De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a hand and wrist condition that can cause significant pain and discomfort for those affected. It is a form of tendonitis that occurs when the tendons around the base of the thumb become inflamed. This can result in wrist pain and thumb pain, making it difficult for individuals to carry out daily activities.
Several factors can contribute to the development of de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis, including hand injury, repetitive strain injury, and occupational injury. The condition is also commonly associated with thumb tendinitis and thumb tendonitis.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a hand and wrist condition that can cause significant pain and discomfort. It occurs when the tendons that control the movement of the thumb become inflamed and irritated as they pass through a narrow tunnel located at the base of the thumb and into the wrist. This inflammation can cause pain and swelling in the wrist and thumb, making it difficult to perform basic daily activities such as gripping objects or twisting the wrist.
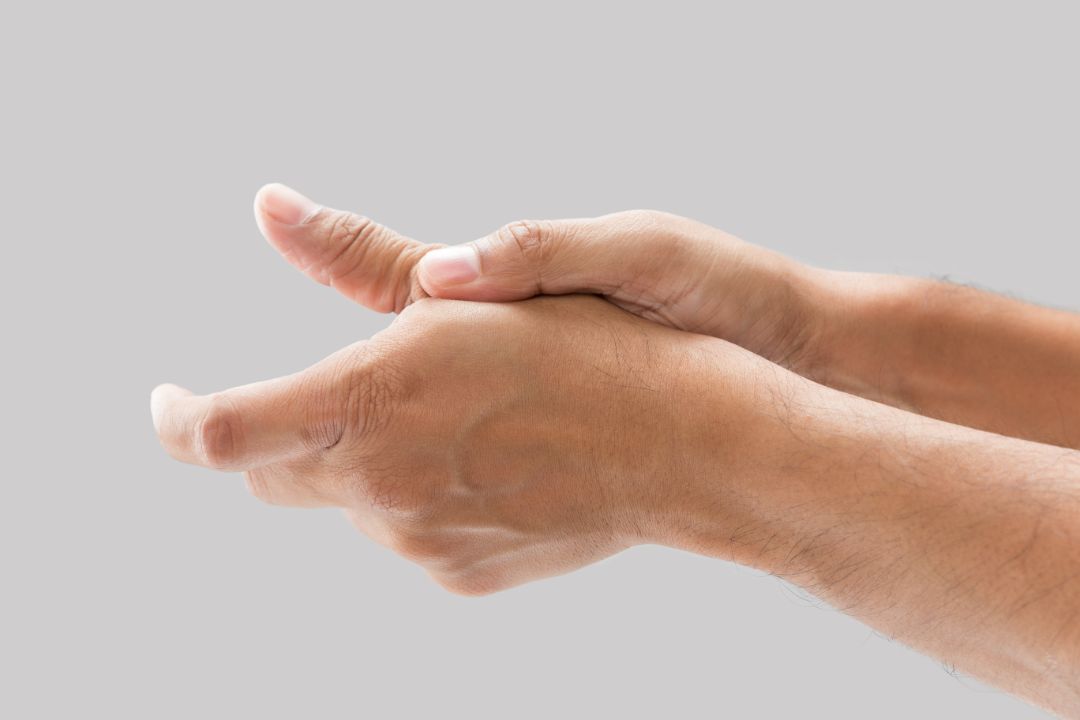

Photo Credit: eddows_arunothai, Envato
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a common condition affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. Women are more commonly affected than men, and it is often linked to repetitive hand and wrist motions, such as those required for activities like gardening, sports, or keyboard use.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a hand and wrist condition caused by inflammation of the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. While the condition’s exact cause is unknown, several factors can contribute to its development.
Individuals with de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis often experience pain and discomfort in their wrist and thumb. The pain can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent. Activities such as gripping, grasping, or twisting can exacerbate the pain. Other symptoms of de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis include:
If you experience persistent or worsening wrist and thumb pain or if your daily activities are significantly impacted, it is important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and improve your overall quality of life.
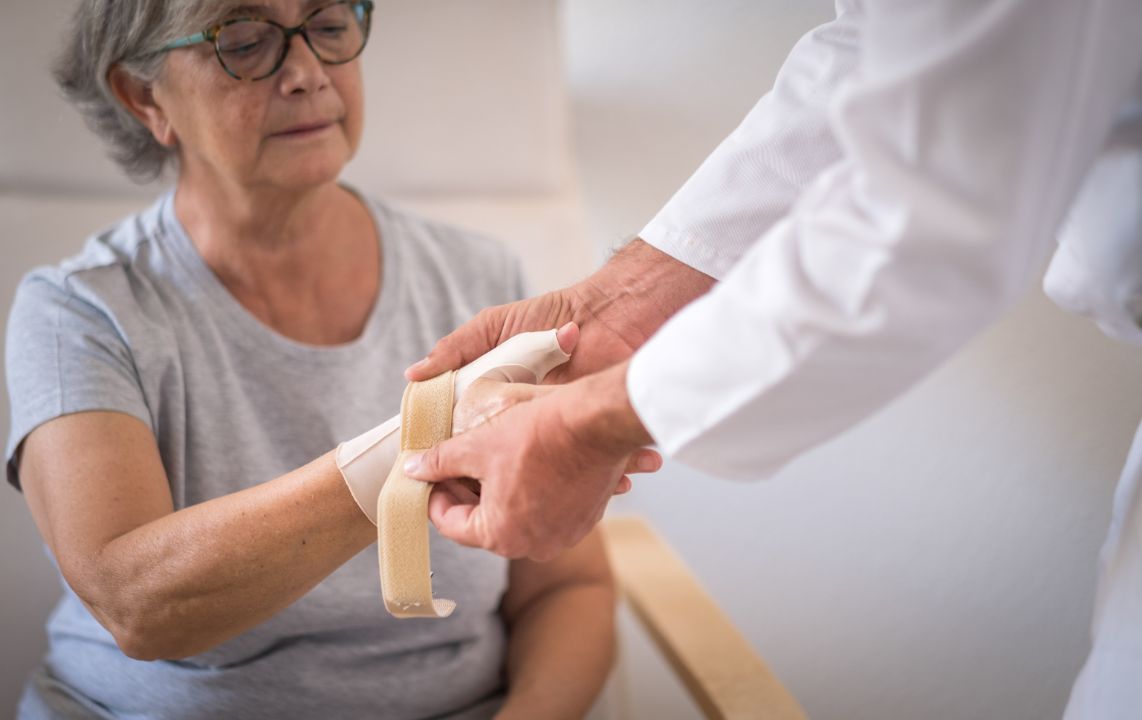
Photo Credit: lucigerma, Envato
Diagnosing de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis typically involves examining symptoms and performing a physical exam. During the physical exam, your doctor will check for tenderness and swelling in the affected area and may perform a Finkelstein test. In this test, you will make a fist with your thumb inside and bend your wrist towards the little finger. If you experience pain, you likely have this condition.
In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, and ultrasounds may be necessary to rule out other possible conditions or to confirm the diagnosis.
Thumb tendinitis is often confused with de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis due to their similar symptoms. However, they are two distinct conditions. Thumb tendinitis is inflammation of a tendon in the thumb, while de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is inflammation of the sheath that surrounds the same tendon.
Diagnostic tests can help differentiate between the two conditions to ensure proper treatment.
Treatment for de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and restore normal hand and wrist function. Treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the condition, underlying causes, and individual circumstances. The following are some common treatment options:
Resting and immobilizing the affected hand and wrist can help reduce inflammation and allow the tendons to heal. A splint or brace can be worn to immobilize the thumb and wrist, limiting movement and providing support. It is important to follow the prescribed period of rest and immobilization to avoid aggravating the condition.
Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation. A doctor may also recommend prescription-strength NSAIDs or corticosteroid injections to provide more targeted and potent relief.
Physical therapy can help restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the hand and wrist. A therapist can provide exercises and stretches that target the affected tendons and muscles and advise on proper ergonomics and posture to prevent further injury.
If non-surgical treatments are ineffective, surgery may be recommended. Surgery involving the release of the constricting sheath around the affected tendons can relieve pressure and reduce pain. However, as with any surgery, risks and potential complications should be considered.
It is also important to address any underlying causes of de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis, such as tendonitis, hand injury, occupational injury, thumb tendinitis, and thumb tendonitis, to prevent recurrence and long-term damage to the hand and wrist.
Individuals with this condition can take steps to manage their hand and wrist condition and minimize its impact on their daily life. This section provides practical tips and strategies for managing de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis in daily life.

Photo Credit: DragonImages, Envato
Effective management of de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis requires addressing underlying causes such as tendonitis, repetitive strain injury, and occupational injury. Individuals experiencing hand and wrist pain should consult a healthcare provider for an evaluation and appropriate treatment options.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a hand and wrist condition characterised by pain and inflammation in the thumb area.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis can be caused by factors such as thumb tendinitis, thumb tendonitis, hand injury, repetitive strain injury, and occupational injury.
The common symptoms of de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis include wrist pain and thumb pain, which other discomforts may accompany.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is diagnosed through the evaluation of symptoms, physical examinations, and potentially imaging tests, to differentiate it from other hand and wrist conditions.
Treatment options for De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis include rest, immobilization, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and surgical interventions for severe cases.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis can be managed daily through ergonomic considerations, activity modifications, and preventive measures. Addressing underlying causes is also crucial.