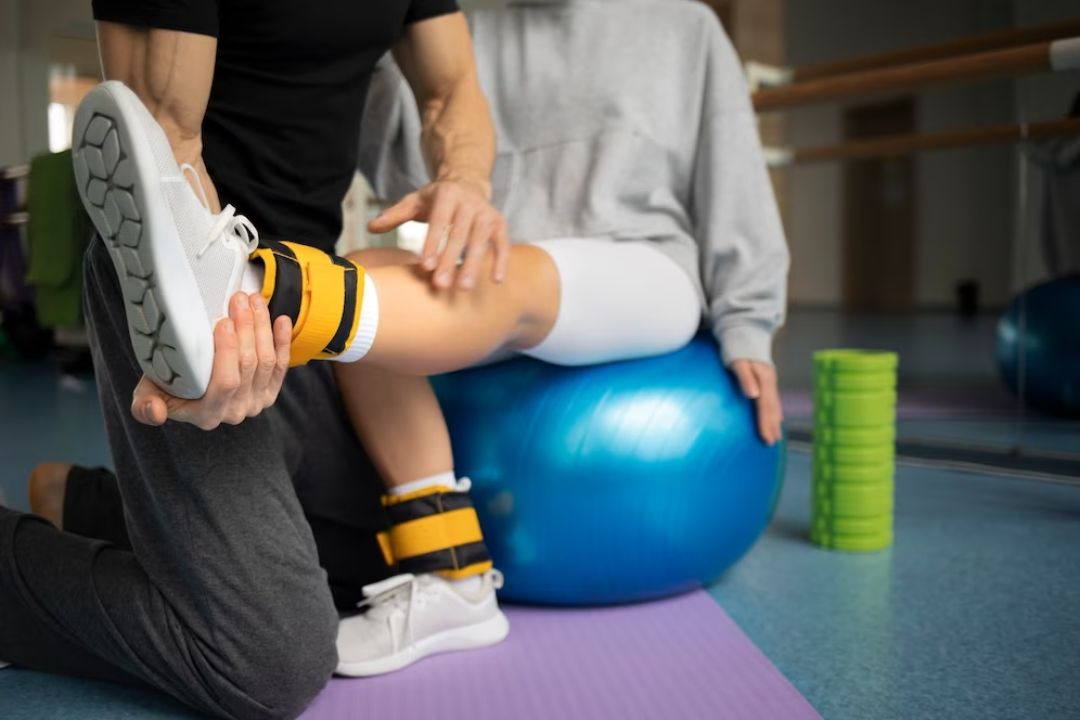

Photo Credit: Freepik
Physical therapy is crucial in managing popliteus syndrome, offering exercises and stretches to increase strength, improve range of motion, and reduce pain. Want to know more about how physical therapy can help? Keep reading!
Exercises and stretches are essential to managing popliteus syndrome and relieving knee pain. Try incorporating these exercises into your daily routine to improve flexibility, strengthen the muscles around the knee, and reduce discomfort:
To effectively manage Popliteus Syndrome, it is crucial to focus on increasing both strength and range of motion in the affected knee. Strengthening exercises targeting the popliteus muscle and surrounding muscles can help improve stability and support around the joint.
These exercises may include leg presses, squats, lunges, and calf raises. Specific stretching and flexibility exercises can help restore the full range of motion in the knee joint.
Regularly engaging in these exercises under the guidance of a physiotherapist can aid in reducing pain, improving function, and promoting overall recovery from Popliteus Syndrome.
Various treatment options can be explored to reduce pain associated with popliteus syndrome. Physical therapy is crucial in managing discomfort and improving overall knee function.
A physiotherapist may recommend specific exercises and stretches to target the popliteus muscle and surrounding structures, helping to alleviate pain and promote healing. Also, techniques such as cold therapy and massage can relieve inflammation and promote blood flow to the affected area.
Along with these interventions, medication such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to help manage pain in the short term. By following a personalised treatment plan focusing on reducing pain, individuals with popliteus syndrome can experience improved comfort and regain mobility more effectively.
Photo Credit: Stories, Freepik
Alternative therapies such as acupuncture and chiropractic treatment can be considered for relieving pain and promoting healing in cases of popliteus syndrome. Supportive resources like educational materials, online forums, and patient support groups can also provide valuable information and emotional support to individuals dealing with this condition.
Alternative therapies can be used alongside traditional treatments to help alleviate symptoms and promote healing for people with knee pain. Here are some alternative therapies that may provide relief:
Several supportive resources and educational materials are available to help individuals with knee pain. Online platforms, such as reputable websites and forums, provide information on knee anatomy, biomechanics, and common knee injuries like Popliteus Syndrome.
These resources offer explanations in simple terms, helping people understand their condition better. Additionally, educational videos and exercise tutorials are tailored specifically for individuals experiencing knee pain.
Physical therapy clinics often provide informational pamphlets or handouts that outline exercises and stretches to help manage knee pain. Furthermore, books written by medical professionals can serve as valuable references for those seeking a deeper understanding of their condition.
Common causes of Popliteus Syndrome include overuse or repetitive strain on the knee joint, improper knee alignment during activities, and muscle imbalances in the lower leg.
Symptoms of Popliteus Syndrome may include pain or discomfort on the inner side of the knee, swelling or inflammation in the affected area, difficulty walking or bending the knee, and a feeling of instability in the joint.
Popliteus Syndrome is typically diagnosed through physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans to rule out other potential conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
Treatment options for Popliteus Syndrome may include rest and avoiding activities that worsen symptoms, ice therapy to reduce inflammation, physical therapy exercises to strengthen muscles around the knee joint, orthotics or shoe inserts for proper alignment support, and surgical interventions that may be considered in more severe cases.