Knee arthroscopy, a surgical procedure, lets doctors view the knee joint interior to diagnose and address issues like meniscus tears, ligament injuries, and patellar misalignment. The procedure involves small incisions, anesthesia, and an arthroscope – a flexible tube with a light and camera. It lets surgeons see the knee interior clearly and address identified issues accordingly.
Compared to traditional open surgery, knee arthroscopy has several benefits. It’s minimally invasive, requiring smaller incisions and causing less tissue damage. The result is a shorter recovery period and less post-operative discomfort.
Thanks to smaller incisions, the procedure leaves less visible scarring and reduces the chances of complications like keloids. Moreover, the risk of post-operative infection is lowered significantly.
Knee arthroscopy’s minimally invasive nature means less trauma to tissues and joints, resulting in faster healing and a quicker resumption of daily activities.
The arthroscope’s use allows surgeons a clear, magnified view of the knee joint’s interior, leading to a more precise diagnosis and treatment. Also, the procedure is versatile, serving as a comprehensive solution for various knee conditions.
Photo Credit: pressfoto, Freepik
In summary, knee arthroscopy, with its reduced scarring, quick recovery, and enhanced visualization, offers multiple advantages over traditional open surgery. By integrating advanced technology with skilled surgical techniques, knee arthroscopy delivers optimal outcomes and facilitates a faster return to active lifestyles.
During knee arthroscopy, the surgeon performs various procedures based on the specific knee problem. These procedures may include:
To prepare for knee arthroscopy, there are several steps you can take to ensure a smooth procedure and recovery:
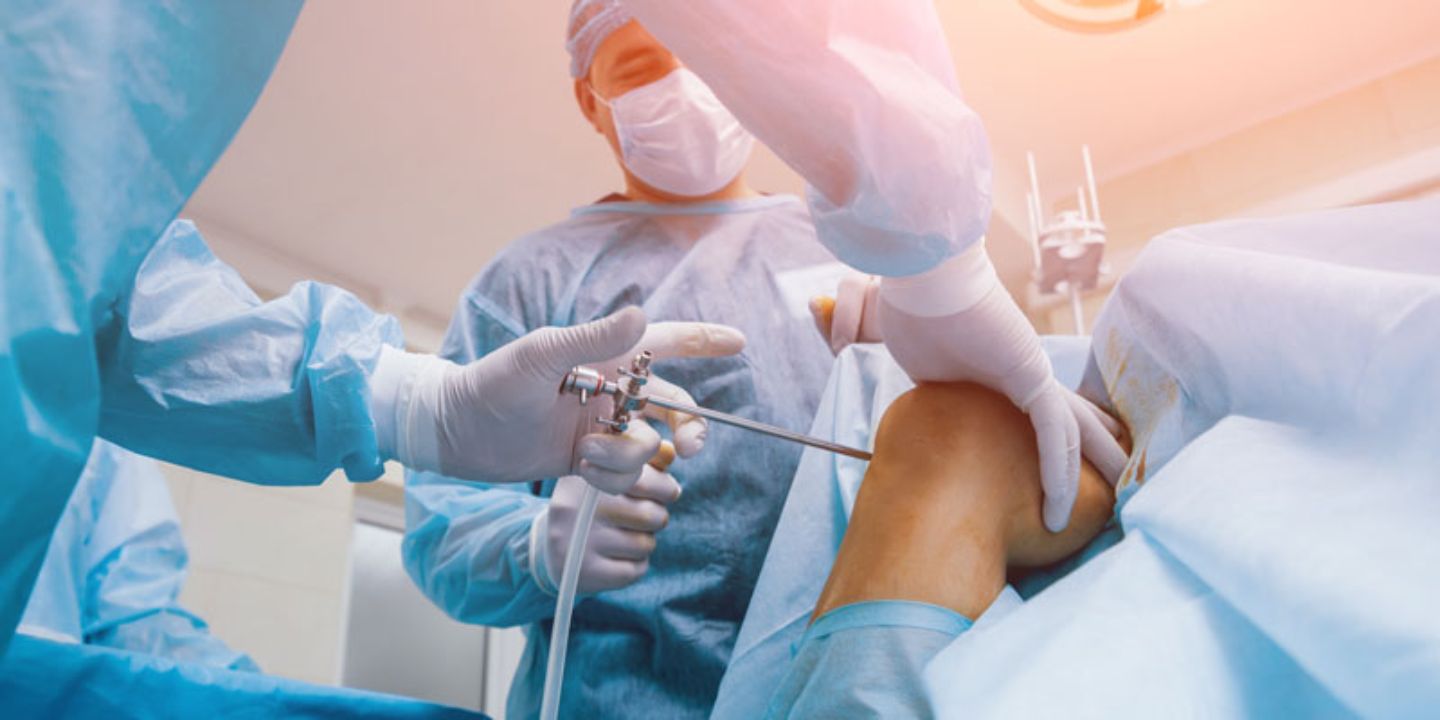
Photo Credit: Florida Orthapaedic Associates
During knee arthroscopy, you will be placed under anesthesia to ensure you are comfortable and pain-free throughout the procedure. The surgeon will make small incisions around the knee and insert the arthroscope and other specialised instruments. The arthroscope will transmit images to a video screen, allowing the surgeon to visualise the inside of the knee and perform necessary repairs or treatments. The length of the procedure can vary depending on the extent of the knee problem, but it typically ranges from 30 minutes to over an hour.
While knee arthroscopy is generally considered safe, there are potential risks and complications that you should be aware of. These risks include:
It is important to discuss these risks with your doctor before undergoing knee arthroscopy, as they can vary depending on individual circumstances.
After knee arthroscopy, following your doctor’s post-operative instructions is crucial to ensure proper healing and recovery. Here are some general tips for post-surgery care:
Photo Credit: tongstocker1987, Freepik
Post-arthroscopy, patients undergo physical therapy to regain strength and mobility in the knee. The intensity and duration of the rehabilitation vary with the specific treatment and individual health condition. The patients are advised to adhere to the surgeon’s guidelines on wound care, pain management, and avoiding activities during the healing period. The outcome is improved knee function, and patients can resume daily activities with proper post-operative care.
Recovery time from arthroscopic knee surgery varies depending on the individual and the extent of the knee damage. Generally, most people can return to office work within a week and more physical jobs within a few weeks. Full recovery, including regaining strength and mobility in the knee, can take several months. Individual experiences can vary, and it’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s advice on recovery and rehabilitation.
Knee arthroscopy is considered a minimally invasive procedure rather than major surgery. It involves small incisions through which a tiny camera (arthroscope) and surgical instruments are inserted to visualize and treat the knee joint’s interior. However, it is still a surgical procedure with potential risks and should be treated as such. It requires anesthesia and carries the risk of infection and blood clots, among other complications.
Walking after a knee arthroscopy will depend on the type of anesthesia used and the specific procedure performed. Some people might be able to walk immediately after the surgery with the help of crutches, while others might need to rest for a couple of days. Your doctor will give you specific instructions about weight-bearing and mobility based on your circumstances.
Knee arthroscopy is generally less painful than open surgery due to the smaller incisions. Pain is usually managed effectively with medications. Some discomfort or pain is expected after the procedure, but this usually improves within a few days. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for pain management, which may include over-the-counter medications, prescription pain relievers, and physical therapy.