Pes Anserine Bursitis is a condition that results in significant knee pain. It’s a common issue, impacting thousands of Australians each year. Despite often being mistaken for typical knee arthritis due to similar symptoms, Pes Anserine Bursitis has distinct characteristics.
The condition involves inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac, located between the shinbone and the three tendons of the hamstring muscle on the inner side of the knee. This inflammation can lead to discomfort and often affects mobility.
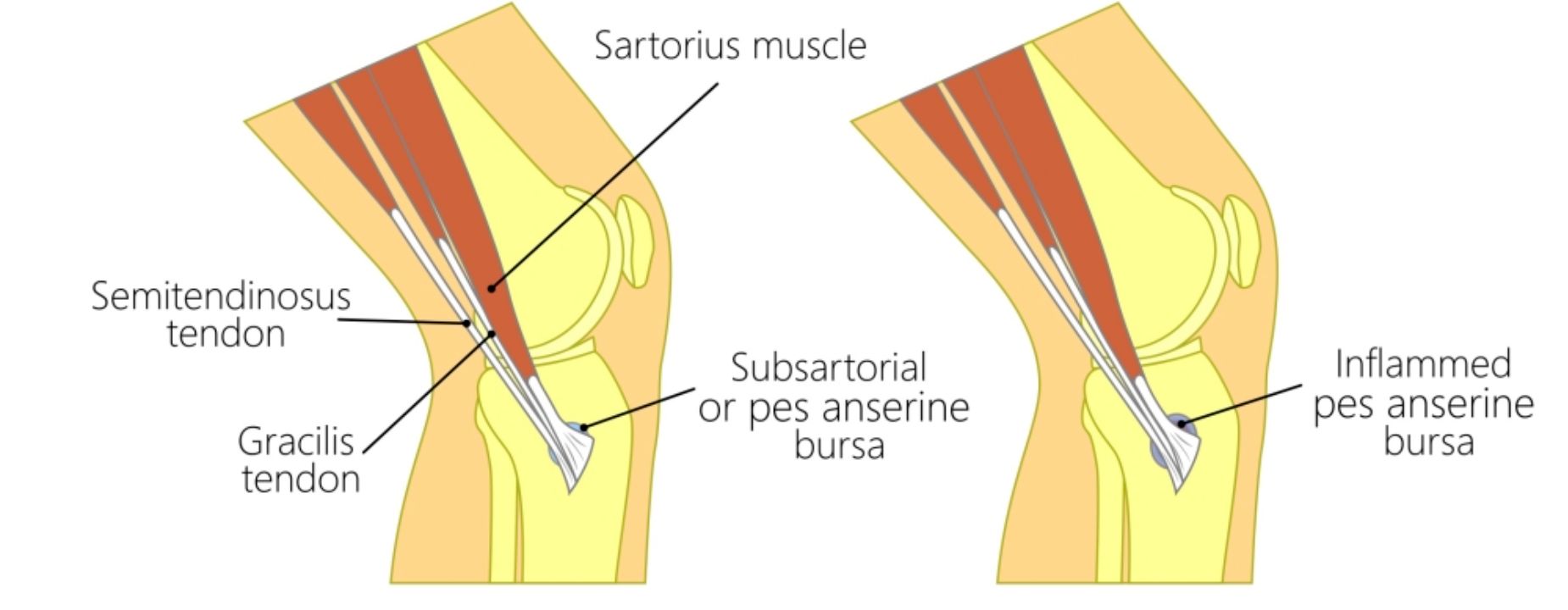
Photo Credit: Sport Doctor London
Pes Anserine Bursitis, a common cause of medial knee pain, often surfaces due to repetitive overuse or strain of the hamstring muscles. This tendon bursitis primarily affects athletes engaged in high-impact sports and individuals suffering from conditions such as knee arthritis.
The condition can also be triggered by meniscal cysts or even obesity, leading to an overburdening of the knee joint.
Symptoms are typically noticeable and distressing for those afflicted. Initial indications include sharp or dull shinbone pain that might worsen with certain activities like climbing stairs and stiffness near the inner part of your knee, which intensifies at night, causing sleep disturbances.
Some patients may notice a palpable mass corresponding to an inflamed bursa beneath their skin — this is another warning sign not to ignore. Over time you might experience weakness in your leg or find yourself dealing with a locking knee – further affecting mobility.
Moreover, inflammation can escalate into visible swelling around the area, adding another layer to discomfort levels.

Photo Credit: Drobotdean, Freepik
Pes Anserine Bursitis is a painful condition that affects the knee. It is caused by inflammation of the bursa, usually due to overuse or injury. The symptoms include knee pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Diagnosis involves physical examination and imaging tests such as MRI or ultrasound. Treatment options include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE therapy), anti-inflammatory medications like NSAIDs, and physical therapy for rehabilitation and strengthening exercises of affected muscles.
Seeking medical attention promptly can help in managing this condition effectively.
Pes anserine bursitis is commonly caused by overuse or repetitive stress on the knee joint, such as excessive running or jumping. It can also result from obesity, improper biomechanics, or trauma to the area.
Common symptoms of pes anserine bursitis include pain and tenderness on the inside of the knee, especially when climbing stairs or after prolonged activity. Swelling and warmth in the affected area may also occur.
A medical professional will typically diagnose pes anserine bursitis through a physical examination and evaluation of your medical history. They may also order imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans to rule out other possible causes for your knee pain.
Treatment for pes anserine bursitis usually involves a combination of rest, ice therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and physical therapy exercises to strengthen muscles around the knee joint. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgical intervention may be necessary
Pes anserine bursitis, if left untreated, can lead to chronic pain and limited mobility in the knee. It can also increase the risk of recurring knee injuries. Therefore, it’s important to seek medical attention if you’re experiencing persistent knee pain.
Yes, age can be a factor. Pes anserine bursitis is more common in adults over the age of 50, primarily because the risk of conditions that can lead to bursitis, such as osteoarthritis, increases with age.
While not all cases of pes anserine bursitis can be prevented, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly to keep your knee muscles strong, and avoiding activities that put excessive stress on your knees can help reduce your risk.
The recovery time for pes anserine bursitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of the treatment. With proper treatment, most people see improvement in their symptoms within a few weeks. However, it’s important to continue with the recommended physical therapy exercises even after the pain subsides to prevent recurrence.