Elbow bursitis, also known as olecranon bursitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation of the bursa located at the tip of the elbow overlying the olecranon process on the lateral side. This bursa, known as the olecranon bursa, is a small fluid-filled sac that normally acts as a cushion to reduce friction between the bony point of the elbow and the soft tissues of the skin and muscles.
Olecranon bursitis, much different from golfer’s elbow, occurs when this bursa becomes irritated and inflamed, resulting in pain, swelling, redness and tenderness over the back of the elbow, affecting the tendon. Excess fluid accumulation in the olecranon bursa causes it to swell up like a rubber ball on the elbow. Olecranon bursitis can be caused by trauma, overuse, arthritis, infection or other medical conditions.
Repeated direct blows or pressure on the elbow are common triggers. The inflammation impedes normal elbow movement and can be quite painful until properly treated. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of olecranon bursitis is important to alleviate symptoms and restore full elbow function.
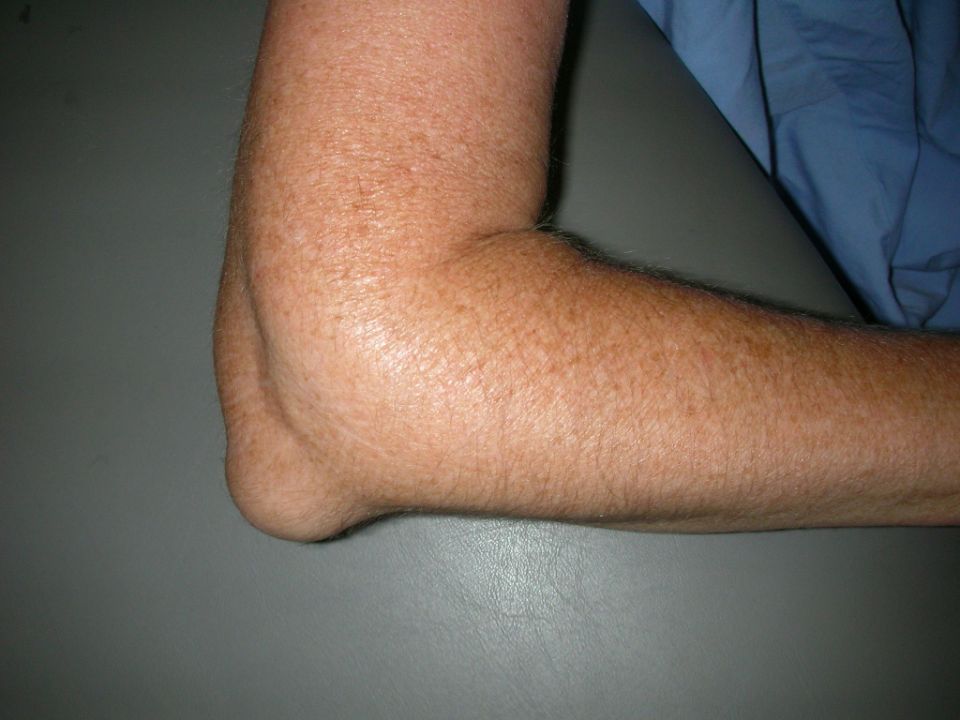
Photo Credit: Orthoinfo
The main symptoms of olecranon bursitis include:
Symptoms often worsen with leaning on the elbow or movements that press on the inflamed bursa. Pain may flare at night, disrupting sleep.
There are several potential causes of olecranon bursitis:
Any condition causing inflammation, irritation or added pressure on the elbow bursa can ultimately trigger painful swelling and olecranon bursitis. Prompt treatment helps reduce complications.
Photo Credit: bignai, Freepik
Factors that raise the risk of olecranon bursitis include:
Protecting elbows from overuse and trauma reduces the chances of developing this painful condition. Early diagnosis prevents complications like rupture or infection.
Olecranon bursitis diagnosis involves:
Distinguishing between non-infectious irritation and septic bursitis is important, as treatment approaches differ. Report any elbow swelling, pain, or fever to your doctor for proper diagnosis.
Most cases of olecranon bursitis improve with nonsurgical treatment:
Avoiding pressure and trauma to the inflamed bursa helps reduce irritation. Use elbow pads for protection.
Aspiration drains excess fluid using a needle, providing relief.
Wrapping the elbow helps minimize swelling and provides stability.
Stretching, strengthening exercises improve mobility once pain decreases.
Removing the irritated bursa if conservative treatment fails.
Seeking treatment early optimizes recovery time. Most patients improve with nonsurgical methods. Call your doctor if symptoms worsen or persist beyond 1-2 weeks.

Photo Credit: Stockking, Freepik
With proper treatment, most cases of olecranon bursitis heal entirely within a few weeks. Seek prompt medical care for optimal recovery.
If left untreated, olecranon bursitis can lead to:
Prompt diagnosis and appropriate rest and treatment helps avoid these potential olecranon bursitis complications.
Most cases of olecranon bursitis resolve well if treated early with conservative measures. Full recovery takes around 2-3 months for the inflamed bursa to heal completely and symptoms to disappear. Recurrence is common if elbow irritation continues, especially due to occupational overuse. Preventive measures include:
People fully recover from olecranon bursitis with proper rest, treatment, and prevention habits. Report any recurring elbow pain or swelling to your doctor to check for infection or other complications requiring further treatment.

Photo Credit: arthritis-health
For those with persistent, recurrent or complex cases of olecranon bursitis not responsive to conventional treatments, emerging therapies include:
Future research aims to find new ways to resolve stubborn cases of elbow bursitis that fail typical treatments. Consulting a sports medicine specialist is advised for recalcitrant cases.
In most people, olecranon bursitis can be effectively treated with rest, elbow protection, medications, drainage, and rehabilitation exercises. Seeking prompt medical care provides the best chance for the fastest recovery and avoiding complications like rupture or infection of the inflamed bursa. Awareness of elbow safety at work and in sports helps prevent this painful condition.
Olecranon bursitis is treated with rest, icing, NSAIDs, aspiration of fluid, padding for protection, antibiotics for infection, and physical therapy to strengthen and stretch the elbow.
Yes, with proper treatment such as rest, anti-inflammatory medications, draining excess fluid, and elbow padding, most cases of olecranon bursitis resolve within 2-3 months.
Often seen in plumbers, the most common causes are repetitive trauma like leaning on the elbow, direct blows to the elbow, arthritis, and sometimes infection. Less commonly, medical conditions like gout or diabetes can contribute.
The first line treatment is resting and protecting the elbow from further irritation and impact, icing to reduce swelling, NSAID medications, and draining excess fluid if present.