Anterior Ankle Impingement, also known as “athlete’s ankle” or “footballer’s ankle,” is a condition characterised by pain and pinching of bone, soft tissue, or scar tissue at the front of the ankle. This condition can occur due to a new or old injury. The swollen tissue or scar tissue gets caught between the bones of the lower part of the leg (tibia) and the upper part of the foot (talus). This impingement can lead to discomfort and restricted movement, affecting an individual’s ability to perform activities that involve the foot and ankle.
The primary symptom of Anterior Ankle Impingement is pain at the front of the ankle, which can be exacerbated by activities that involve moving the foot upwards (dorsiflexion). Other symptoms may include:
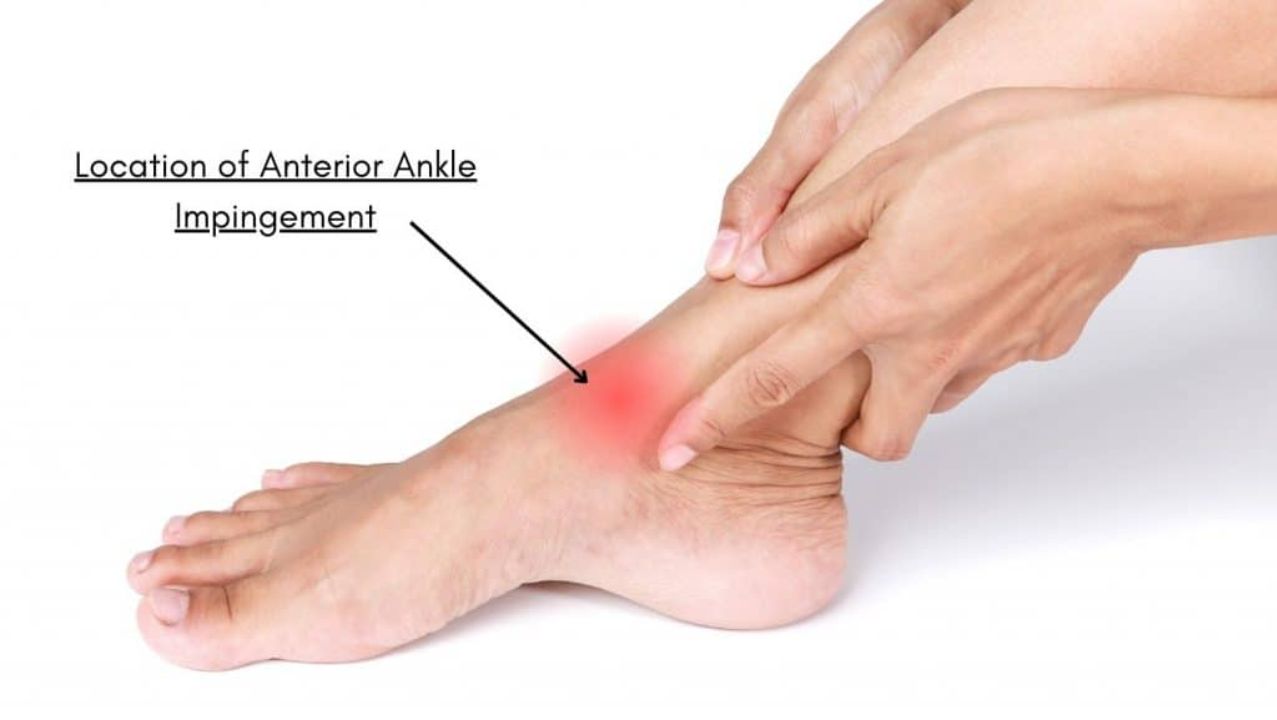
Photo Credit: James McCormack
A variety of factors can cause Anterior Ankle Impingement. Some of the most common causes include:
Diagnosis of Anterior Ankle Impingement typically involves a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. During the physical examination, the doctor may manipulate the ankle to assess the range of motion and identify any areas of pain. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound, may be used to visualise the bones and soft tissues of the ankle and identify any abnormalities, such as bone spurs or inflammation.
Treatment for Anterior Ankle Impingement typically involves a combination of conservative measures and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Conservative treatments may include:
In cases where conservative treatments are not effective, surgical intervention may be considered. This could involve arthroscopic surgery to remove bone spurs or other abnormalities that are causing the impingement.

Photo Credit: Drazen Zigic, Freepik
Managing Anterior Ankle Impingement typically involves a combination of treatment and lifestyle modifications. These may include:
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in treating and managing Anterior Ankle Impingement. A physical therapist can provide a range of treatments, including:
When dealing with Anterior Ankle Impingement, it’s important to avoid certain common mistakes that can exacerbate symptoms or delay healing. These include:

Photo Credit: peoplecreations, Freepik
While Anterior Ankle Impingement can often be managed with conservative treatments, there are some situations where it’s important to seek immediate medical attention. These include:
The prognosis and recovery time for Anterior Ankle Impingement can vary depending on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and the effectiveness of treatment.
With appropriate treatment, most individuals can expect to see improvement in their symptoms within a few weeks. However, in some cases, it may take several months for symptoms to resolve completely. It’s important to follow your treatment plan closely and to keep all follow-up appointments with your doctor to ensure the best possible outcome.
Treatment for anterior ankle impingement typically involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and medication to reduce inflammation. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Treatment aims to reduce pain and inflammation, improve mobility, and prevent further damage.
Anterior ankle impingement, also known as “athlete’s ankle” or “footballer’s ankle,” is a condition characterised by pain and pinching of bone, soft tissue, or scar tissue at the front of the ankle. This condition can occur due to a new or old injury. The swollen tissue or scar tissue gets caught between the bones of the lower part of the leg (tibia) and the upper part of the foot (talus), leading to discomfort and restricted movement.

Photo Credit: leszekglasner, Envato
Fixing ankle impingement usually involves a combination of treatments. Resting and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain can help to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the ankle muscles, improve flexibility, and promote healing. Medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be considered to remove bone spurs or other abnormalities causing the impingement.
With appropriate treatment, the symptoms of anterior ankle impingement can improve over time. The recovery time can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. Following the treatment plan provided by your healthcare provider can help ensure the best possible outcome. However, it’s important to note that in some cases, it may take several months for symptoms to resolve completely.
Anterior ankle impingement can cause significant discomfort and limit mobility. If left untreated, it can lead to chronic pain and further complications. It’s important to seek medical attention if you’re experiencing symptoms of this condition
Symptoms of anterior ankle impingement can include pain at the front of the ankle, especially during activities that involve flexing the ankle, such as climbing stairs or running. Swelling and limited mobility may also occur
The recovery time for anterior ankle impingement can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. Following the treatment plan provided by your healthcare provider can help ensure the best possible outcome.
Anterior ankle impingement is commonly caused by repeated injuries to the foot or ankle, poor warm-up before physical activity, or poor physical conditioning
Treatment options for anterior ankle impingement include anti-inflammatory medicines, cold and heat therapy, orthopedic aids such as a brace or walking boot, physical therapy, steroid injections, and in some cases, surgery.