Thumb sprains are common injuries that can occur in individuals of all ages and activity levels. This type of injury can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, overuse, or a sudden twisting motion.
Symptoms of a thumb sprain can include pain, swelling, and limited range of motion. Depending on the severity of the injury, treatment options can range from non-surgical approaches such as rest and physical therapy, to more invasive surgical procedures.
Thumb sprains are a common injury that can be caused by a variety of factors. They occur when the ligaments surrounding the thumb are stretched beyond their normal range of motion, leading to inflammation and pain.

Photo Credit: alfotomp, Envato
Several mechanisms can cause this pain, including:
Thumb sprains can also be classified based on severity, with some causing only mild discomfort while others resulting in significant pain and limited hand function.
Understanding how a thumb sprain occurs is important for preventing future injuries. Common activities or situations that may lead to this include playing sports, participating in manual labour, or engaging in activities that require repetitive gripping or twisting motions.
Thumb sprains often cause significant discomfort, impacting the ability of patients to complete daily tasks requiring grip and pinch strength. Understanding the symptoms of a thumb sprain is crucial to seek appropriate treatment and promote healing.
Pain is the most common symptom of a thumb sprain. Patients may experience pain in the thumb joint or throughout the entire thumb. The pain may worsen with movement and can range from mild to severe.
Swelling is another common symptom of a thumb sprain. The affected area may look red, feel warm to the touch, and appear swollen. Patients with severe sprains may also develop bruising.
A thumb sprain can cause stiffness and limited range of motion. Patients may find it difficult to complete tasks such as writing, typing, or holding objects. Difficulty performing these types of movements can significantly impact daily life, making it crucial to address the injury’s root cause.
In severe cases, patients may experience numbness and tingling in the affected thumb or fingers. This symptom can indicate nerve damage and requires immediate treatment from a medical professional.
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention promptly. Early treatment can significantly improve the outcome of a thumb sprain and reduce the risk of further complications.
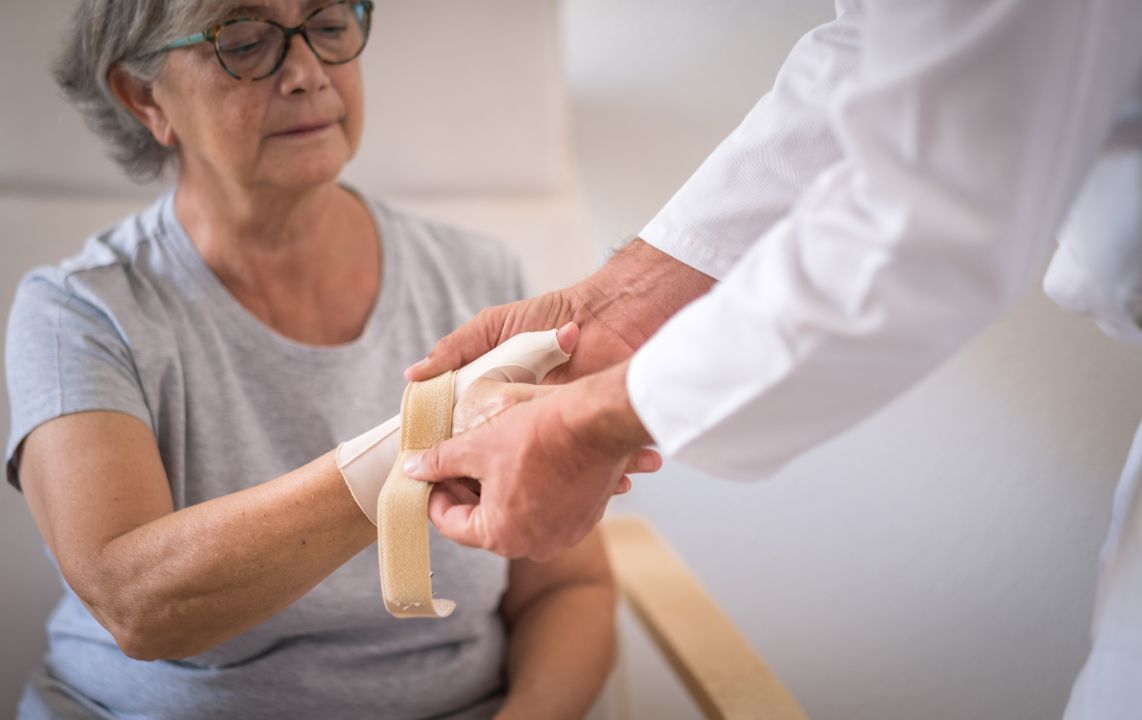
Photo Credit: lucigerma, Envato
When it comes to treating a thumb sprain, there are various options available. In some cases, non-surgical treatment methods may be effective, while surgery may be necessary in other cases. The severity of the injury and the individual’s overall health will determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
If the case is mild-to-moderate, non-surgical treatment may be recommended. This may involve:
Surgery may be necessary if the condition is severe or does not respond to non-surgical treatment methods. This may involve:
After surgery, individuals will typically need to participate in physical therapy to regain strength and range of motion in the thumb.
No matter the treatment approach, allowing sufficient time for the thumb to heal properly is essential. Rushing back into activities too soon can exacerbate the injury and prolong recovery.
After a thumb sprain, rehabilitation is a crucial step towards regaining strength and range of motion in the thumb. The following exercises can help with rehabilitation:
It’s important to perform these exercises under the guidance of a medical professional or physical therapist. They can also recommend additional exercises based on your injury’s severity and recovery progress.
In addition to exercises, rest and immobilization are also crucial for recovery. Your medical professional may recommend a splint or cast to keep your thumb immobile, allowing it to heal properly.
As you recover, your medical professional may also recommend functional exercises specific to your daily activities. This can help you safely return to normal activities without re-injuring your thumb.

Photo Credit: eddows_arunothai, Envato
Thumb sprains can be painful and inconvenient, but fortunately, there are steps you can take to prevent them from occurring in the first place.
Before engaging in any activity that puts strain on the thumbs, it’s important to properly warm up the hands and wrists. This can be done through gentle stretches and range-of-motion exercises that help increase blood flow to the area.
If you engage in activities that put your thumbs at risk, such as playing sports or working with tools, it’s important to wear protective gear. This may include wrist guards or gloves that provide added support and cushioning.
Repetitive and prolonged thumb movements can also put you at risk for a sprain. To reduce the risk, it’s important to practice good ergonomics, such as using proper posture and positioning when typing or using electronic devices.
Maintaining good thumb health is also important in preventing sprains. This may include exercises and stretches to improve strength and flexibility, as well as maintaining a healthy diet and staying hydrated to promote overall joint health.
By taking these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of a thumb sprain and maintain optimal hand health.
Thumb sprains are commonly caused by overstretching or tearing the ligaments in the thumb. This can occur due to a direct impact, such as a fall or sports injury, or repetitive motions that stress the thumb joint.
The symptoms of a thumb sprain may include pain, swelling, bruising, difficulty gripping or pinching, and limited range of motion in the thumb joint.
Treatment for a thumb sprain may include rest, immobilisation with a splint or brace, ice therapy, pain medication, and physical therapy. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Rehabilitation exercises can benefit individuals recovering from a thumb sprain. These exercises can help improve strength and flexibility in the thumb joint and aid recovery.
To prevent thumb sprains, it is important to practice proper warm-up techniques, wear protective gear when engaging in activities that stress the thumb, and maintain good thumb health through regular exercise and ergonomic practices.