Wrist tendinopathy is a condition caused by damage to the tendons surrounding the wrist joint. It is a common issue among athletes, musicians, and individuals who perform repetitive motions with their hands and wrists.
The resulting wrist pain can be debilitating and negatively impact daily activities.
Wrist tendinopathy is a condition that affects the tendons in the wrist, causing pain and discomfort. This condition is often associated with tendonitis, which is the inflammation of the tendons due to overuse or repetitive motions. It can also be caused by trauma, aging, and medical conditions that affect the tendons.
When one or more tendons in the wrist are damaged due to tendinopathy, it can result in pain and stiffness in the wrist. This can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks like typing or holding objects. The severity of the wrist distress can vary, from mild discomfort to severe pain that affects daily activities.
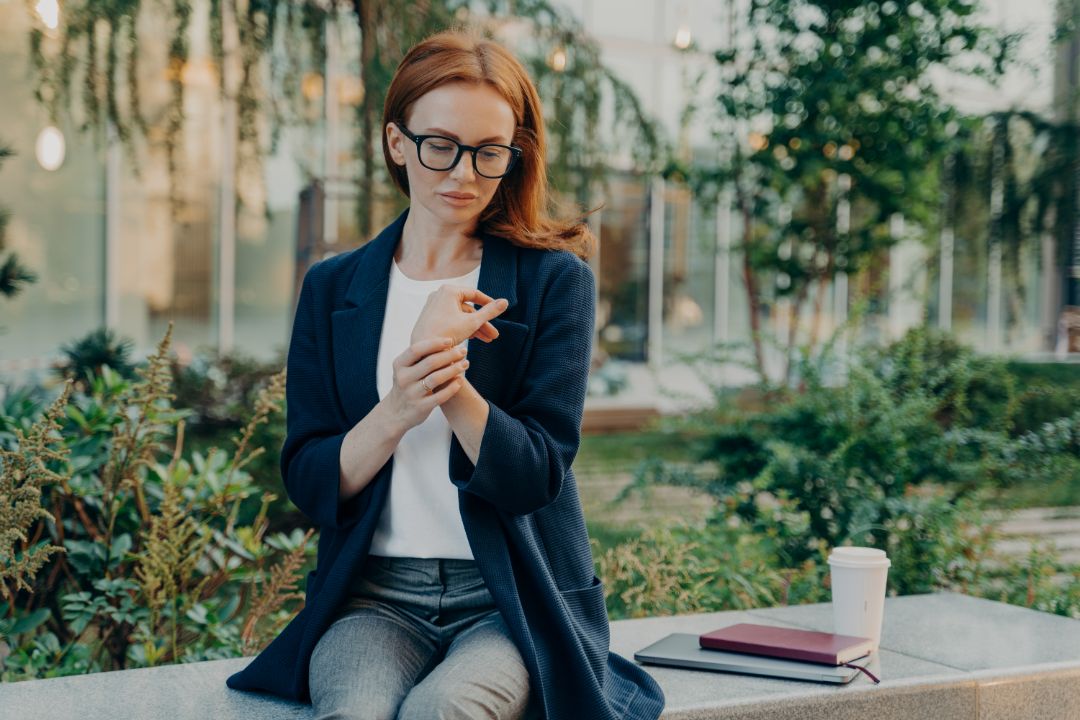

Photo Credit: StudioVK, Envato
While wrist tendinopathy can affect anyone, it is commonly seen in athletes and those who perform repetitive motions with their hands and wrists. This includes people who work on computers or do manual labor, such as construction workers or assembly line workers.
A variety of factors can cause wrist tendinopathy. The most common causes include:
It’s important to note that combining these factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. For example, someone who engages in repetitive wrist motions at work and plays sports in their free time may be more at risk than someone not exposed to these factors.
Wrist tendinopathy is characterised by various symptoms that can cause discomfort and hinder daily activities. The severity of symptoms varies based on the extent of the injury.
Pain is the most common symptom of wrist tendinopathy. The pain is usually sharp and sudden and may increase with activities requiring repetitive wrist motion or gripping. The pain may also occur at rest and worsen with pressure on the affected tendon.
Stiffness is another common symptom of wrist tendinopathy. The stiffness can make it difficult to move the wrist freely and may occur after periods of rest or prolonged inactivity.
Swelling in the affected area is another symptom of wrist tendinopathy. The swelling can make the wrist appear puffy and inflamed. It can occur along the path of the affected tendon.
It can restrict the wrist’s range of motion, making it difficult to perform daily activities that require wrist movement. This limited range of motion can result from stiffness, pain, or swelling in the affected area.
If you experience any of these symptoms, seeking medical attention is crucial. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and potentially leading to chronic pain and disability.
Diagnosing wrist tendinopathy usually involves a physical examination and a discussion of symptoms and medical history. The doctor may inquire about the patient’s daily activities contributing to wrist pain, such as repetitive motions or overuse. They may also ask about any recent trauma to the wrist or hand.
The doctor may perform various physical tests to assess the wrist’s range of motion, strength, and sensitivity. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or an MRI, may also be ordered to rule out other potential causes of wrist pain, such as arthritis or a fracture.
Sometimes, the doctor may refer the patient to a specialist for further evaluation and treatment. This may include an orthopedic surgeon or a hand specialist with the expertise to perform more complex diagnostic tests or surgical interventions if necessary.
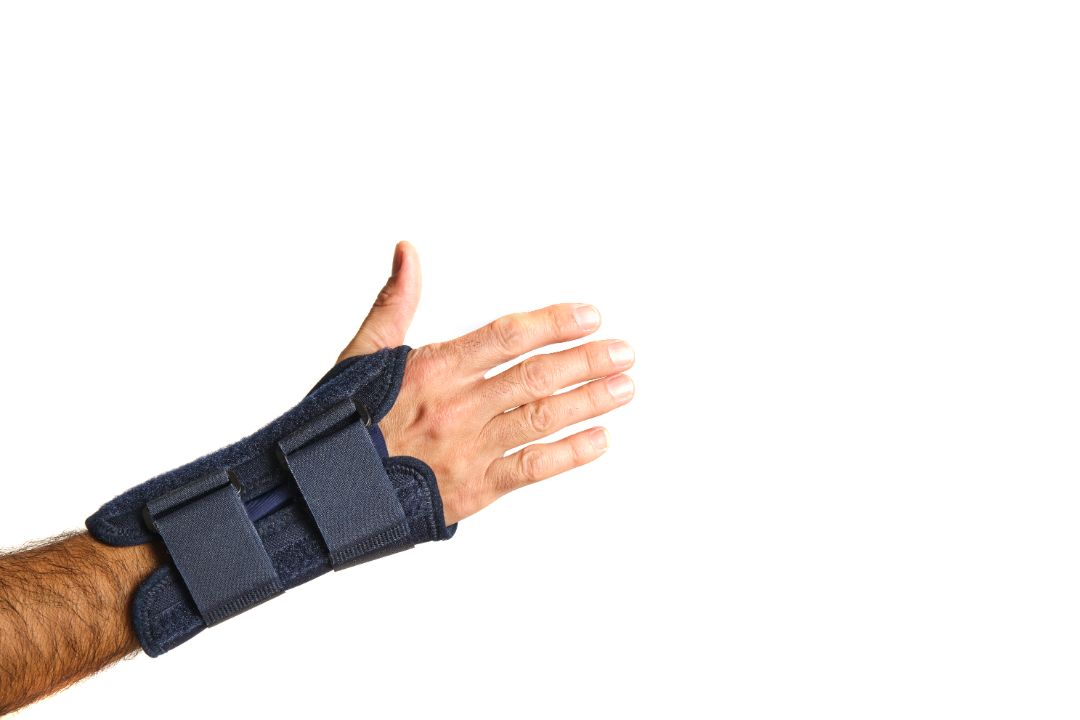
Photo Credit: alfotomp, Envato
There are several treatment options available for those suffering from wrist tendinopathy. The treatment choice will depend on the severity of the condition, the underlying cause, and the individual’s medical history.
Physical therapy can help to reduce pain, improve flexibility, and strengthen the wrist muscles and tendons. This can be achieved through various exercises, stretches, and manual therapies.
Your physical therapist will tailor your treatment plan to your specific needs, including heat therapy, ice therapy, ultrasound therapy, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). Physical therapy can be a highly effective non-surgical treatment for wrist tendinopathy.
Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help to reduce pain and swelling associated with this condition. Your doctor can prescribe these medications and are available over the counter.
In some cases, your doctor may also prescribe corticosteroids, which are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that can be injected directly into the affected tendon. However, this treatment is usually reserved for severe cases of wrist tendinopathy.
Splinting can help to immobilise the wrist and reduce the strain on the affected tendon. This can be particularly effective for those with this ailment caused by overuse or repetitive motions.
Your doctor or physical therapist may recommend a wrist splint or brace, which should be worn for a period of time to allow the tendon to heal and reduce the risk of further injury.
In rare cases, surgical intervention may be required to treat this condition. This usually involves removing damaged tissue or repairing the affected tendon.
Your doctor will only recommend surgical intervention if all other treatment options have been exhausted and if the benefits outweigh the risks. Surgery may require a period of rehabilitation and recovery, which will be guided by your doctor or physical therapist.
Wrist rehabilitation exercises can help to improve strength and flexibility in the wrist muscles and tendons. Your doctor or physical therapist can provide a specific exercise plan tailored to your needs and abilities.
Pain relief techniques such as ice therapy, massage, and acupuncture may also be used to manage pain and swelling associated with wrist tendinopathy.
Preventing wrist tendinopathy is essential in maintaining overall wrist health and avoiding the debilitating symptoms of the condition. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of developing this ailment:
One of the most effective ways to prevent wrist tendinopathy is by practising proper ergonomics. This includes maintaining a neutral wrist position when typing on a keyboard or using a mouse.
Ensure the keyboard and mouse are at the right height and distance to avoid awkward wrist angles. It is also essential to take regular breaks at work and perform wrist exercises to reduce the risk of developing wrist tendinopathy.
Repetitive motions can strain the wrist tendons, increasing the risk of developing tendinopathy. To reduce this risk, try to vary your tasks throughout the day and avoid performing the same motion for an extended period.
It is also advisable to take breaks and stretch your wrist muscles to prevent wrist tendinopathy from occurring. Avoiding sudden and forceful movements can also help reduce the risk of wrist injuries leading to tendinopathy.
Maintaining overall wrist health is critical in preventing wrist tendinopathy. This includes exercising regularly to strengthen the wrist muscles and using wrist braces during activities that can strain the wrist tendons.
It is also advisable to avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake, as these habits can weaken the wrist tendons and increase the risk of tendinopathy. A healthy diet rich in nutrients that support wrist health, such as calcium and vitamin D, can also help prevent wrist tendinopathy.
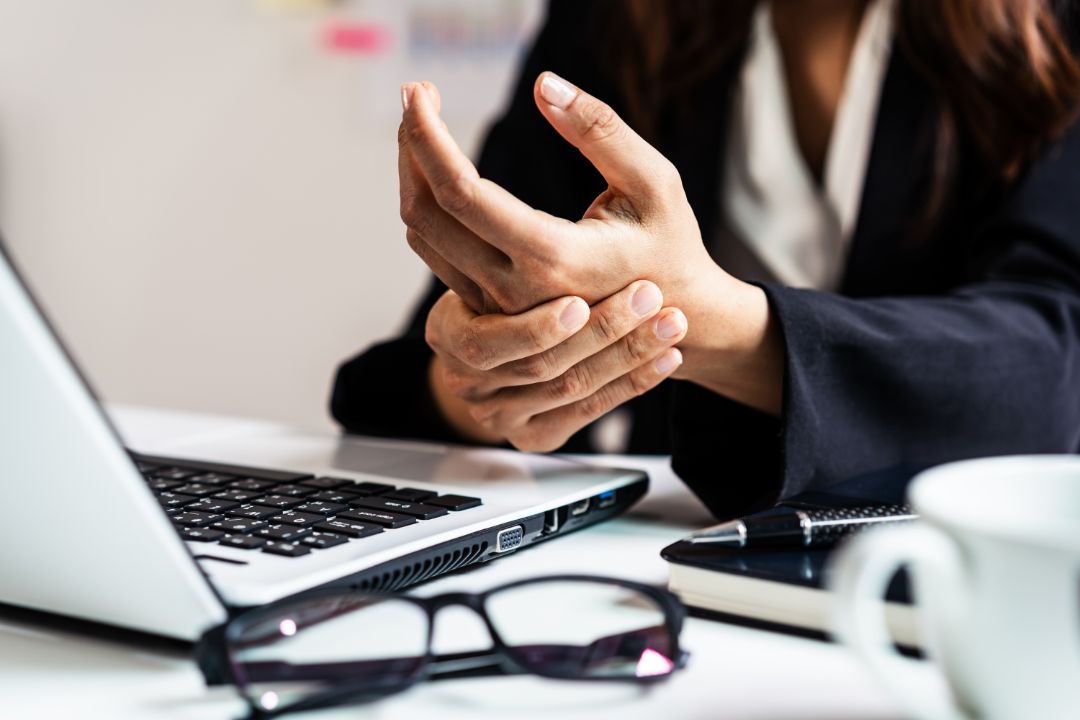

Photo Credit: kitzstocker, Envato
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing this condition and maintain the overall health of your wrists. If you experience any symptoms of wrist tendinopathy, seeking medical attention promptly to avoid further damage to the wrist tendons is essential.
Wrist tendinopathy is a condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the tendons in the wrist, leading to wrist pain and limited mobility.
Wrist tendinopathy is often used interchangeably with wrist tendonitis, as both terms refer to inflammation or damage to the wrist tendons.
Wrist tendinopathy can be caused by repetitive movements, overuse of the wrist, traumatic injury, or natural degeneration due to age.
Symptoms of wrist tendinopathy include pain in the wrist, stiffness, swelling, and limited range of motion.
Diagnosis of wrist tendinopathy typically involves a physical examination, imaging tests, and possibly referral to a specialist for further evaluation.