Achilles Tendinopathy – an injury that affects the Achilles tendon and often goes undiagnosed – is characterised by pain and discomfort in the heel area. It is common among athletes and individuals who engage in physical activities that involve repetitive stress on the calf muscles.
Achilles Tendinopathy can significantly impact an individual’s mobility, and if left untreated, it may even lead to achilles tendon rupture, requiring surgery.
The Achilles tendon is the largest and strongest tendon in the human body and is crucial for everyday movement. It connects the calf muscles to the heel bone and allows us to move our foot up and down. However, repetitive stress or overuse can cause the tendon to become damaged, resulting in Achilles Tendinopathy.
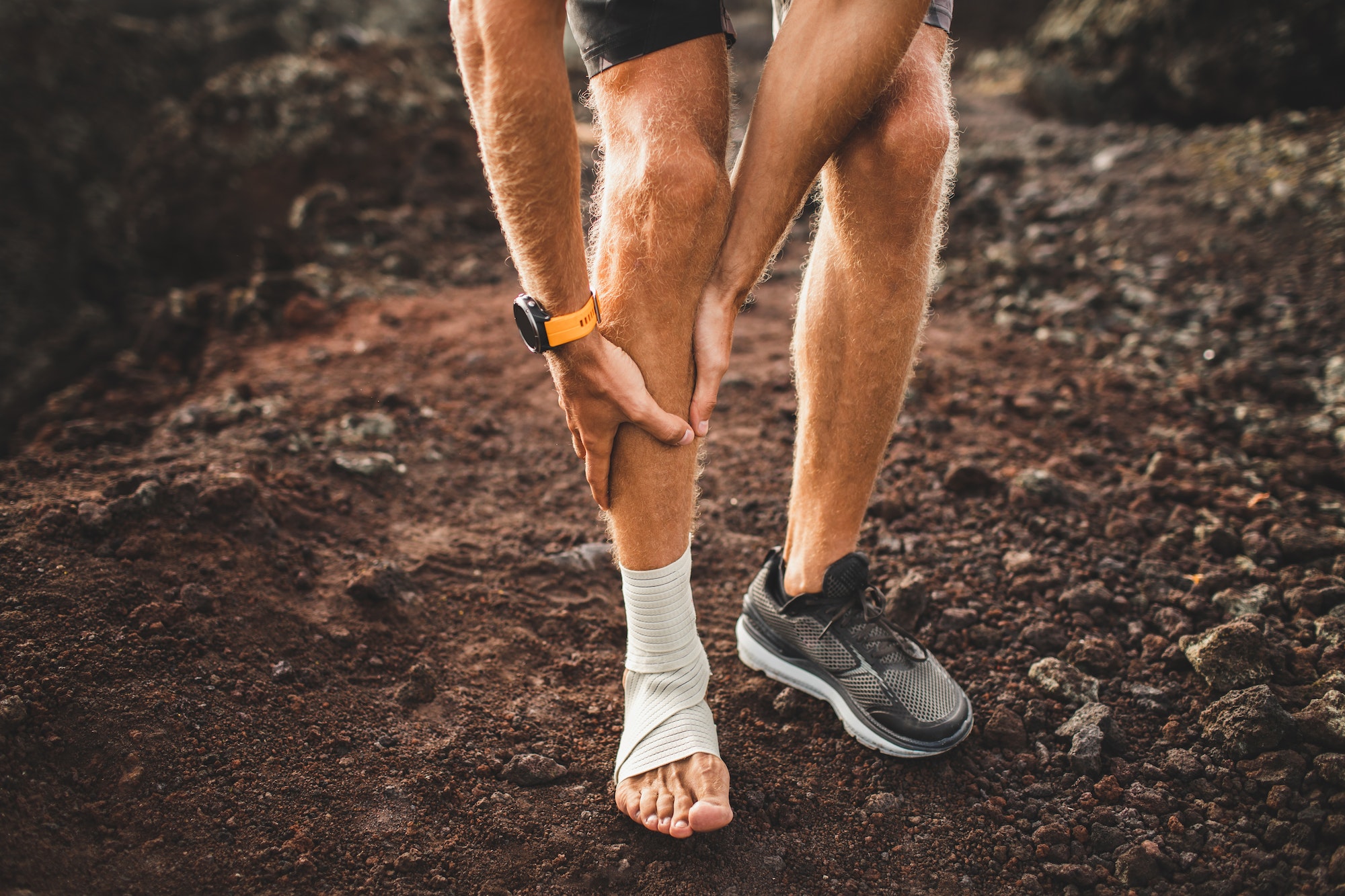 Photo Credit: olegbreslavtsev | Envato
Photo Credit: olegbreslavtsev | Envato
Both athletes and non-athletes can suffer from achilles tendinopathy. It can occur from activities that involve jumping, running, or sudden changes in direction, placing strain on the Achilles tendon. Additionally, individuals who have tight calf muscles or weak tendons are at higher risk for developing this condition.
The specific symptoms associated with Achilles Tendinopathy can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include pain and stiffness in the heel and calf (Calf Injury), swelling, and difficulty moving the foot and ankle.
Several factors can contribute to developing Achilles Tendinopathy, including:
By understanding the anatomy of the Achilles tendon and the risk factors that contribute to Achilles Tendinopathy, individuals can take steps to prevent injury and protect their tendon. In the next section, we will discuss how Achilles Tendinopathy is diagnosed.
Achilles tendinopathy is a condition that affects the Achilles tendon, which is located at the back of the ankle. It is often associated with overuse or repetitive stress on the tendon. The main symptom of Achilles tendinopathy is pain, which typically begins as a mild ache or stiffness in the back of the ankle or lower calf region. This pain may worsen with activity or prolonged periods of standing or walking.
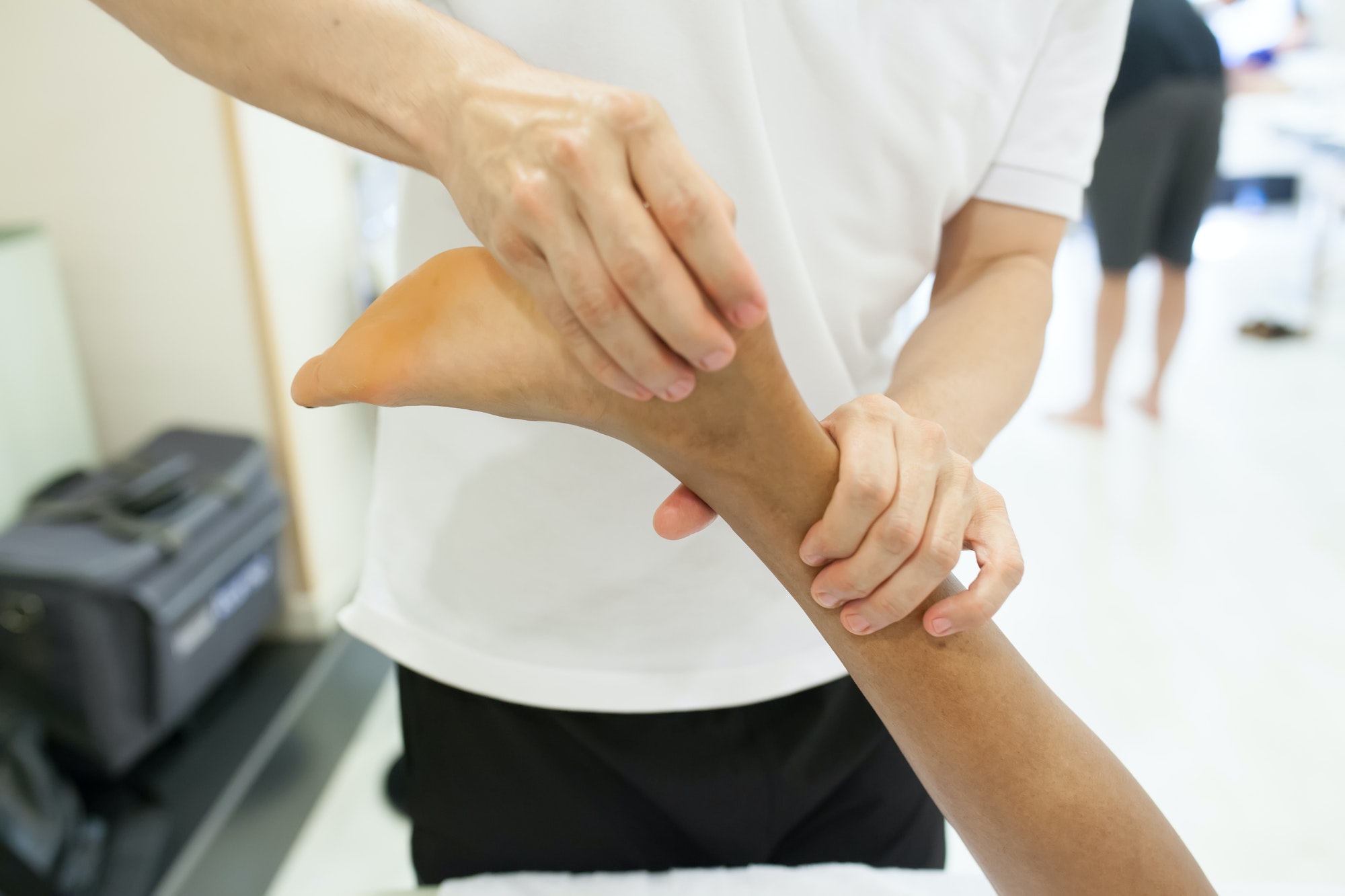 Photo Credit: dfuentesphotostock | Envato
Photo Credit: dfuentesphotostock | Envato
In some cases, the pain may become more severe and sharp, making it difficult to bear weight or participate in physical activity. Other common symptoms include swelling, tenderness, and a thickening or enlargement of the Achilles tendon. In severe cases, the tendon may become weakened and there is a risk of a rupture or tear. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing Achilles Tendinopathy requires a careful examination by a healthcare professional. The diagnosis can be confirmed through physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests.
During the physical examination, the healthcare professional will evaluate the affected area for signs of inflammation, swelling, or tenderness, especially around the Achilles tendon if the injury occurs in the mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy, it would often result in an obvious, tender lump. The examination will typically involve palpation of the Achilles tendon and calf muscle to assess their condition. In some cases, the healthcare professional may ask the patient to perform specific movements to help identify the location and extent of the injury.
A medical history is an essential component of diagnosing Achilles Tendinopathy. The healthcare professional will ask about the patient’s symptoms, including symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy, and when they first noticed them. They may also inquire about the patient’s physical activity level and any previous injuries or medical conditions that may have contributed to developing Achilles Tendinopathy.
Imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI scans can help confirm the diagnosis of Achilles Tendinopathy and assess tendon thickness, detecting any possible tendon rupture or damage. X-rays are useful for identifying any associated damage to the heel bone, while MRI scans can provide more detailed information about the structure of the Achilles tendon. In some cases, an ultrasound may also be used to evaluate the condition of the tendon and surrounding structures.
If the Achilles Tendinopathy is suspected to be insertional, an MRI scan can provide valuable information about the condition of the Achilles tendon where it inserts into the heel bone.
There are several treatment options available for individuals diagnosed with Achilles Tendinopathy, depending on the severity of the injury. The primary goal of treatment is to relieve pain and restore function to the affected Achilles tendon.
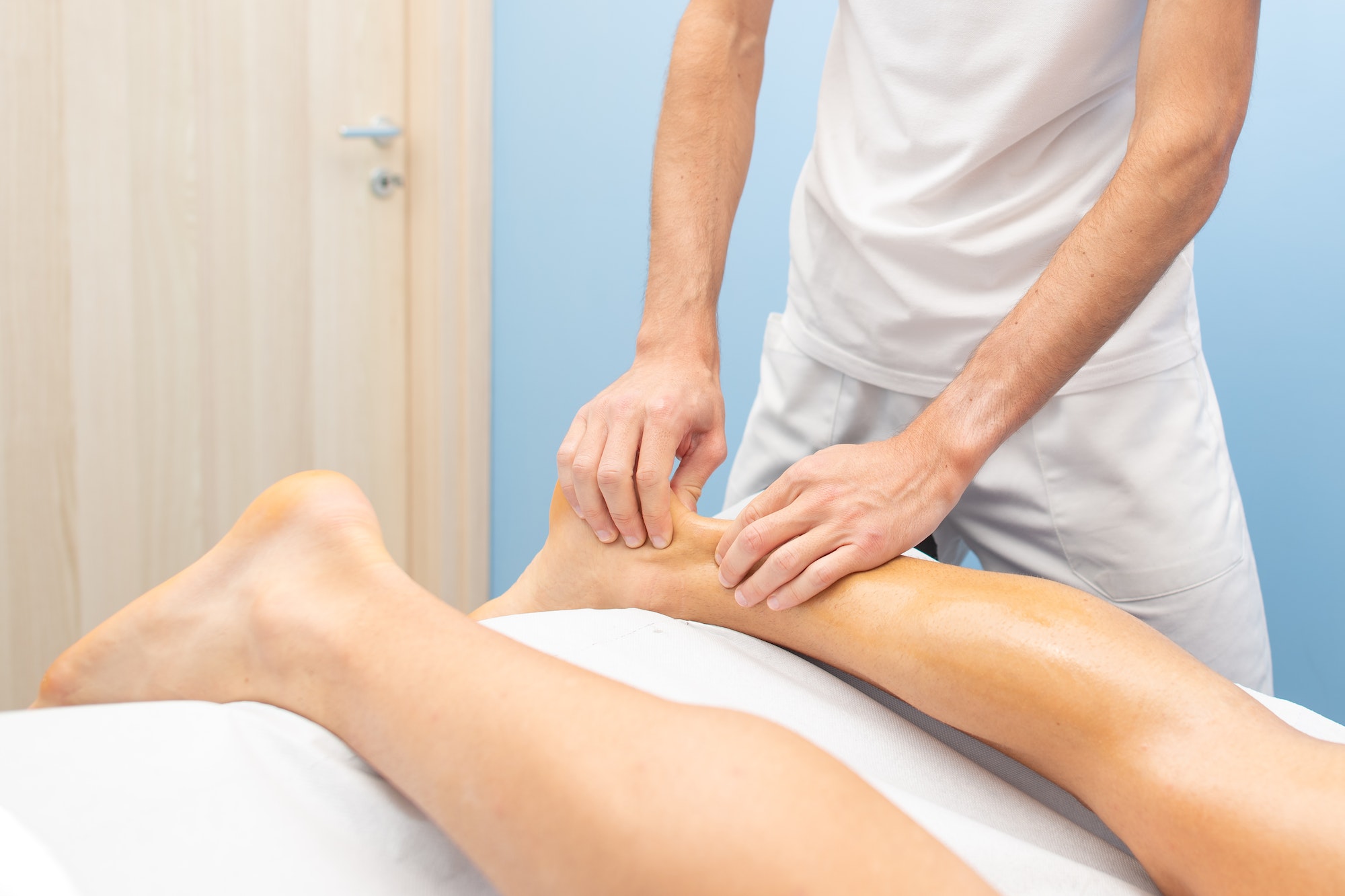 Photo Credit: michelangeloop | Envato
Photo Credit: michelangeloop | Envato
Overall, the key to managing Achilles Tendinopathy is early diagnosis and prompt treatment. With the appropriate care and rehabilitation, individuals with this injury can make a full recovery and resume their normal daily activities, free from pain and discomfort.
Preventing Achilles Tendinopathy is much easier than treating it. Proper warm-up and stretching techniques can go a long way in the management of Achilles Tendinopathy. Gradual training progression is also essential to give your body time to adjust and avoid unnecessary stress on your Achilles tendon.
Before starting any exercise routine, it is essential for patients with achilles tendinopathy to engage in a proper warm-up to avoid strain on the Achilles tendon. A warm-up can help loosen up the calf muscles and increase blood flow, preparing the body for physical activity. Adequate stretching can also help prevent Achilles Tendinopathy by keeping the calf muscles flexible.
Proper warm-up and stretching techniques should be implemented before any form of exercise, including running, jogging, or weightlifting.
Gradual training progression is essential to avoid placing sudden stress on the Achilles tendon. To reduce the risk of Achilles Tendinopathy and prevent tendon rupture, it is crucial to slowly increase the intensity and duration of the workout. Gradually increasing the load of the tendon can help strengthen the structure of the tendon and reduce the risk of developing Achilles Tendinopathy.
Individuals should also incorporate periods of rest into their exercise routine. Rest allows the body to recover and repair any damage that may have occurred during exercise.
Stretch your calf muscles and Achilles tendon; strengthening exercises for the calf muscles can help support the Achilles tendon and prevent future injuries. Exercises such as calf raises can target the muscles responsible for lifting the heel, reducing the strain on the Achilles tendon. Stretching exercises, such as the wall stretch, can help keep the calf muscles flexible (also see Calf Muscle Tear) .
It is essential to speak with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise routine, especially if you have a history of Achilles Tendinopathy or have experienced Achilles tendon injuries.
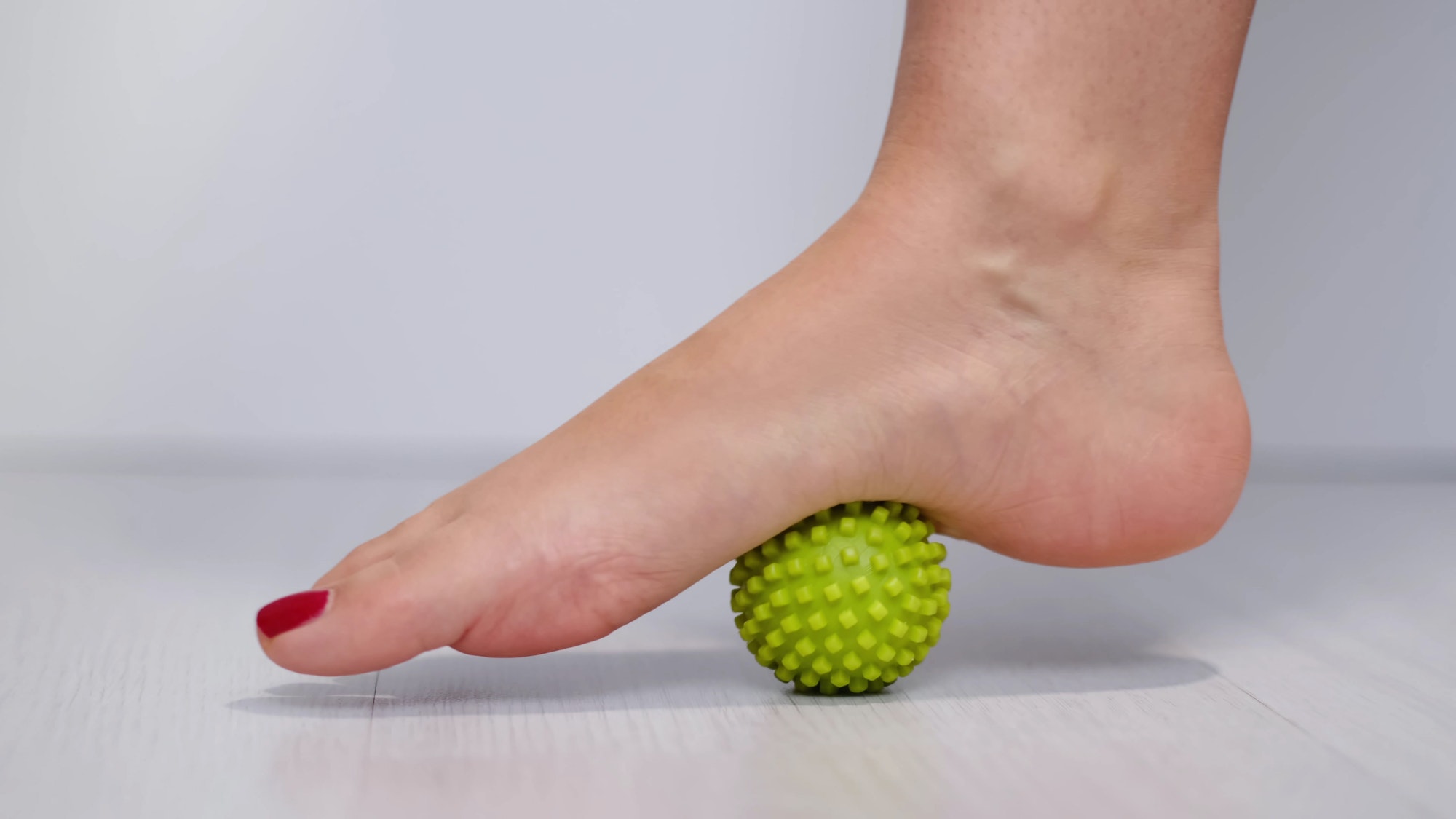 Photo Credit: yavdat | Envato
Photo Credit: yavdat | Envato
In conclusion, preventing Achilles Tendinopathy requires adequate warm-up and stretching techniques, gradual training progression, and incorporating strengthening exercises. If you experience any symptoms associated with Achilles Tendinopathy or Achilles tendon pain, seek medical attention as soon as possible. With proper care and treatment, it is possible to recover from Achilles Tendinopathy, Achilles tendinitis, and Achilles tendon injuries, preventing future injuries and promoting a healthy, pain-free lifestyle.
Treatment for Achilles tendinopathy typically involves rest, ice, over-the-counter pain relievers, and physiotherapy exercises to strengthen the tendon and improve its flexibility. In more severe cases, other treatments such as corticosteroid injections, extracorporeal shockwave therapy, or even surgery might be recommended.
The recovery time for Achilles tendinopathy can vary widely depending on the severity of the condition and individual factors. but it often takes several weeks to months for symptoms to improve substantially. Chronic cases may take longer to fully recover.
Achilles tendonitis is a type of Achilles tendinopathy, but the latter is a broader term that encompasses a range of conditions affecting the Achilles tendon, including both inflammatory and degenerative changes (a chronic condition causes degeneration of the Achilles, also known as Achilles tendinosis). It’s essential to differentiate between the two as the treatment approach and management may vary depending on the specific type and severity of the condition. If you suspect you have any issues with your Achilles tendon, it’s best to seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Achilles tendinopathy is a condition that causes pain, swelling, and impaired function in the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Overuse or repetitive strain on the tendon, often causes it, such as from running or jumping activities.
It includes both inflammatory and degenerative changes within the tendon. Achilles tendinopathy can be classified into two main types: